WORLD RELIGIONS
advertisement

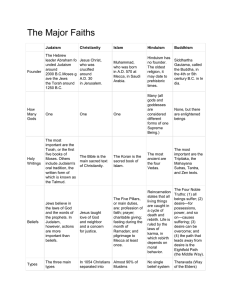
WORLD RELIGIONS Culture Religion = critical part of culture • Core values and beliefs come from religion • Enmeshed with our cultural and social systems Tied to pop growth Politics Design and structure of cities Sacred space Marriage, family, education, laws, health code Commonalities among world relig: Implied value system (right and wrong) Notion of sacred texts and space Idea about place of humans in universe Most have creation story Most believe in higher power/force Most include teachings about many facets of life – law, politics, fitness, diet, cleanliness, etc. Organizational Divisions Branches: fundamental division (Catholic, Protestant, Orthodox) Denominations: division of branch that unites a # of local congregations (Methodist, Presbyterian, S. Baptist) Sects: small group that has broken away from a denomination Migration Diffusion Migrants usually take their religion with them, but unlike language, they usually maintain it for several generations. i.e. places of immigration are usually very religiously diverse (United States) World Religions World Religions Largest World Religions Largest Religious Groups in US (US = 82% Christian) 1.) Protestant 53% (Baptist, Methodist, Lutheran, Presbyterian) 2.) Catholic 23% (New England, Southwest) 3.) Mormon 2% (Utah, Idaho, Arizona, CO, Southern CA) 4.) Orthodox 1% US Religious Distribution CHRISTIANITY – universalizing, global religion Christianity - @ 2 billion followers = world’s largest religion and most geographically dispersed Doctrines: • Monotheistic • Origins in Judaism (Old Testament) • Christ = son of God, promised Messiah, Savior, way to salvation • Sacred Text: Bible (OT and NT) • Sacred Places: Israel, holy lands Where Distributed? Christianity = major religion in all of Americas, Europe, Australia, New Zealand, and countries w/ Christian majority exist in Africa and Asia 3 Major Branches: • Catholic (50%), SW and E Europe, LA, parts of N. America) • Protestantism (25%):N. Europe, Australia, NZ, N. America • Eastern Orthodox (10%): 14 self governing churches in E. Europe (i.e. Russian Orthodox, etc.) Pope Benedict Martin Luther Henry VIII Origins of Christianity Jesus – virgin birth in Bethlehem, literal son of God, raised as a Jew, called disciples, organized church, referred to as “the Christ, Messiah,” atonement, resurrection • Catholics = Pope = head of church • E. Orthodox: split from Catholics in 1054 b/c rivalry betwn Pope in Rome and Patriarch in Constantinople • Protestantism: split 1517 – Martin Luther later Henry VIII Diffusion of Christianity Christianity is diffused by relocation, hierarchical, and contagious diffusion Hearth = Palestine 1st diffusion by relocation: after Christ’s death missionary apostles carried his etchings along Roman empire (i.e. Paul) Spread within Roman empire by contagious diffusion – contact between Christians and Pagans Diffusion – contd. Dominance was assured in Roman empire by hierarchical diffusion – Emperor Constantine converted Migration, missionary activity, and British colonialism (1500-today) spread Christianity worldwide Acculturation: conversion and intermarriage of natives, Africans, etc. Christian Calendar EASTER – commemorates Christ’s resurrection and the pending resurrection of all men CHRISTMAS – commemorates the birth of Christ – Virgin Mary, literal Son of God Organization of Space – Places of Worship Church: comes from Greek word meaning “Lord” or “Master” “church” can refer to the building and the group of people Traditionally churches placed in town center - largest, tallest, prettiest buildings. Church architecture varies from branch to branch, denomination to denomination (Protestant churches usually more simple) Cemeteries – bury dead underground ISLAM – universalizing relig about 1 billion followers #2 behind Christianity Followers found worldwide, but especially in: • Middle East and N. Africa • Indonesia (most populous Muslim country) • Pakistan • Bangladesh ISLAM - Doctrines Also has roots in Judaism (accepts many OT stories and prophets) Monotheistic – one God – Allah Prophet Mohammad = last and greatest prophet Koran 5 Pillars – Faith, Prayer, Pilgrimage, Alms, Fasting ISLAM – Distribution Two Major branches • Sunni = 83% of Muslims – in ME and N. Africa • Shiites= 16% - in Iraq, Iran and Azerbaijan (caliph must be descended from Muhammad’s blood line) • Muslim population in Europe and N. America has increased in recent yrs. because of immigration • Arabic = lingua franca of Muslim world (Koran is in Arabic) ISLAM - Origins Abraham: Hagar and Ishmael – ancestors Muhammad & Arabic line Muhammad – born @ 570 AD in Mecca (Saudi Arabia). Received revelations from God through Angel Gabriel (Koran). Gained following in Medina, returned to Mecca & established Islam. From there diffused to rest of ME, N. Africa, E. Asia, etc. Diffused by Muslim Empires – Ottoman, Mogul, Persian ISLAM – Holy Places Mecca: holiest city (hajj) contains al-Ka’ba – thought to be built by Abraham and Ishmael and contains black stone given to Abraham by Gabriel as sign of the covenant (in Saudi Arabia – pilgrimage) ISLAM – holy places cont’d Medina: Muhammad’s tomb here (in Saudi Arabia) Jerusalem: Muhammad ascended to heaven here (Dome of the Rock – pictured below) – i.e. conflict w/ Jews Places of worship = mosques call to prayer by the muzzan from the minaret tower mosque in Indonesia BUDDHISM – universalizing religion Buddhism = 3rd largest universalizing religion w/ 300 million followers Founded by the Buddha – Siddhartha Gautama BUDDHISM - Doctrines 4 Noble Truths: suffering, why it exists, how to prevent it (change desires) 8 Fold Path – way to achieve “Nirvana” i.e. complete redemption (right…understanding, intention, speech, action, livelihood, effort, mindfulness, concentration) Reincarnation BUDDHISM – where distributed 3 main branches • Mahayanists – 56% China, Japan, Korea • Theravadists – 38% - Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Sri Lanka • Tantrayanists – 6% - Tibet, Mongolia Actual # of Buddhists difficult to know because it doesn’t require exclusive adherence. Many Buddhists also follow a local/ethnic religion BUDDHISM- Origins Founder – Siddhartha Gautama – born 1563 BC present day Nepal. • Son of a lord • Led privileged life • 4 trips changed his life Decrepit old man Disease ridden man Corpse…pain, suffering, felt guilty about own life Monk – taught him about withdrawal from world Buddha At 29 yrs – fled palace, lived in forest 6 yrs meditating. Emerged as “The Buddha” – the enlightened one. Spent 45 years preaching views in modern day India 2 main branches • Theravada – oldest, believe Buddhism is full time occupation, become monk • Mahayana – split off 2,000 yrs ago, less demanding, emphasize Buddha’s self help and introspection BUDDHISM - Diffusion Began in NE India – spread east by traveling monks to Asia 1st Century – AD Merchants brought Buddhism to China – truly became a Chinese religion From China diffused to Korea and Japan BUDDHISM – holy places Important places are associated w/ life of Buddha in Nepal and NE India Pagoda: contains relics believed to be from Buddha. Pagodas not used for congregational worship Temples and monasteries used for individual prayer and meditation SIKHISM – universalizing relig about 24 million followers almost all in Punjab region of India 1st guru (religious teacher) in late 1400s in present day Pakistan God is perfect – people become like him by continual improvement – take responsibility for actions, surrender to God Men – wear turbans, don’t cut hair Holy Place = Golden Temple - Punjab Sikhism Sikh Golden Temple in Punjab region – N. India JUDAISM – Ethnic relig about 6 million in US, 4 million in Israel, 2 million in former USSR, 2 million elsewhere. In U.S. Jews heavily concentrated in large cities (NYC) Jews geographically scattered from historical captivities and conquering Jewish Doctrine 1st monotheistic religion – 1 God and Jews are his covenant people (through Abraham, Isaac, Jacob, 12 tribes) God gave land of Canaan to Abraham and his seed – divided among tribes Ten Commandments Torah – Old Testament (do NOT accept NT or Jesus as the Christ) Distribution/Diffusion Jews dispersed by Romans about 70 AD- Diaspora – scattered throughout Europe A people without a nation for hundreds of years. Some in Europe assimilated. Others persecuted • Russia and Romania – pogroms in late 1800s and early 1900s • Nazis – Holocaust – 1930s-1940s ZIONISM – the return Zionism – call for Jews to return to their promised land Always existed, but not a major movement until the Holocaust Holocaust survivors return to land of Palestine – have historical and spiritual claim on land (but Palestinians there for 2,000 yrs) Israel recognized as a nation by UN in 1948 backed by US and GB….conflict ever since Jewish Calendar Rosh Hashanah – New Year Yom Kippur – Day of Autumn Hanukkah – Festival of Lights Passover – commemorates Israeli liberation from slavery in Egypt – destroying angel passed over Israeli’s first borns. God led Moses with many miracles to deliver his people to their land Jewish Holy Places Synagogues Land of Palestine – ZION Wailing Wall – remnant of original Jewish temple destroyed by Romans (Muslim Dome of Rock is located just in front…significance of shared sacred space has fueled conflict HINDUISM – ethnic relig Hinduism = largest ethnic religion about 820 million In general the 3rd largest religion worldwide behind Christianity and Islam HINDUISM - Doctrines No single authority Vedas - collection of sacred writings Up to individual to decide best way to worship God Caste System – reincarnation – you move up by good karma Ahisma – do not eat any living being - vegetarian HINDUISM Where distributed – INDIA and Nepal Origins – no specific founder. The term “Hindusim” originally referred to people living in India. Diffusion – very little; not seeking converts Holy Places – tied to India • Ganges River – purifies • Temples – shrines home to various Gods Other Ethnic Religions Most people in China and Japan practice ethnic religions that co-exist with Buddhism. Very different from Western concept of exclusive religious adherence….i.e. many Chinese are both Buddhist and Confucian Confucianism Confucius – 551-479 BC– Chinese philosopher and teacher Emphasized ancient Chinese tradition of “li” – correct behavior…how to treat others, stresses responsibility, respect, public service Ethnic religion because strongly rooted in traditional Chinese values DAOISM (Taoism) Created by Lao-Zi 604-531 BC – a contemporary of Confucius Writings emphasized the mystical and magical to explain events Stresses introspection – seek dao – the way or the path Today in China and Taiwan SHINTOISM Ethnic religion of Japan Focus on forces of nature – sun, moon, rivers, etc. Later regarded emperors as divine (turned into a political cult i.e. WWII) Still in Japan today – references ancestors, pilgrimages to shrines believed to house deities Ethnic African Religions about 10% of African’s follow animism – inanimate objects (trees, stones, river) have spirit/conscious life No holy books, passed down by oral tradition Practitioners of animism have decreased as Christianity and Islam have spread (Africa = about 50 % Christian, 40% Muslim Concepts of Sacred Space Sacred Space: geographic intersection between the divine and the mortal Concepts of Sacred Space Landscape of the dead • Christians, Muslims, Jews bury dead in cemetery (dates back to ancient Roman catacombs) • Hindus – cremation – wash body in Ganges River and burn on funeral pyre • Ancient Zoroastrians – expose dead to scavenging birds and animals to strip body of unclean portions. Don’t want body to contaminate sacred elements of earth, fire, water Sacred Space Religious Settlements – entire settlement around religious purposes • i.e. utopian communities • Often theocracies – church and political leaders = the same • Examples….. Puritans – Massachusetts, city on a hill, 1600s Moravians – 1700s – Bethlehem, PA and Salem, NC Mormons 1800s – Nauvoo, Ill, SLC, UT RELIGIOUS CONFLICT Recent resurgence of fundamentalism (literal interpretation and intense adherence to principles of religion)….often causes divide within the religion and problems with others - Taliban – Afghanistan - Hindus – caste system - Christian fundamentalism – Eric Rudolph - 911 suicide bombers Religion and Communism Communism countered religion – Marx says religion is “opium” of the people and threat to the state USSR – 1918 – Communist Revolution – government nationalizes all church property; religion dwindles No religious freedom – if you go, go to Orthodox services controlled by government Fall of Communism in the late 80s early 90s – resurgence of religion in E. Europe Relig V. Relig – interfaith boundaries….Palestine Palestine..Jews,, Christians, and Muslims have fought for over 2,000 yrs for small piece of land Jews and Palestinians claim historical and spiritual tie to land (Abraham) Great Britain opened door for Jewish return (Balfour Declaration) 1948 Israel recognized by UN – no nation of Palestine…refugees Palestine – cont’d 3 subsequent wars….’56, ’67, ’73…each time Israel wins and expands into more land Israel would not exist without U.S. backing…..big reason why U.S. hated by Middle East Israel = tiny nation surrounded on all sides by countries that want to destroy it City of Jerusalem = especially problematic because it contains religious sites for Jews, Christians, and Muslims Religion V. Religion - IRELAND Ireland = 92% Catholic N. Ireland = (northern portion of island…part of UK) 58% Prot, 42% Cath Ireland got independence in 1937 and created republic of Ireland in 1949. But 6 N. counties voted to stay with the UK Catholics in N. Ireland = victims of discrimination in jobs and education Religion V. Religion - IRELAND Continuous cycle of demonstrations and protests IRA – Irish Republican Army – Catholics in Ireland and N. Ireland – militant organization dedicated to Irish unity – use terrorism, bombings, etc. about 3,000 dead over the years in N. Ireland Majority willing to live peacefully – militants disrupt peace for all – fuel fires, polarize sides, etc.