AP US Government Year in Review
advertisement

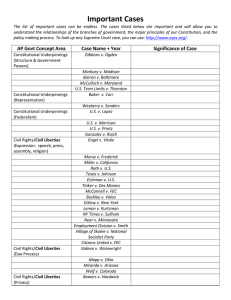
AP US Government Year in Review Constitutional Underpinnings and Federalism Influences on the Constitution Articles of Confederation Accomplishments Weakness John Locke and Federalist Essays Constitutional Underpinnings and Federalism Adoption of the Constitution Components of the Major Articles Amending Process Key Amendments Electoral College Process Impeachment Process Constitutional Underpinnings and Federalism Separation of Powers War Raising Revenue Confirmation Impeachment Constitutional Underpinnings and Federalism Elite Theories of Democratic Government Interest Group pluralism/hyperpluralism Elitism Belief in equality of opportunity NOT results Constitutional Underpinnings and Federalism Federalism Define federal, unitary, and confederate forms of gvts How has the relationship between the Federal and state governments changed? McCulloch v Maryland Unfunded mandates Types of sanctions (cross over/ cross- cutting) Block Grants Political Beliefs and Behaviors Beliefs that citizens hold about their government and their leaders Mistrust Trends in Presidential approval Process by which citizens learn about politics – Political Socialization – Selective perception Political Beliefs and Behaviors Demographic beliefs and voter behavior ID major demographic groups and identify their political behavior (voting patterns and turnout) Educated/uneducated White/minority Rich/poor Young/old Political Beliefs and Behaviors The nature sources and consequences of public opinion (dealignment) Ways people participate in politics Voting/statistics/obstacles to turnout Other forms of political participation Factors that make citizens differ from one another in beliefs and behaviors Political Parties, Interest Groups and Media Parties/elections Functions Organize competition Get candidates elected Provide loyal opposition – Organization • Nation v. grass roots party membership • Two party systems/ multi-party systems Political Parties, Interest Groups, and Media Development of Parties Realignment Obstacles for 3rd Parties Describe the decline of the political party (changes in membership) Effects on the political process Political Parties Electoral laws and systems Plurality elections, winner-take-all, proportional representation Primary, caucus, convention How do Dems/GOP nominate Presidential Candidates Electoral College Describe contemporary political campaigns Interest Groups Range of interests represented? Activities? Techniques / resources Examples of groups and resources Effects on the Process Fed 10 Incumbency advantage Interest Groups PAC’s - Federal Election Campaign Act of 1974 - McCain-Feingold and Buckley v. Valeo Media Functions and structures of the Media Impact of media on politics Campaigns (watchdog) Gatekeeper Horse race journalism IV. Institutions of Government (A) Congress Describe the demographics of congress Explain the incumbency advantages Define gerrymandering / ID Supreme Court Limits on gerrymandering Congress Factors that influence congress Divided government Party discipline Interest group pluralism District concerns Congress Legislative Process Advantages of the majority party Importance of committees Speaker of the House Rules committee Standing committees Committee assignments Leadership positions Filibuster/cloture Pork barrel politics (ear-marks) Congress Non-Legislative Roles Oversight of the bureaucracy Confirmation politics (Senate) Impeachment / removal (House and Senate) Investigations (Watergate/ Whitewater/ Monica Lewinski) What are the differences in the House and Senate? House Power of the purse (ways and means) Closest to the people More rules Fewer staff Less prestigious 2 year terms 25 years old Senate More prestigious Less formal, fewer rules Confirmations/Treaties Filibusters 6 year terms 30 years old The Presidency What are the Constitutional Powers of the President? What are the informal powers of the president? (Where are they found?) President & Congress How has the President gained power over Congress? Executive orders Executive Agreements Impoundment War Powers Veto / veto threats Courts Who creates courts? How are federal judges selected? How is the court system organized? Describe basic jurisdictional issues What is habeas corpus? How do most court cases end? Courts Describe Supreme Court procedure What cases have original jurisdiction in the Supreme Court? How do Justices decide to grant cert? How can outside groups influence the court? Who is the solicitor general? What is concurring / dissenting opinion What is Judicial Activism? What is judicial restraint? Id/ describe major rulings of the Warren and Bureaucracy ID Cabinet, independent agencies, EOP, and Government Corporations. Describe quasi-legislative and quasi-judicial functions What are iron triangles? ID rules of the bureacucracy Hatch Act Freedom of Information Act Pendleton Act Civil Liberties and Civil Rights The development of CL’s by judicial interpretation Know rights and liberties Limits on Free speech Interpretations on Separation between Church and State Lemon v Kurtzman New Jersey School Bus ruling Civil Liberties and Civil Rights Development to the Right of Privacy Development of Due Process The impact of the 14th amendment on the development of rights and liberties Barron v Baltimore Gitlow v NY Gideon v. Waingright Key SC Cases Bakke v California Brown v Board Engel v Vitale Gideon v Wainright Gitlow v NY Griswold v Conn. Heart of Atlanta Hotel Lemon v Kurtzman Marbury v Madison Mapp v Ohio McCulloch v MD Miranda Miller v Cali New Jersey School Bus Roe v. Wade Schenck v US Westbury Baker Public Policy Formation of policy agendas Role of institutions in the enactment of policy Role of the bureaucracy and courts in policy implementation Identify a “policy network” Know what “entitlements” are. Identify the US tax policy as “progressive”