H 3.5.5 AUXINS – What you will need to Objectives
advertisement

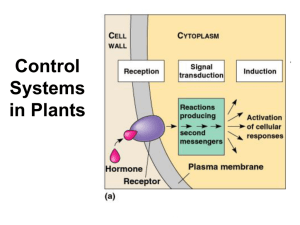
H 3.5.5 AUXINS Objectives – What you will need to know from this section Study auxin as an example of a plant growth regulator under the headings of : production initiator production site(s), function, different effects. AUXINS -- HIGHER LEVEL Auxins affect virtually every aspect of plant development, and how they respond to environmental stimuli. AUXINS influence includes phototropism, geotropism, cell enlargement and growth, apical dominance, root growth, fruit development, vascular development, and senescence [aging]. AUXINS Promote cell enlargement and growth Are involved in phototropism—stem bends towards light. Are responsible for apical dominance, where the main bud inhibits the growth of buds lower down stem. Regulate the differentiation of the vascular tissue (xylem and phloem). Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) is the most abundant naturally-occurring auxin, IAA (Indoleacetic acid) is an auxin that is made in the meristems of shoots, buds and root, and in the tips of coleoptiles [of grasses]. Auxin travels backwards from the tip in the vascular tissue and causes cells to elongate (get longer). This makes the zone of elongation grow and so the tip is pushed further upwards (in shoots) and downwards (in roots). Movement is by active transport from cell to cell – this requires energy. Auxins promote cell enlargement and growth, are involved in phototropism and apical dominance PHOTOTROPISM APICAL DOMINANCE LEARNING CHECK • • • • • • • What is an auxin? List 4 effects of auxins in a plant. List the properties of auxins. What does elongation mean? What is IAA? What is a meristem? What is a coleoptile? A tropism is a plant’s response to a stimulus coming from one direction, e.g. sunlight, gravity. Phototropism is a growth response of a stem towards light, so that it can receive the maximum amount of light for photosynthesis. APICAL DOMINANCE Auxins are responsible for apical dominance, where the main bud inhibits the growth of buds lower down stem. This photograph shows side buds sprouting when the main stem is cut off [pruned]. In shoots, light causes auxin to move down the shaded part of the stem, causing the shoot to grow towards the sunlight. This is called PHOTOTROPISM. Quicker growth here due to more hormones Artificial auxins can also be used to kill weeds, stimulate root formation in cuttings, … Uses of plant regulators Artificial auxins are used in rooting powders to stimulate root formation in stem cuttings. A synthetic auxin [2,4-D] is used as a selective weedkiller, making the plants grow too fast. Fruit is transported green and unripe, and can then be quickly ripened by spraying it with ethene. LEARNING CHECK • What is phototropism? • What is apical dominance? • If you remove the apical bud from a stem, what happens next? • Give 3 uses of plant growth regulators.