WOODLAND HILLS SECONDARY LESSON PLANS
advertisement

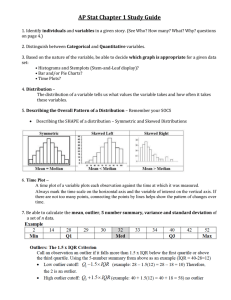
Name: John Toney Date: 1-12-15 WOODLAND HILLS SECONDARY LESSON PLANS Content Area: Mathematics Length of Lesson: 25 days STAGE I – DESIRED RESULTS Lesson Topic (Modules, if applicable): Unit 12 : Probability and statistics Stem and leaf plots Box whisker plots Multiple counting principle Permuations and Combinations Independent probability Multiplying probabilities Adding probabilities Statistical Measures Normal Distribution Binomial experiments Big Ideas: KEYSTONE ANCHORS: 2.6.8.B: Organize and display one-variable data using appropriate data display, such as stem-and-leaf and box-and-whisker plots, and two variable data with scatterplots. 2.6.11.A: Design and conduct an experiment using random sampling. 2.6.11.C: Select or calculate the appropriate measure of central tendency, calculate and apply the interquartile range for one-variable data, and construct a line of best fit and calculate its equation for two-variable data. 2.7.11.A: Use probability to predict the likelihood of an outcome in an experiment. 2.7.11.C: Compare odds and probability. 2.7.11.E: Use probability to make judgments about the likelihood of various outcomes. ELIBIBLE CONTENT: M8.E.3.1.1: Find the probability for a mutually exclusive or an independent event (written as a fraction in simplest form). M8.E.3.2: Determine the number of combinations and/or permutations for an event. M11.E.1.1.1 Create and/or use appropriate graphical representations of data, including box-andwhisker plots, stem-and-leaf plots, scatter plots, line/double line, bar/double bar and circle graphs. Understanding Goals (Concepts): Analysis of one and two variable (univariate and bivariate) data Solve problems involving independent and dependent events using the counting principle. Solve problems involving linear permutations and combinations. Find the probability and odds of events Find the probability of mutually exclusive and inclusive events Use measures of central tendency (Mean, median, mode) to represent a set of data and describe how outliers affect measures of central tendency. Find measures of variation (range & interquartile range) for a set of data. Answer questions based on data displays (box-and-whisker, stem-and-leaf, scatter plots with lines of best fit, and bar graphs). Student Objectives (Competencies/Outcomes): Students will be able to: Solve problems involving independent and dependent events using the counting principle. Solve problems involving linear permutations and combinations. Find the probability and odds of events Find the probability of mutually exclusive and inclusive events Use measures of central tendency (Mean, median, mode) to represent a set of data and describe how outliers affect measures of central tendency. Find measures of variation (range & interquartile range) for a set of data. Answer questions based on data displays (box-and-whisker, stem-and-leaf, scatter plots with lines of best fit, and bar graphs). M11.E.1.1.2 Answer questions based on displayed data (box-and-whisker plots, stem-and-leaf plots, scatter plots, line and double line graphs, bar and double bar graphs and circle graphs). M11.E.2.1.1 Find/select/use the appropriate measure of central tendency (mean, mode or median) of a set of data given or represented on a table, line plot, or stem-and-leaf plot. M11.E.2.1.2 Calculate and/or interpret the range, quartiles and interquartile range of sets of data. Essential Questions: How do you decide which functional representation to choose when modeling a real world situation, and how would you explain your solution to the problem? How can we use univariate and bivariate data to analyze relationships and make predictions? Vocabulary: Outcome, (2) Sample Space (2) , Event, Independent Events, Dependent Events, (3) Fundamental Counting Principle, (2) Permutations, (2 Combinations, (2) Probability, Odds, (1) Compound Event, (2) Mutually Exclusive, Inclusive, (3) Measures of Central Tendency, Mean, Median, Mode, Range, (2) Interquartile Range, (3) Box-and-Whiskers, (2) Stem-and-Leaf (2) STAGE II – ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE Performance Task: Formative Assessments: Students will demonstrate adequate understanding via a chapter test. Pre-assessments, open-ended questions, Think-Pair-Share STAGE III – LEARNING PLAN Interventions: Flexible grouping, students will be encouraged to attend math lab Materials and Resources: Textbook, notes “Mini Lesson” Students will continue to solve independent and dependent probability problems. They will check HW problems and begin practice problems from ws pg 717-718. 12-4 ws. pg 719 Tuesday Date: 1/13 Day: AB “Do Now” Independent and dependent probability practice problem. Wednesday Date: 1/14 Day: A “Do Now” Independent and dependent probability practice problem. Thursday Date: 1/15 Day: B “Do Now” – Get started on review worksheets as soon as they arrive to class Friday Date: 1/16 Day: A “Do Now” – Have review worksheets out and ready for going over. “Mini Lesson” Students will fill in guided notes on solving mutually exclusive and mutually inclusive probability problems. They will work on guided practice problems in their notebooks then begin independent practice problems. 12-5 NB HW “Mini Lesson” Students will continue to solve mutually exclusive and mutually inclusive probability problems. They will check HW problems and begin practice problems from ws pg 723-724. “Mini Lesson” Review CH 12 SECTION 1-5 Students will work on review worksheets with partner in class and finish for homework if necessary. “Mini Lesson” Review CH 12 Section 1-5 Students will check answers to review worksheets and ask questions as needed. 12-5 ws. pg 725 Finish review worksheets Assign ments Procedures Instructional Procedures*: Monday Date: 1/12 Day: A “Do Now” Independent and dependent probability practice problem. *Include Do Now, Mini Lesson, Guided Practice, Independent Practice, Summations/Formative Assessments, Reflections Study for test Tuesday