History of the World 8/31-9/22
advertisement
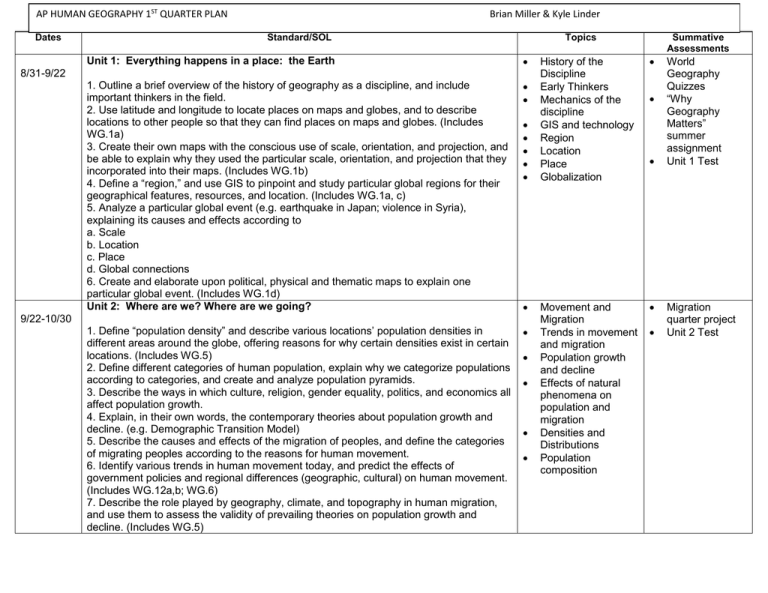
AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY 1ST QUARTER PLAN Dates Brian Miller & Kyle Linder Standard/SOL Topics Unit 1: Everything happens in a place: the Earth 1. Outline a brief overview of the history of geography as a discipline, and include important thinkers in the field. 2. Use latitude and longitude to locate places on maps and globes, and to describe locations to other people so that they can find places on maps and globes. (Includes WG.1a) 3. Create their own maps with the conscious use of scale, orientation, and projection, and be able to explain why they used the particular scale, orientation, and projection that they incorporated into their maps. (Includes WG.1b) 4. Define a “region,” and use GIS to pinpoint and study particular global regions for their geographical features, resources, and location. (Includes WG.1a, c) 5. Analyze a particular global event (e.g. earthquake in Japan; violence in Syria), explaining its causes and effects according to a. Scale b. Location c. Place d. Global connections 6. Create and elaborate upon political, physical and thematic maps to explain one particular global event. (Includes WG.1d) Unit 2: Where are we? Where are we going? 1. Define “population density” and describe various locations’ population densities in different areas around the globe, offering reasons for why certain densities exist in certain locations. (Includes WG.5) 2. Define different categories of human population, explain why we categorize populations according to categories, and create and analyze population pyramids. 3. Describe the ways in which culture, religion, gender equality, politics, and economics all affect population growth. 4. Explain, in their own words, the contemporary theories about population growth and decline. (e.g. Demographic Transition Model) 5. Describe the causes and effects of the migration of peoples, and define the categories of migrating peoples according to the reasons for human movement. 6. Identify various trends in human movement today, and predict the effects of government policies and regional differences (geographic, cultural) on human movement. (Includes WG.12a,b; WG.6) 7. Describe the role played by geography, climate, and topography in human migration, and use them to assess the validity of prevailing theories on population growth and decline. (Includes WG.5) 8/31-9/22 9/22-10/30 Summative Assessments History of the Discipline Early Thinkers Mechanics of the discipline GIS and technology Region Location Place Globalization Movement and Migration Trends in movement and migration Population growth and decline Effects of natural phenomena on population and migration Densities and Distributions Population composition World Geography Quizzes “Why Geography Matters” summer assignment Unit 1 Test Migration quarter project Unit 2 Test








