WOODLAND HILLS HIGH SCHOOL LESSON PLAN
advertisement

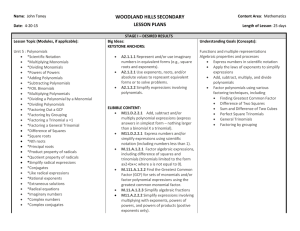
WOODLAND HILLS HIGH SCHOOL LESSON PLAN SAS and Understanding By Design Template Name _Witon___________ Date _9-1--14_ Edline was updated this week: Yes My class website was updated this week: Yes Length of Lesson _20 days_____ Content Area _Algebra 3_________ STAGE I – DESIRED RESULTS LESSON TOPIC: Polynomials (Ch 5) BIG IDEAS: There are some mathematical relationships that are always true and these relationships are used as the rules of arithmetic and algebra and are useful for writing equivalent forms of expressions and solving equations and inequalities. (Content standards, assessment anchors, eligible content) objectives, and skill focus) UNDERSTANDING GOALS (CONCEPTS): M11.D.2.2.1 Add, subtract and/or multiply polynomial expressions (express answers in simplest form – nothing larger than a binomial X a trinomial). M11.D.2.2.1 Express numbers and/or simplify expressions using scientific notation (including numbers less than 1). M.11.A.1.2.1 Factor algebraic expressions, including difference of squares and trinomials (trinomials limited to the form ax2+bx+c where a is not equal to 0). M.111.A.1.2.2 Find the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) for sets of monomials and/or factor polynomial expressions using the greatest common monomial factor. M.11.A.1.2.3 Simplify algebraic fractions M11.A.2.2.2 Simplify expressions involving multiplying with exponents, powers of powers, and powers of products (postive exponents only). ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: Students will understand: Functions and multiple representations Algebraic properties and processes 1. Express numbers in scientific notation 2. Apply the laws of exponents to simplify expressions 3. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials 4. Factor polynomials using various factoring techniques, including a. Finding Greatest Common Factor b. Difference of Two Squares c. Sum and Difference of Two Cubes d. Perfect Square Trinomials e. General Trinomials i. c > 0 ii. c < 0 iii. a 1 f. Factoring by grouping How is scientific notation useful in economics? How do square roots apply to eceanogrphy? How does factoring apply to geometry? how do polynomials apply to financial situations? VOCABULARY: *Monomial, constant, coefficient, degree, power, standard notation, scientific notation *Polynomial, terms, like terms, trinomial, binomial *Factor, greatest common factor STUDENT OBJECTIVES (COMPETENCIES/OUTCOMES): Students will be able to: Represent functions (linear and non-linear) in multiple ways, including tables, algebraic rules, graphs, and contextual situations and make connections among these representations. Choose the appropriate functional representation to model a real world situation and solve problems relating to that situation. Use algebraic properties and processes in mathematical situations and apply them to solve real world problems. STAGE II – ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE PERFORMANCE TASK: Students will demonstrate an adequate understanding via a FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT: think pair share thumbs up profolio chapter test. participate in class discussions, guided practice, computer work, Students will actively participate in class examples, discussion, classwork, open ended assessments, graphic organizers, exit tickets, daily warm ups, homework, Study Island and, unit tests, quizzes, and other formative assessments. STAGE III: LEARNING PLAN INSTRUCTIONAL PROCEDURES: MATERIALS AND RESOURCES: DO NOW: DO NOW will include a spiraling review of prior knowledge as well as the upcoming lesson. We will use Collins writing 1 and 2 daily Textbook Notebook Projector Warm ups & Exit polls Homework Guided practice and Enrichment from Glencoe Grab & Go workbooks Mini Lesson: Mini lessons will vary daily based upon student needs and informal assessments. We will use Active Engagement and Scaffolding within each lesson. Guided Practice: Note Taking, Modeling, Whole Class Response, Partnering, Higher Level Thinking Skills Guided Notes, Chunking, Build on prior Knowledge, Teacher Prompting, Visual Support Independence Practice: Check for understanding using practice pages and text as well as school/SAS developed activities. Summative/Formative Assessments: Quizzes as needed for understanding. Unit test is summative as well as cumulative for constant knowledge retention. Students will actively participate in class examples, discussion, class work, whiteboards, open ended assessments, graphic organizers, exit tickets, daily warm ups, homework, Study Island and, unit tests, quizzes, and other formative assessments. Reflections: Check for understanding using do now, homework, or formative assessment questioning to determine whether to continue as needed or do interventions as needed. INTERVENTIONS: Struggling students will be referred to guidance/SAP (RTI) Small group/ flexible grouping will occur when necessary. Study Island A+ Math Math Lab. Think Through Program ASSIGNMENTS: p. 226-227 p. 231-232 p. 236-237 p. 242-243 Various Worksheets (Model, spiral scaffolding, ins truct/reteach as needed) Teacher reflection: