WOODLAND HILLS HIGH SCHOOL LESSON PLAN STAGE I – DESIRED RESULTS
advertisement

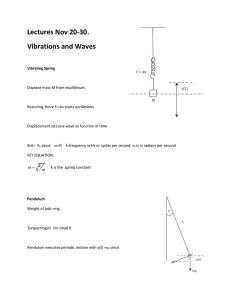
WOODLAND HILLS HIGH SCHOOL LESSON PLAN SAS and Understanding By Design Template Name: Andrew Heffner Date: 04/06/15 Length of Lesson: 21 Periods/3 Weeks Content Area: AP Physics STAGE I – DESIRED RESULTS LESSON TOPIC: BIG IDEAS: (Content standards, assessment anchors, eligible content) objectives, and skill focus) Simple Harmonic Motion, Oscillation, Amplitude, Period, Frequency, Phase Angle, Simple Pendulum, Physical Pendulum, Damping, resonance, Mechanical Wave, Medium, Transverse, Longitudinal, Intensity, Interference, Superposition, Boundary Conditions, Standing Waves, Nodes, Antinodes, Fundamental Frequency, Harmonics, Loudness, Pitch, Timbre, Beats, Doppler Effect, Shock Wave, 3.2.10.B5.1: Understand that waves transfer energy without transferring matter. 3.2.10.B6.1: Explain how energy follows predictable patterns defined by laws. 3.2.10.B7.4: Formulate and revise explanations and models using logic and evidence. S11.A.3.3: Compare and analyze repeated processes in patterns. S11.C.2.1: Analyze energy sources and transfer of energy, or conversion of energy. All simple harmonic motion can be explained using force and torque. Objects that move in simple harmonic motion can result in the production of waves that travel through space. UNDERSTANDING GOALS (CONCEPTS): ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: The simple harmonic motion of an object can be quantitatively described using the sine and cosine trig functions. Simplest harmonic motion can be characterized by one part, an inertial mass, which remains in one vicinity while oscillating about an average position. The oscillatory behavior results from the interplay of two opposite tendencies: a return force and an inertial mass. The return force tries to return the inertial mass to the resting position, while the inertial mass resists changes in motion. Waves produced by simple harmonic motion interact with other waves and matter and result in the phenomena of superposition, interference, reflection, refraction, and resonance. Mechanical and electromagnetic waves are described in terms of wavelength, amplitude, velocity, and frequency and can be produced by objects in harmonic motion or electrical circuits. Traveling waves transfer energy exerted as force to distant objects that absorb or reflect the traveling waves. What causes a spring to oscillate? How much energy is in an oscillator? How can I describe SHM in words? What is wave motion, and how is it produced? What happens when waves collide? What properties of waves are related to the sounds I hear? How does emitter velocity affect the production of waves? VOCABULARY: STUDENT OBJECTIVES (COMPETENCIES/OUTCOMES): Simple Harmonic Motion, Oscillation, Amplitude, Period, Frequency, Phase Angle, Pendulum, Resonance, Mechanical Wave, Medium, Transverse, Longitudinal, Intensity, Interference, Superposition, Standing Waves, Nodes, Antinodes, Fundamental Frequency, Harmonics, Loudness, Pitch, Timbre, Beats, Doppler Effect. Students will be able to: …Define simple harmonic motion and its causation. …Describe SHM in terms of Amplitude, Period, Frequency, and Wavelength. …Compare the wave functions of amplitude, velocity, acceleration, and force. …Identify and calulate the total energy in an oscillation system. …Contrast transverse and longitudinal waves. …Describe the superposition of waves at boundaries and in collisions …Calculate the fundamental frequency of standing waves, with nodes and antinodes …Apply understanding of waves to the perception of sound in multiple ways STAGE II – ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE PERFORMANCE TASK: Oscillator Graphing Task Doppler Effect Demo Slinky-Wave Lab Rubber Band/Tube Investigation OTHER EVIDENCE: Exit Slips, Interactive Polls, HTML5 Concept Check Results Peer Review & Argumentation, MOPS Codes STAGE III: LEARNING PLAN INSTRUCTIONAL PROCEDURES: MATERIALS AND RESOURCES: DO NOW : Daily Collins Warm-Up Questions ML : Direct Instruction Examples with demos and student participation GP : Lab investigations, reasoning skill tasks IP : Physics Interactives, MOP Modules FA : Peer Review and discussion of lab results, epolling, exit slips, individual reflective writing. Springs of many sizes. Masses, slinkies, sinusoidal graphs, rubber bands, sound equipment, tuning forks. INTERVENTIONS: ASSIGNMENTS: Students will be working on the board on examples and present throughout unit. Multiple hand-on labs Students will be working in cooperative groups Online Practice Jigsaw practice of analysis Homework Homework packets, MOPS directions, PP presentations, AP Exam Practice Questions Peer tutor partners Physics Lab Tutoring Procedural writing prompt within the discipline. Edmodo Supplementals Lab reports MOPS Concept Checks Physics Interactives