2015-16 (worth 150 pts)
advertisement

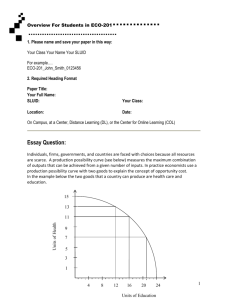
2015-16 (worth 150 pts) AP Comp Gov’t Resource Information and Summer Assignment AP Comparative Government students should purchase the following texts and study guides for the upcoming school year. Text: (required for each student) Additional AP Study Guides: (these resources will help with AP exam prep) AP Comparative Government Summer Assignment Your assignment consists of two parts - vocabulary and book review. Both assignments are due 1st week of classes in September of the upcoming school year. Late assignments will be penalized 15 pts each day it is late. Part I – Vocabulary (50pts) You can use “Introduction to Comparative Government and Politics: An Essential Course Book and Study Guide” and the websites below to complete the vocabulary assignment. For each term, please explain, define, provide an example and create a picture/graphic for each. A thorough understanding of these vocab terms is tantamount to your success in this course. All parts of the vocabulary assignment MUST be hand-written. Please be neat. There will be a test on these terms the first week of class. Websites for Political Science Terms http://www.auburn.edu/~johnspm/gloss/political_science http://www.socialsciencedictionary.com/ Part II – Reading The book is Ian Bremmer’s The J Curve: A New Way to Understand Why Nations Rise and Fall (New York: Simon & Schuster, 2006). The book is available from Amazon.com new for $18.00 and as low as $1.53 for a used copy. It is, of course, available for KINDLE. Things get worse before they get better. Economists noticed that a country's trade deficit follows this pattern when the value of its currency falls. A weakened U.S. dollar, for example, tends to increase the U.S. trade deficit in the short term because, while the price of imports increases immediately, contracts remain constant. After demand shifts from imports to domestic goods, the trade balance improves—often the goal of intentional currency devaluation. This pattern resembles a "J" on graphs and is therefore called the J curve. Ian Bremmer, a political scientist who built a business on understanding risk, noticed that countries also follow a J curve when moving from a state of isolation to a state of openness. In this case, the curve describes the relationship between a country's openness and its stability, which is detailed in Bremmer's new book. Bremmer's premise is that "as the energies of globalization open up the least politically and economically developed areas of the world, as the citizens of closed states learn more about life beyond their borders and discover that they don't have to live as they do, tyrants must expend more and more effort to isolate their societies" (p. 265), a point echoed by Natan Sharansky in his justification for democracy promotion. But Bremmer's point is that openness, not democracy, should be the tool of change. The task of the most open countries should be to work with international institutions to help the more closed countries through the rocky transition to openness and more enduring political stability. In fact, one can argue it is an ethical imperative. PART III: ESSAY (100 pts) After reading the novel, write a well-developed essay that addresses the application of the JCurve’s basic economic model in expressing the stability of a nation. Your essay should be typed in 12pt font double-spaced, 2-3 pages in length with 1”margins. Internal citations are required. In the upper right hand corner of the first page please type: AP Comparative Government Summer Assignment School Year 2015-16 Mrs. Austin/Mr. McNamara /Mr. Gough Your Name (student’s name) You will be graded on the strength of your arguments as well as the quality of your writing. Please be sure that your essay is concise – in other words, make your point and move on. It is not necessary to paraphrase the text and there should not be any direct quotes from the book. This is YOUR analysis and critique of Bremmer’s arguments. You are not writing about HOW he makes the arguments – but the actual merit of his arguments. EXTRA CHALLENGE (1st Day Warm-Up) Head of State and Head of Government for each country in the AP Curriculum with some additional information about each leader (this information can be found by reading the leaders’ profiles on the country’s government webpage). Senior Year will be so much fun…….. :) 1 Autocracy 2 Bicameral 3 Bureaucracy 4 Civil Society 4 Cleavage (as it relates to Political Science!) 6 Confederation 7 Democratization 8 Devolution 9 Executive 10 Federalism 11 Head of Government 12 Head of State 13 Illiberal Democracy 14 Interest Groups 15 Judicial Review 16 Judiciary 17 Legislature 18 Legitimacy 19 Liberal Democracy 20 Mixed Electoral System 21 Multi-Member District 22 Nation 23 Nationalization 24 Nation-state 25 Non-Governmental Organization (NGO) 26 Oligarchs (Especially as they relate to Russia & Mexico) 27 Parliamentary System 28 Patronage 29 Pluralism 30 Plurality Electoral System 31 Political Culture 32 Political Efficacy 33 Political Elites 34Political Ideology 35 Political Recruitment 36 Political Socialization 37 Presidential System 38Privatization 39 Proportional Representation 40 Referendum 41 Regime 42 Republic 43 Rule of Law 44 Separation of Powers 45 Single-Member District 46 Sovereignty 47State 48Theocracy 49 Transparency (as it relates to government) 50 Unicameral