Weight Management Chapter Nine © McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.

Weight Management
Chapter Nine
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Current Trends
The National Institutes of Health reports the following:
– About 66% of American adults are overweight
– More than 31% of American adults are obese
– The rate of obesity has doubled since 1960
– At current rates, all American adults will be overweight by 2030
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Controlling body weight is really a matter of controlling body fat
Managing body weight is not a mysterious process, even though it is not fully understood by many people
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Weight of Americans age 20 and
Older
(Table 9.1)
Group
Both sexes
All races, male
All races, female
White, male
White, female
African American, male
African American, female
Latino, male
Latino, female
Percent of poverty level
Below 100%:
100%–less than 200%:
200% or greater:
Percent
Overweight
66.0
70.5
61.6
71.0
57.6
67.0
79.6
74.6
73.0
63.4
66.2
66.1
Percent
Obese
31.4
29.5
33.2
30.2
30.7
30.8
51.1
29.1
39.4
33.7
33.6
30.0
SOURCE: National Center for Health Statistics. 2006. Health, United
States, 2006, with Chartbook on Trends in the Health of Americans.
Hyattsville, Md.: National Center for Health Statistics.
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Health Implications of Overweight and
Obesity
As rates increased in the United States, so has the prevalence of health conditions, including:
Type II diabetes
Pre-mature deaths
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Moderate weight loss can have a significant positive impact on health
A weight loss of just 5-10% can reduce the risk of these conditions in obese individuals
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Factors Contributing to Excess
Body Fat
Genetic Factors
Physiological
Factors
– Metabolism and
Energy Balance
– Hormones
Lifestyle Factors
– Eating
– Physical Activity
– Psychosocial
Factors
Other possible factors include:
– Fat Cells
– Weight Cycling
– Carbohydrate Craving
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Adopting a Healthy Lifestyle for
Successful Weight Management
The following lifestyle factors are considered critical for success:
Diet and eating habits
Total Calories
Portion Sizes
Energy Density
Fat, Protein, and
Carbohydrate amounts
Physical activity and exercise
Thoughts and emotions
Coping strategies
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Approaches to Overcoming a Weight
Problem
Doing it yourself
Diet books
Dietary supplements and diet aids
Weight-loss programs
Non-commercial and commercial weight loss programs
Online Weight-loss
Programs
Clinical Weight-loss
Programs
Prescription drugs
Surgery
Psychological help
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
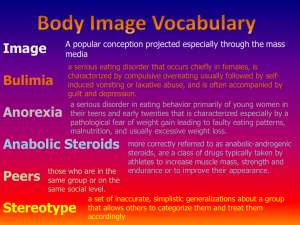
Body Image
Body image is the mental representation a person holds about her or his body
It consists of perceptions, images, thoughts, attitudes, and emotions
Media images are linked to a negative body image
Different cultures have different ideas of the “ideal” body type
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Severe Body Image Problems
Poor body image can cause significant psychological distress
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) is:
– Related to obsessive-compulsive disorder
– Can lead to depression, social phobia, and suicide
– Treated with medication and psychotherapy
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Muscle dysmorphia is a disorder characterized by a distorted body image that inaccurately perceive themselves as having small, underdeveloped muscles
Eating Disorders affect about 10 million American females and 1 million males
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Eating Disorders
An eating disorder is a serious disturbance in eating pattern or behavior, characterized by a negative body image and concerns about body weight or body fat
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Major types of eating disorders:
– Anorexia nervosa
– Bulimia nervosa
– Binge-eating disorder
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Anorexia Nervosa
Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by a refusal to maintain body weight at a minimally healthy level and an intense fear of gaining weight or becoming fat
– Affects 2 million Americans, 95% being female
– Based on a distorted body image
– Consequences result in severe medical complications, including death
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of binge eating and purging: overeating and then using compensatory behaviors such as vomiting and excessive exercise to prevent weight gain
– Begins in adolescence or young adulthood
– During a binge, a person may consume 1,000 to
60,000 calories
– Binge-purge cycle places tremendous stress on the body
Research suggests that about 5% of college-age women have bulimia
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Binge-Eating Disorder
Binge-eating disorder is an eating disorder characterized by uncontrollable eating without any compensatory purging behavior
Common eating patterns are:
– Eating very rapidly
– Eating until uncomfortably full
– Eating when not hungry
– Eating alone
This is usually followed by feelings of guilt, shame, and depression
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Treating Eating Disorders
Must address both problematic eating behaviors and the misuse of food to manage stress and emotions
Averting a medical crisis by restoring adequate body weight
Dealing with psychological aspects
Stabilizing eating habits
Changing behavior patterns and thoughts
Possibly involving medication and/or hospitalization
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.
Creating an Individual Weight-
Management Plan
Assess Your
Motivation and
Commitment
Set Reasonable Goals
Assess Your Current
Energy Balance
Make Changes in Your
Diet and Eating Habits
Increase Your Physical
Activity Levels
Put Your Plan into
Action
Write Daily
Get Others to Help
Think Positively
© McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved.