& Unit Rubric U N
advertisement

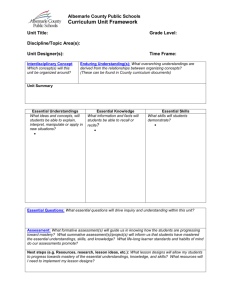
UNDERSTANDING BY DESIGN (UbD) & DIFFERENTIATED INSTRUCTION (DI) Unit Rubric CATEGORY Established Goals Expert - 4 Student is able to write all the lesson goals, match them with the Mississippi Framework/Standards and code them. All are assessed in Stage 2. Essential Questions Student is able to write all essential questions correctly. Ninety percent of them are divergent and the remaining are convergent type questions. All essential questions are written for student guided inquiry on the topic. All essential questions are topical and specific enough to focus on student learning and assessment. All of the essential questions are written in student language. Students are able to write all the Big Idea as understanding statements. The understandings are ALL aligned with the content standards and objectives of the framework. All the understandings are topical and specific enough to focus on student learning and assessment. All the understandings are written as generalizations. All the understandings are uncovered, not just covered. Students will understand that… Students will know… Knowledge & Skill Student is able to list the all things his/her students will need to know by the end of the unit. All of the knowledge and skills are written to ensure student understanding of the topic. Proficient - 3 Student is able to write most of the lesson goals and to match them with the Mississippi Framework/Standards and code them. Most of them are assessed in Stage 2 Student is able to write most essential questions correctly. Eighty percent of them are divergent and the remaining are convergent type questions. Most essential questions are written for student guided inquiry on the topic. Most essential questions are topical and specific enough to focus on student learning and assessment. Most of the essential questions are written in student language. Students are able to write some of the Big Idea as understanding statements. Some of the understandings are aligned with the content standards and objectives of the framework. Some of the understandings are topical and specific enough to focus on student learning and assessment. Some understandings are written as generalizations. Some of the understandings are uncovered, few covered. Emergent - 2 Student is able to write a few of the lesson goals and to match them with the Mississippi Framework/Standards and code them. Few of them are assessed in Stage 2. Student is able to write a few essential questions correctly. Seventy percent of them are divergent and the remaining are convergent type questions. Few essential questions are written for student guided inquiry on the topic. Few essential questions are topical and specific enough to focus on student learning and assessment. Few of the essential questions are written in student language. Students are able to write a few of the Big Idea as understanding statements. Few of the understandings are aligned with the content standards and objectives of the framework. Few of the understandings are topical and specific enough to focus on student learning and assessment. Few of the understandings are written as generalizations. Few of the understandings are uncovered, most covered. Student is able to list some of the things his/her students will need to know by the end of the unit. Most of the knowledge and skills are written to ensure student understanding of the topic. Student is able to list a few of the things his/her students will need to know by the end of the unit. Few of the knowledge and skills are written to ensure student understanding of the topic. Novice - 1 Student is not able to write the lesson goals and/or match them with the Mississippi Framework/Standards and code them. None of them assessed in Stage 2 Student is not able to write essential questions correctly. Most of the questions are convergent type questions. None of the essential questions are written for student guided inquiry on the topic. None of the essential questions are topical and specific enough to focus on student learning and assessment. None of the essential questions are written in student language. Students are not able to write the Big Idea as an understanding statement. None of the understandings are aligned with the content standards and objectives of the framework. None of the understandings are topical and specific enough to focus on student learning and assessment. None of the understandings are written as generalizations. None of the understandings are uncovered, all are covered. Student is not able to list the things his/her students will need to know by the end of the unit. None of the knowledge and skills are written to ensure student understanding of the topic. S The performance task is aligned with the desired results in Stage 1. The task shows student understanding. The performance task shows a real world application of the identified knowledge, skill, and understandings. The performance tasks are written in the GRASPS form. The performance tasks allow students to demonstrate understandings by allowing choice, options and a variety of performance and products. The performance task uses one or more of the six facets of understandings. The performance task rubric includes many traits of understanding and successful performance. The performance task is aligned with the desired results in Stage 1. The task shows some student understanding. The performance task is aligned with the desired results in Stage 1. The task shows a little student understanding. The performance tasks for the most part are written in the GRASPS form. The performance tasks allow students to demonstrate understandings mostly by allowing choice, options and a variety of performance and products. The performance task uses one of the six facets of understandings. The performance task rubric includes some traits of understanding and successful performance. The performance tasks contain a few GRASPS components. The performance tasks allow students to demonstrate understandings by a few choices, options and a variety of performance and products. Other Evidence Student lists 4 other types of assessments to measure whether students are learning. Students are allowed to self-assess and reflect upon their learning and performance. Learning Plan Student develops a lesson with an activator and summarizer. Student lists 3 other types of assessments to measure whether students are learning. Students are for the most part allowed to self-assess and reflect upon their learning and performance. Student develops a lesson with either an activator and/or summarizer. The learning plan is written so that students can follow the plan with some difficulty. It contains their performance goals and how their work will be Student lists 2 other types of assessments to measure whether students are learning. Students are occasionally allowed to self-assess and reflect upon their learning and performance. Student develops a lesson with no activator or summarizer. The learning plan is written so that students can follow the plan with a lot of difficulty. It contains their performance goals and how their work will be Diagnostic assessments are used at the beginning to check for any misunderstandings. assessed. W Diagnostic assessments are mostly used at the beginning to check for any misunderstandings. assessed. W Diagnostic assessments are used at the beginning to check for any misunderstandings. W W W The learning plan shows the students will be engaged in their The learning plan shows the students are for the most part engaged in The learning plan shows the students are very little engaged in their learning. H The learning plan is written so that students will receive the necessary experiences to understand the Big Ideas, and the needed their learning. H The learning plan is written so that students will receive for the most part necessary experiences to understand the Big learning. H The learning plan is written so that students will have a lot of difficulty understanding the Big Ideas, and the needed information and Performance Task The learning plan is written so that students can follow the plan easily. It contains their performance goals and how their work will be assessed. W The performance task rubric includes few traits of understanding and successful performance. The performance task does not align with the desired results in Stage 1. The task shows no student understanding. The performance task shows NO real world application of the identified knowledge, skill, and understandings. The performance tasks are NOT written in the GRASPS form. The performance tasks DOES NOT allow students to demonstrate understandings by allowing choice, options and a variety of performance and products. The performance task uses none of the six facets of understandings. The performance task rubric includes no traits of understanding and successful performance. Student lists 1 other type of assessment to measure whether students are learning. Students are NOT allowed to self-assess and reflect upon their learning and performance. The learning plan is written so that students can not follow the plan easily. It contains their performance goals and how their work will be assessed. W Diagnostic assessments are not used at the beginning to check for any misunderstandings. W The learning plan shows the students are not engaged in their learning. H The learning plan is written so that students will NOT understand the Big Ideas, and the needed information and skills upon which the information and skills upon which the understandings and performances are based. E Six Facets of Understanding – Cubing Activities Blooms TaxonomyCubing Activities Grade/Level E E Few opportunities are provided for students to reflect, rethink, and to revise their work based on feedback and No opportunities are provided for students to reflect, rethink, and to revise their work based on feedback and guidance. R Ongoing assessments are made through out the lesson of individual and group progress with feedback and guidance. guidance. R Some ongoing assessments are made through out the lesson of individual and group progress with feedback guidance. R Few ongoing assessments are made through out the lesson of individual and group progress with feedback guidance. R No ongoing assessments are made through out the lesson of individual and group progress with feedback and guidance. E2 and guidance. E2 Some of the learning has been personalized with DI activities to accommodate the different learning styles of students by providing content, process, and products tailored for their individual and guidance. E2 A little of the learning has been personalized with DI activities to accommodate the different learning styles of students by providing content, process, and products tailored for their individual E2 differences. T The sequences of learning activities are for the most part easy to follow and have been organized for student activity and differences. T The sequences of learning activities are very difficult to follow and have been organized for student activity and differences. T The sequences of learning activities are not easy to follow and have been organized for student activity and productivity. O productivity. O Student develops TWO different DI activities, some materials are prepared and demonstrated, and template hand-out available for participants. Students are able to use the Sternberg’s Triarchic Theory in developing some THINKDOTS DI cubing activities Students are able to use the 6 Facets of Understanding in some of these stages Stage 1, Stage 2, and Stage 3 Students are able to use the 6 Facets of Understanding in developing some DI cubing activities Students are able to use the 6 levels of Blooms Taxonomy in developing some DI cubing activities B 85 – 94% Student develops ONE DI activity, materials are prepared and demonstrated, and template hand-out available for participants. Student develops ONE DI activity, some materials are prepared and demonstrated, and template hand-out available for participants. Students are able to use the Sternberg’s Triarchic Theory in developing a few THINKDOTS DI cubing activities Students are able to use the 6 Facets of Understanding in a few of these stages Stage 1, Stage 2, and Stage 3 Students are able to use the 6 Facets of Understanding in developing a few DI cubing activities Students are able to use the 6 levels of Blooms Taxonomy in developing a few DI cubing activities C 75 – 84% Students are not able to the Sternberg’s Triarchic Theory in developing THINKDOTS DI cubing activities Students are not able to use the 6 Facets of Understanding in Stage 1, Stage 2, and Stage 3 of the UbD lesson. Students are not able to the 6 Facets of Understanding in developing DI cubing activities Students are not able to the 6 levels of Blooms Taxonomy in developing DI cubing activities D 70 – 74% productivity. O Six Facets of Understanding E understandings and performances are based. Some opportunities are provided for students to reflect, rethink, and to revise their work based on feedback and differences. T The sequences of learning activities are easy to follow and have been organized for student activity and ThinkDOTS & Sternberg’s Triarchic Theory skills upon which the understandings and performances are based. Opportunities are provided for students to reflect, rethink, and to revise their work based on feedback and The learning has been personalized with DI activities to accommodate the different learning styles of students by providing content, process, and products tailored for their individual DI Activities Ideas, and the needed information and skills upon which the understandings and performances are based. Student develops THREE different DI activities, materials are prepared and demonstrated, and template hand-out available for participants. Students are able to use the Sternberg’s Triarchic Theory in developing ALL THINKDOTS DI cubing activities Students are able to use the 6 Facets of Understanding in Stage 1, Stage 2, and Stage 3 Students are able to use the 6 Facets of Understanding in developing ALL DI cubing activities Students are able to use the 6 levels of Blooms Taxonomy in developing ALL DI cubing activities A 95 – 100% The learning has not been personalized with DI activities to accommodate the different learning styles of students by providing content, process, and products tailored for their individual productivity. O