A Cladogram of Plant Groups – shows evolutionary relationships of plants
advertisement
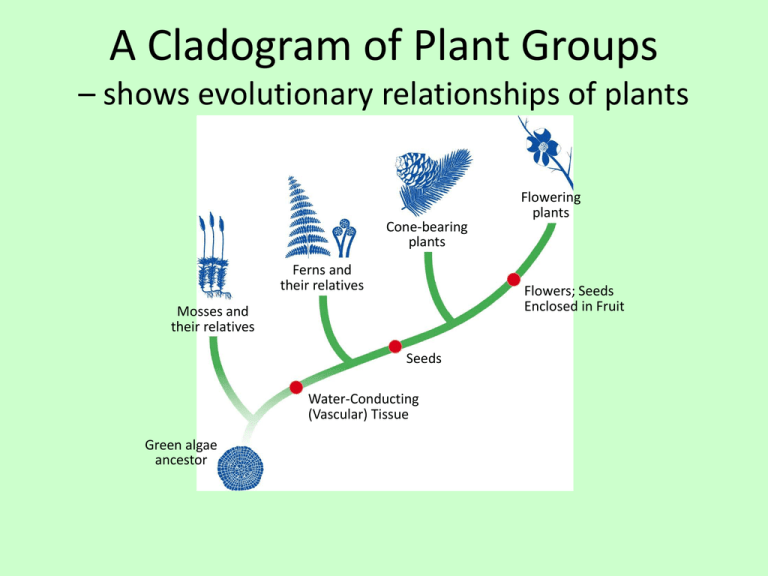
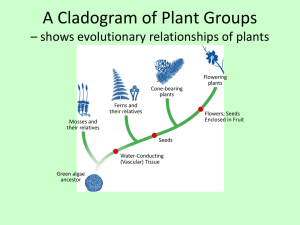
A Cladogram of Plant Groups – shows evolutionary relationships of plants Cone-bearing plants Ferns and their relatives Flowers; Seeds Enclosed in Fruit Mosses and their relatives Seeds Water-Conducting (Vascular) Tissue Green algae ancestor Flowering plants The Diversity of Plants Cone-bearing plants 760 species Ferns and their relatives 11,000 species Mosses and their relatives 15,600 species Flowering plants 235,000 species Structure of a Leaf - the cuticle protects the leaf against transpiration Cuticle Veins Epidermis Palisade mesophyll Xylem Phloem Spongy mesophyll Epidermis Stoma Guard cells Vein Plants are categorized as Annuals Biennials Perennials that complete their life cycle in that complete their life cycle in that complete their life cycle in 1 growing season 2 years More than 2 years Types of Plants – Seedless • Mosses (Bryophytes) • Ferns (Pterophyta) Types of Plants - seeds • Cone Bearing (Gymnosperms) • Flowering (Angiosperm) Gymnosperms vs Angiosperms Comparing Features of Seed Plants Feature Gymnosperms Angiosperms Seeds Bear their seeds on cones Bear their seeds within flowers Reproduction Can reproduce without water; male gametophytes are contained in pollen grains; fertilization occurs by pollination Can reproduce without water; male gametophytes are contained in pollen grains; fertilization occurs by pollination Examples Conifers, cycads, ginkgoes, gnetophytes Grasses, flowering trees and shrubs, wildflowers, cultivated flowers Flower Functions • Sexual Reproduction! • Flowers are pollinated by: – Wind – Insects – Birds FLOWER PARTS • Pistil – female part of the plant – Contains the stigma, style and ovary (surround and protect the seeds) FLOWER PARTS • Stamen – male part of the plant – Contains the anther and filament FLOWER PARTS • Petals – colorful, leaflike structures • Sepals – green leaflike structures at the base of the flower The structure of a flower. Stamen Anther Filament Ovule Carpel Stigma Style Ovary Petal Sepal Fruit – after pollination the ovary develops a wall of tissue surrounding the seed Figure 22–25 Comparison of Monocots and Dicots Comparison of Monocots and Dicots Monocots Dicots Seeds Single cotyledon Two cotyledons Leaves Parallel veins Branched veins Flowers Floral parts often in multiples of 3 Floral parts often in multiples of 4 or 5 Stems Vascular bundles scattered throughout stem Vascular bundles arranged in a ring Roots Fibrous roots Taproot Transpiration A B Evaporation of water molecules out of leaves. Pull of water molecules upward from the roots.