Opposing morphogen gradients pattern the D-V axis of the spinal cord
advertisement
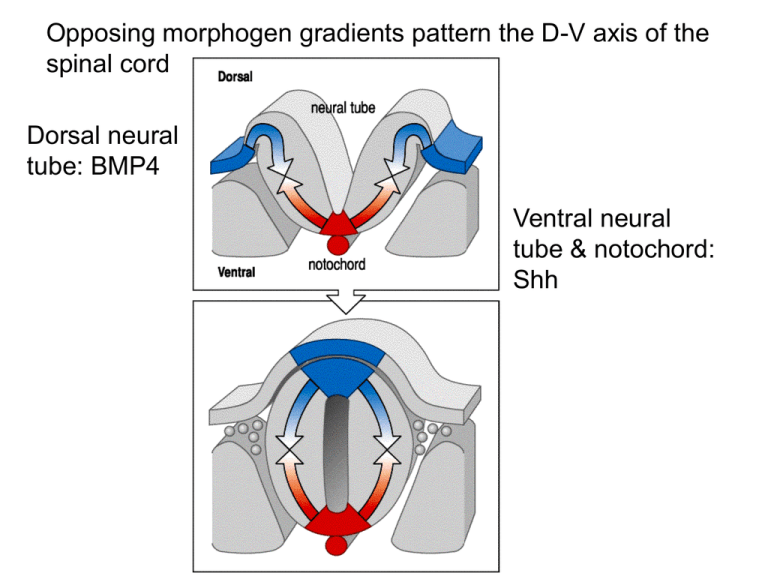
Opposing morphogen gradients pattern the D-V axis of the spinal cord Dorsal neural tube: BMP4 Ventral neural tube & notochord: Shh Motor neuron differentiation depends on Shh and the notochord Sonic hedgehog One notochord Two notochords Neuronal fate of the intermediate zone of the spinal cord is “plastic” & dependent on levels of Shh low Shh: dorsalized fate; high Shh: ventralized Increasing BMP/dorsal roof plate ectoderm dorsalizes neurons Neural plate folds into neural tube to generate brain & spinal cord; neural crest will form sensory neurons, autonomic NS BMP vs. Shh Brain forms from neural tube with 3 divisions: largest= TE/DE (FB) Frog mesoderm/endoderm involutes at blastopore, then extends along A/P axis during gastrulation Neural tissue is induced by mesoderm & the notochord (neurulation) Head organizer forms, neurulation occurs where BMP is inactive Head organizer forms from the first endoderm + mesoderm Signaling molecules retinoic acid (RA), FGFs & Wnts further divide the developing nervous system along the A-P axis Retinoic acid (vitA derivative) is essential to neural plate posterior patterning RA acts via homeobox (Hox) gene transcription to control specific positional coding along the A-P axis High RA: posteriorizing increasing RA loss of head structures RA secreted by paraxial mesoderm at posterior Position of homeobox genes on the chromosomes correlates with their regional expression pattern Hox genes: highly conserved in sequence and function A P Each rhombomere in the hindbrain contains specific populations of cranial motor neurons Hox genes pattern cranial motor neurons (R1-R7) & the vagus nerve (organs from heart to colon) Homeobox gene mutations disrupt rhombomere development and lead to cranial nerve deletions Vertebrate brain has a signaling center at the MB/HB boundary expressing homeobox gene Engr Engr Engr Patterns of gene expression at the midbrain-hindbrain border Irx: activates Otx2 & Gbx2 Fgf8: regulates growth of NPCs Fgf8 is a critical component of the MB-HB organizer Opposing gradients of Emx2 & Pax6 establish brain regions -/- Fgf8: functions at MB/HB boundary, & in anterior FB Fgf8 and BMP expression position the somatosensory map Fgf8 BMP Increased anterior Fgf8 displaces SS map to posterior Fgf8 at the posterior causes duplication of the SS map Ectopic Fgf8 at posterior leads to mirror duplication of the barrel cx Cyt oxidase staining (layer IV) The fruit fly nervous system arises from ectoderm adjacent to ventral mesoderm Neuroblast delamination In Drosophila NB GMCs (many) 1 GMC pair neurons or glia GMC= ganglion mother cell Embryonic ectodermal cells can switch their fate to neural Lateral inhibition via As-c signaling generates a neuroblast more Asc Proneural cluster Asc+ Delta ON Lateral inhibition Notch Notch ON/Delta OFF (neighbors) NB selected Neuroblast Asc+ & epidermal cells Proneural cell clusters initially express achaete-scute … then the clusters become refined to 1 As-c+ NB