Lewy Body Diseases
advertisement

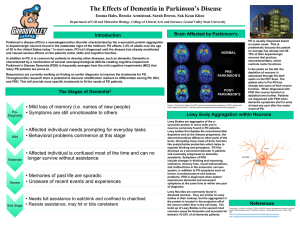
Lewy Body Diseases Lewy body dementia is a clinicopathological syndrome that may account for up to 20% of all cases of dementia in older patients, typically in their seventh and eighth decades. Diseases with Lewy bodies should also be considered in the differential diagnosis of a wide range of clinical presentations including episodic disturbances of consciousness, syncope, sleep disorders, and unexplained delirium. (Brown, 1999) There are three major syndromes associated with the appearance of Lewy bodies. These are: the movement disorder known as Parkinson disease, autonomic nervous system failure, and dementia. Parkinsonism, the most common syndrome with Lewy bodies, is a disease developing in middle age. In older persons, a mixture of cognitive, autonomic, and motor dysfunction is more common. Some older persons with dementia who are thought to have Alzheimer disease may actually have diffuse Lewy body disease, and some of those persons may have a movement disorder resembling Parkinson disease. Conversely, some patients initially presenting with Parkinson disease may develop manifestations of Lewy body dementia. (Brown, 1999) (Kosaka, 2000) The clinical presentation of Lewy body disease varies according to the site of Lewy body formation and associated neuronal loss. In Parkinson disease, the Lewy bodies are found in the substantia nigra of the midbrain, coupled with the loss of pigmented neurons. In persons with the dementia of diffuse Lewy body disease, there are Lewy bodies in the neocortex. Some persons have the Lewy bodies in both locations. The basal ganglia and diencephalon may also be involved in some cases. (Kalra et al, 1996) (Kosaka, 2000) Lewy bodies are spherical, intraneuronal, cytoplasmic, eosinophilic inclusions comprising abnormally truncated and phosphorylated intermediate neurofilament proteins, alpha-synuclein, ubiquitin, and associated enzymes. With idiopathic Parkinson disease, Lewy bodies are typically found in the substantia nigra, nucleus basalis of Meynert, dorsal raphe, locus ceruleus, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve, and hypothalamus. In cases Lewy body dementia, cortical Lewy bodies are prominent, but there are typically findings of Alzheimer disease as well. (Kövari et al, 2009)