Constants and equations for final exam. You may detach this...
advertisement

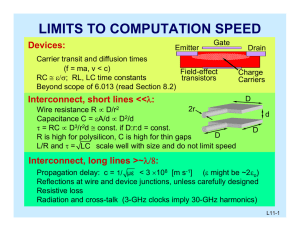
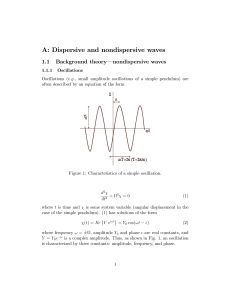
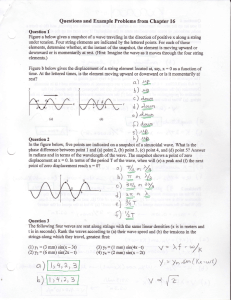
Physics 123 Final Exam May 8, 2007, Tuesday 8:30 to 10:30 am Constants and equations for final exam. You may detach this page if you wish. Speed of light in vacuum c = 3.00 x 108 m/s Planck's constant h = 6.63 x 10-34 Js = 4.14 x 10-15 eV s Electron mass me = 9.11 x 10-31 kg=0.511 MeV/c2 Electron charge e = -1.60 x 10-19 C 1 nm = 10-9 m 1 eV = 1.60 x 10-19 J 1 MeV = 106 eV Ionization energy of hydrogen= 13.6 eV hc = 1240 eV nm h h / 2 1.055 10 34 J s 0.66 10 15 eV s Geometric Optics Sign convention Positive concave converging always always real upright upright Focal distance for mirrors, f Focal distance for lenses, f Distance to object, do Object height, ho Distance to image, di Image height, hi Magnification, m Negative convex diverging never never virtual inverted inverted Mirror equation, lens equation Magnification: 1 1 1 d0 di f m Focal distance for mirrors: f=r/2, Waves v=f; D=D0sin(kx-t+), hi d i h0 do Lens power: P=1/f, f – in m, P in diopter (D= m-1) k=, f, f=1/T For a wave traveling from a source in 3D: Intensity I1 /I2 =r22/r1 2, Amplitude D1/D2 =r2/r1 Sound level in decibels =10log(I/I0), I0=10-12W/m2 Doppler effect: f’=f/(1-vs/v) Light as EM wave: Law of reflection: i= r c=f Index of refraction: n=c/v Total internal reflection: n1 sin1>n2 Snell’s law: n1 sin1=n2 sin 2 Wave reflection: shift in phase by if n1<n2, no shift if n1>n2 Wave in medium: Phase shift over extra path =2l/, n=/n Young’s experiment: extra path l=dsin Constructive interference if relative phase =2m m=0,1,2,3,4… Rayleigh criterion for angular resolution =1.22/D Half-width of the first diffractive maximum sin=/D 1 destructive if =2 (m+1/2) Special relativity: t0 t , 1 v2 / c2 m0 c 2 E , 1 v2 / c2 ΔL L0 1 v 2 / c 2 m0 v p KE E m0 c 2 , 1 v2 / c2 E 2 p 2 c 2 m0 c 4 2 Particles and waves Photons: E= hf = hc/, p= h/, Photoelectric effect: E = W0+ KE DeBroglie waves of matter (electrons, tennis balls, ...) = h/(mv)=h/p Electrons (non-relativistic case): KEe = mev2/2 Compton effect (relativistic electron!): E E ' K e , ' h (1 cos ) , p p ' pe mc Quantum mechanics xp x h h 2 d 2 U ( x) E Heisenberg uncertainty principle 2 tE h 2m dx 2 2 h k n n2h2 2 En k n p / h n / L ; sin k n x ; 2m 8mL2 L Schrödinger equation: Particle in a box: n 2m(U 0 E ) h 2 Wave function: probability to find in dV: | | 2 dV , normalization – integral over all space | | 2 dV 1 Tunneling probability T=exp(-2GL), G Hydrogen-like ion (nucleus charge Z): Z 2e4m 1 En 2 2 2 8 0 h n 2 Hydrogen atom: En = -(13.6 eV)/n , Bohr’s radius: r0 100 1 r 3 0 h 2 0 1 0.529 10 10 m 2 Z Zme e r / r0 ; 200 1 32r 3 0 (2 r / r0 )e r / 2 r0 Pr 4r 2 | | 2 Complex atoms: n=1,2,3,… l 0,1,2,3,...(n 1) ml l;(l 1);(l 2),...0 Electron shells s: l=0 p: l=1 3s2 means “2 electrons on n=3 level with l=0 ” Maximum number of states: 2n2 electrons on nth level; Some trigonometry: Cos(2x)=Cos2x-Sin2x 2Sin2x= 1-Cos(2x) Sin(2x)=2Cos(x)Sin(x) 2Cos2x=1+Cos(2x) d: l=2 2 f: l=3 2(2l+1) electrons on nth level on lth shell d(Cos(x))/dx= - Sin(x) d(Sin(x))/dx= Cos(x) Sin(a+b)=Sin(a)Cos(b)+Cos(a)Sin(b) ms 1 / 2