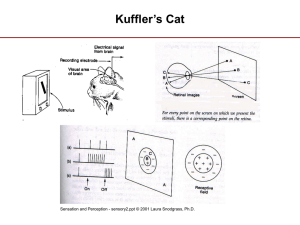
Perception
advertisement

Perception • The study of how the “contents” of the mind got there! • How we gain knowledge of reality • Our only access to the world “outside” our body • Some philosophers argued that there is no physical reality - only our ideas Sensation and Perception - intro.ppt © 2001 Laura Snodgrass, Ph.D. How do we know that we share the same reality? • • • • • Color blindness Blindness Deafness Schizophrenia Virtual reality Sensation and Perception - intro.ppt © 2001 Laura Snodgrass, Ph.D. Characteristics of Perception • Selective - limited range, voluntary attention • Appropriate to the environment – adaptive • Objective - defines reality • Controlled by “patterns” - responds only to change • Active - interpretive and requires stimulation Sensation and Perception - intro.ppt © 2001 Laura Snodgrass, Ph.D. Four Fields Of Study • Physiology - anatomy and pathways • Psychophysics - relationship between our conscious experience and changes in the stimulus • Perception- processes that build an internal representation (often unconscious) • Cognition - changes in perception due to learning, personality, etc. Sensation and Perception - intro.ppt © 2001 Laura Snodgrass, Ph.D. Metatheories • Gibsonian - “direct perception” – perception as an adaptation to the environment • Information Processing – stages that construct an internal representation • Computational – mathematical and computer modeling Sensation and Perception - intro.ppt © 2001 Laura Snodgrass, Ph.D.