Cold War – Pt. 1 – The student will assess the
advertisement

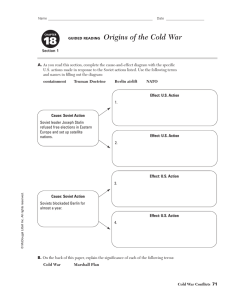
By: Becky Rampey Cold War – Pt. 1– The student will assess the successes and shortcomings of United States foreign policy since World War II. Origins of the Cold War • Major philosophical differences between the U.S. and Soviet Union during and at the end of WWII. –Both want to protect and preserve what they believe in… end up in a Cold War – (State of tension between the U.S. and Soviet Union after WWII) Consequences • Domestic – FEAR / UNKNOWN – (Duck and Cover, Red Scare, McCarthyism) • Foreign – World divided into two sides – fight hot battles around the world for control and to keep one side from getting the upper hand – (Korea, Berlin, Cuba, Vietnam, etc…) • Iron Curtain – Term coined by Winston Churchill to reflect to • Marshall Plan – Aide to countries ravaged by WWII… goal help them rebuild – keep them from turning to Soviet Union for help! • Truman Doctrine – Aide to countries trying to fight off communism. • Berlin Airlift – Soviet Union attempts to force western powers out of Berlin. U.S. and Britain send in supplies for almost 1 year. • Berlin Wall – Soviets build a wall through Berlin to keep anyone from leaving East Berlin. • Bay of Pigs – U.S. trains rebels to try and overthrow the new communist government in Cuba. FAILURE! • Cuban Missile Crisis – Soviets attempt to install Missiles in Cuba (90 miles off U.S. coast) ALLIANCES and World Organizations • United Nations – U.S. will be a key player in the development of UN following WWII. Designed to give the world a place to work on troubles in order to keep from going to another World War. • NATO – North Atlantic Treaty Organization – formed by U.S., Canda and several western European Countries – Goal protection against communist threats. – WARSAW PACT – Soviets reaction to NATO Nuclear Weapons • Proliferation – The spread of nuclear weaponery, technology, and information across the world. • Nuclear Weapons – Atom Bomb, Hydrogen Bomb, Nuclear Bomb, Missiles, etc… • Arms Race – Competition to stock pile nuclear weapons between U.S. and S.U. Containment Policies and Efforts • This policy stated that the United States should resist Soviet attempts to expand its power. • Domino Theory • Europe – – Truman Doctrine - Marshall Plan - Berlin Airlift • Asia – – Vietnam, Korea, and others • Latin America – – Refer back to Monroe Doctrine – We intervene and put in governments that will follow us rather than the Soviets! Major Crisis’ • Berlin Airlift – S.U. wants to shut down western control in Berlin. – Soviet Issue – loss of population in Eastern Europe – Western Issue – Soviets cut off all supplies / transportation to W. Berlin • Berlin Wall – S.U. still experiencing loss of population through W. Berlin – Soviets build a wall to separate the two parts of the city. • Cuban Missile – Soviets placing missiles in Cuba – 90 miles off the Florida coast. (13 Days)