IDEA Student Ratings System Loyola University September 9 & 10, 2015
advertisement

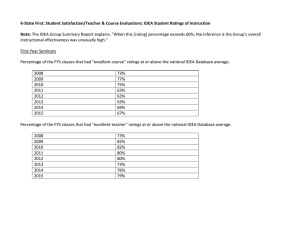
IDEA Student Ratings System Loyola University September 9 & 10, 2015 Jake Glover, PhD Senior Education Officer Session Plan – Review IDEA System (brief) – Strategies for Selecting Learning Objectives – A Look at the New Reports – IDEA2 – What Else is New in IDEA? – Review – Q&A What Makes IDEA Unique? Wouter de Bruijn 1. Focus on Student Learning 2. Focus on Instructor’s Purpose 3. Adjustments for Extraneous Influences 4. Validity and Reliability 5. Comparison Data 6. Flexibility Reflective Practice At home, in class, in lab Try new ideas Collect Feedback Improve Colleagues, IDEA users Reflect & Discuss Interpret Results Read & Learn Resources keyed to reports Context, comparisons Student Learning Model Prioritizing where to focus first by better understanding the relationships between: - Teaching Methods - Learning Objectives - Influential Factors The Foundations of SRI System Teaching Methods: 20 Learning Objectives: 12 Influential Factors: Class Size, Student Motivation, Work Habits, Others Key Influences: • • • • Faculty/Student Collaboration Kellogg Foundation Bloom’s Taxonomy Others… Key Resources: • • • • POD IDEA Notes IDEA Papers (#50 good start) Blog Other on website Conditions for Good Use Campus Culture • Teaching excellence high priority • Resources to improve provided • Student ratings appropriate weight Conditions for Good Use Evaluation Process • 30-50% effective teaching evaluation • Sufficient N (6-8 classes, more if < 10 students per course) Include Multiple forms of Assessment Student Ratings Artifacts External Perspective Balanced Plan for Summative Evaluation Key Factors of the FIF Types of learning must reflect the instructor’s purpose, which will be different across courses and disciplines Key Factors of the FIF Teaching effectiveness is determined by student’s learning on those objectives stressed by the instructor FIF: Getting Started TEACHING & LEARNING TEACHING & LEARNING For Students FIF: Selecting Objectives Selecting Objectives 3-5 as “Essential” or “Important” 1. Is it a significant part of the course? 2. Do you do something specific to help students accomplish the objective? 3. Does the student’s progress on the objective influence his or her grade? Be true to your course Selecting Objectives • How to select “important” or “essential” IDEA objectives related to the course – Use the Teaching Goals Inventory to help select objectives – Use the Three Guiding Questions – Match IDEA with course objectives – Use a Relevant Learning Theory (i.e. Bloom’s Taxonomy) Selecting Objectives IDEA OBJECTIVES 1. Gaining factual knowledge 2. Principles, generalizations, theories 3. Application for improved thinking 6 4. This profession’s points of view, skills 10, 11 5. Team skills 6. Creative capacities 10, 11 3, 8, 9 2, 7 1 7. Broad, liberal education 8. Expressiveness (written and oral) 9. Find & use resources 10. Personal values 11. Analyze and critically evaluate ideas 12. Learn more by asking questions Selecting Objectives: Misconception Students are expected to make significant progress on all 12 learning objectives in a given course. Diagnostic Report Overview Progress on Relevant Objectives What did students learn? Mapping a Program Name of Course 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Senior Research Project X X X Introduction to Psychology I X X X Introduction to Psychology II X X X Developmental Psychology X Cognitive Psychology X X Neurobiological Psychology Clinical Psychology History of Psychology Research Methods 12 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X 11 X X X X X Collect Feedback Improve Read & Learn KNOWLEDGE Reflect & Discuss INFORMATION DATA WISDOM Interpret Results Additional Questions Additional Questions What if you do not select any Learning Objectives? Questions so far? A fowl story with a happy ending… normanack Page 3: What might I do differently? Relationship of Learning Objectives to Teaching Methods Diagnostic Report Overview Formative Page What can I do differently? Resources for Improvement IDEAedu.org • Research and Papers – POD IDEA Notes on Learning – POD IDEA Notes on Instruction – IDEA Papers • IDEA blog Diagnostic Report Overview Progress on Relevant Objectives What did students learn? Summative View How did I do? Description of Course and Students Diagnostic Report Overview Overall Ratings • Excellent Teacher and Excellent Course • 50% of Summary Evaluation Score Quantitative View Statistical Detail - Any additional insights? Adjusted Scores, Converted Averages, and Comparison Scores Adjusted Scores Raw Scores Adjusted Scores Adjusted Scores Impact of student and course characteristics • Most relevant: – Student Work Habits – Student Motivation • Relevant to potentially important: – Class Size – Student Effort – Course Difficulty Adjusted Scores Description of Course and Students Impact of Extraneous Factors Average Progress Ratings: Gaining factual knowledge Work Habits (Item 43) Student Motivation (Item 39) High High Avg. Avg. Low Avg. Low High 4.48 4.38 4.28 4.13 4.04 High Avg. 4.38 4.29 4.14 3.96 3.76 Average 4.28 4.14 4.01 3.83 3.64 Low Avg. 4.15 4.05 3.88 3.70 3.51 Low 4.11 3.96 3.78 3.58 3.38 Raw or Adjusted Scores Purpose Raw or Adjusted? How much did students learn? Raw What were the instructor’s contributions to learning? Adjusted How do courses compare? Adjusted Converted Averages Compare scores on the same scale T Scores • Average = 50 • Standard Deviation = 10 Not percentiles or percentages Similar: Middle 40% (45-55) Comparison Scores IDEA Database Discipline Comparison Validity To what extent do student rating items accurately measure some aspect of teaching and learning that is important to effectiveness? jkfid Validity: IDEA • IDEA Research Report #2 • Technical Report #18 • IDEA Paper # 50 Concurrent Validity • Student ratings of instruction are positively correlated with: – – – – – – Instructor self-ratings Ratings by administrators Ratings by peers Ratings by alumni Ratings by trained observers Review of course materials More Evidence of Validity There are positive correlations between student selfreports of progress on relevant objectives and performance on course exams. Generally performed better on course exams than those who rated their progress as moderate or less. Benton, S. L., Duchon, D., & Pallett, W. H. (2011): Validity of student self-reported ratings of learning, Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education. Diagnostic Feedback Form • 47 questions • Full assessment of student ratings of instruction using teaching methods and learning objectives • Analysis is highly sophisticated, and changes based on relevant learning objectives • Summative ratings • Formative ratings • Development materials connected Footer - Presentation Title Learning Outcomes 18 questions Assessment of relevant learning objectives Assessment of teaching at summative level Assessment of course at summative level Concentrates on course outcomes, rather than faculty performance • Good for clinicals, preceptorships, internships, etc., where faculty interaction is not as integral as student experience • • • • • Footer - Presentation Title Pilot 2015, Ultimate Objective Update learning objectives and teaching methods in our Student Ratings of Instruction tools to better reflect current trends in higher education Pilot 2015, why now? • IDEA research – New items were identified that align with national standards, including the AAC&U, regional accreditors, and other recognized learning organizations – Some current items were identified as less relevant or dated and were eliminated or revised • Principle of continuous improvement What is being added… • Teaching Methods: diversity, self-reflection, and service-learning • Learning Outcomes: diverse perspectives and global awareness, ethical reasoning and decision making, civic engagement, and quantitative literacy • Student and Course Characteristics; self-efficacy and background and preparation Pilot 2015 Process IDEA-CL Platform (courses ending May 2015) •13 items will be added to the existing student ratings Diagnostic Feedback instrument •6 new (or newly revised) Learning Outcomes will be added to the existing FIF • Individual faculty reports will include statistical data for the new items; there will be no other changes to the existing reports IDEA 2 Following successful pilot: •Diagnostic Feedback 2.0, updated and shorter diagnostic instrument (approx. 40 items) •FIF 2.0, revised Faculty Information Form •Learning Outcomes 2.0, formerly referred to as the “Short” form, updated NEW: Teaching Essentials New 12-item instrument includes specific teaching methods and external variables greatest impact on student ratings of overall course and instructor excellence No FIF required Application EOT- End of term- April (tentative) ARS-Automatic Response System- Summer (tentative) IDEA 2 Instruments Items (est.) Application Diagnostic Feedback 2.0 40 items Comprehensive assessment of overall teaching effectiveness Learning Outcomes 2.0 19 items Best for courses where outcomes rather than teaching methods are the focus, such as clinical, practicum, and lab Teaching Essentials 12 items Provides a screening of fundamentals of teaching for quick review of faculty performance Students View of Feedback Faculty Views Faculty Web Reports Diagnostic Feedback Teaching Essentials • Comprehensive assessment • Thorough diagnostic • Short • Basic screen Learning Outcomes • Outcomes based • Not diagnostic Instant Feedback • Immediate • Base-level assessment If you love something let it go… Yutaka Tsutano From Evaluation to Engagement (Response Rates) • Create Value for Students – Let them know their input is valuable and actually used to make changes • Utilize In-Class Capture – Take 20 minutes in class to administer survey – Now easier online with mobile administration – Prepare students by putting it in syllabus • Monitor and Communicate – Use real-time reports of response rates – Utilize effective follow-up emails Selecting Objectives 3-5 as “Essential” or “Important” 1. Is it a significant part of the course? 2. Do you do something specific to help students accomplish the objective? 3. Does the student’s progress on the objective influence his or her grade? Be true to your course FIF: Getting Started FIF: Selecting Objectives For Further Study Final questions/thoughts? THANK YOU!