Making the Case for Teaching Professor Pip Pattison Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Education)
advertisement

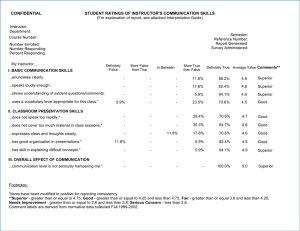
Making the Case for Teaching Professor Pip Pattison Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Education) Academic Promotions Applicant Information Session 2015 What do we mean by ‘teaching’ in this context? An inclusive sense: › Undergraduate teaching › Graduate coursework teaching › Research higher degree supervision › Curriculum design and development › Educational design, instructional design, learning design › Learning support and learning enrichment › Educational leadership (course, faculty, university, discipline, profession) 2 Structuring the case A compelling narrative setting out purpose and method: - What are you trying to achieve? - Why? - How? Evidence for success – how can you establish that: - Your educational approach is effective? - Your students are inspired and motivated to learn? - Your students are achieving excellent outcomes? - You are improving student outcomes, including through effective feedback cycles? - You are contributing beyond the units of study in which you teach directly? - Your contribution is innovative? - You are contributing to research/scholarship in education? - You are contributing to educational leadership in the University or beyond? 3 Sources of evidence (1) New and prevailing evidence › The scholarly literature (existing evidence for effective practice, e.g. for ‘high impact’, inquiry-based and/or collaborative methods) › Contributions to the scholarly literature (new evidence for effective practice) › Evidence of impact of practice on student learning (unpublished evidence) › Use of student feedback and student learning to inform practice Judgments by experts and peers › External and internal awards › Other peer reviews and reports (e.g. Group of Eight Quality Verification System) › Invitations to share insights and expertise within school, beyond school, faculty, university (and even university sector) › Invitations for educational consultancies, even commercialisation opportunities › Uptake of educational innovations 4 Sources of evidence (2) Student views of the learning experience › Unit of Study Evaluation/new Unit of Study Survey results (reported concisely but comprehensively) › Other sources of data on students’ learning experience Evidence of student outcomes › Evidence of student learning › Evidence of student retention › Benchmarking, external assessment of student learning › Uptake of further learning pathways where relevant › Judgments of students by others (e.g. employers, external supervisors) › External recognition of student learning (e.g. prizes and awards) 5 Sources of evidence (3) Documentation of educational approach and innovation › Curriculum › Learning design › Learning activities › Resources › Assessment strategy › Improvement strategies Evidence of broader impacts › Evidence of leadership impact (curriculum, discipline) › Evidence of contribution to professional learning in learning and teaching › Evidence of community, industry or professional impact of teaching › Educational thought leadership › Judgments of mentees 6 Strength of evidence Evidence is most convincing where: › It is aligned with your compelling narrative of purpose and method › It is ‘independent’ (as far as possible) › It is consistent › It draws from multiple sources and perspectives › It involves substantial student cohorts Needless to say: › everything is relative and needs to be understood in context! 7 MINIMUM STANDARDS FOR PROMOTION TEACHING AND RESEARCH STREAM – Minimum required standards Promotion sought Teaching standard Research standard Service standard Comment Level A to Level B; Level B to Level C; Level C to Level D Superior or Outstanding Superior or Outstanding Superior At least one Outstanding is required in either Teaching or Research Level D to Level E Outstanding Outstanding Superior N/A EDUCATION FOCUSSED STREAM – Minimum required standards Promotion sought Teaching standard Research standard Service standard Comment All Exceptional Superior or Satisfactory Superior or Satisfactory At least one Superior is required, in either Research or Service RESEARCH FOCUSSED STREAM – Minimum required standards Promotion sought Teaching standard Research standard Service standard Comment All Superior or Satisfactory Exceptional Superior or Satisfactory At least one Superior is required, in either Teaching or Service 8 Making sense of the all-important descriptors... › Exceptional: highly significant achievements and contributions at level to which promotion is sought › Outstanding: achievements and contributions meet criteria at level to which promotion is sought › Superior: highly significant achievements and contributions at current level › Satisfactory: achievements and contribution meet criteria at current level 9 Some important resources ITL workshops and resources › Please see Academic Promotions (teaching) at the ITL website: itl.usyd.edu.au 10 A final word of advice... Tell your educational (short*) story! *There is a word limit 11 QUESTIONS? Email: pip.pattison@sydney.edu.au Taking account of level-dependent criteria... › Level A: ... contribute ... under supervision... › Level B: ... education-related scholarly activities which have resulted in improvements of teaching quality and/or educational outcomes › Level C: ... disseminate knowledge in L&T to benefit and promote good practice ... › Level D: ... Contribution to national efforts to enhance curriculum ... Sustained track record of effective leadership in teaching teams ... Evidence of major original and innovative contributions ... › Level E: ... international recognition for scholarship ... enhance University’s operations ... enhance University’s international reputation 13