Negative Lens: Spreads Light Out.
advertisement
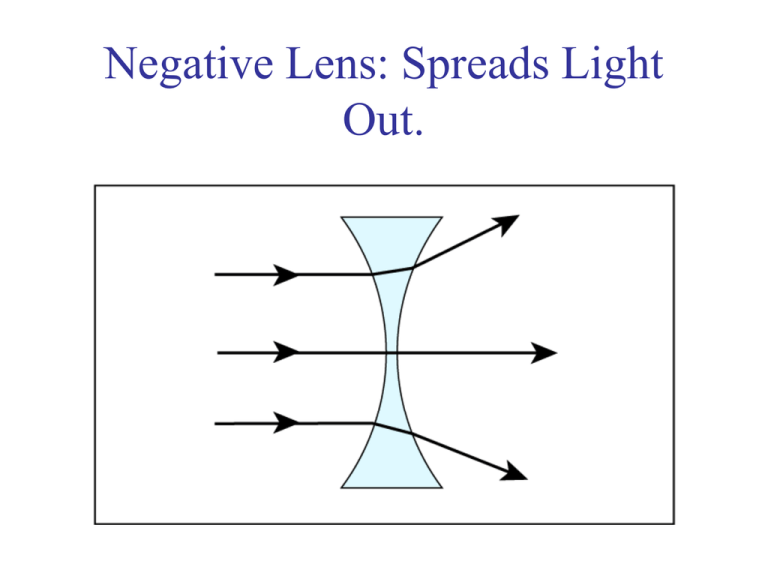
Negative Lens: Spreads Light Out. Myopia corrected Myopia is corrected with a negative lens that compensates for the excess power of the cornea and lens. The focus point is moved backwards. Surgical Corrections • • • • RK: small cuts around edge of cornea PRK: laser reshapes surface of cornea LASIK: laser reshapes internal layers of cornea Implantable lens and rings Hyperopia (Farsighted) When the eye is hyperopic, the eye is too short and the point of focus is in behind of the retina. A blurry image falls on the retina. Positive Lens: Focuses Light; Magnifier Hyperopia corrected Hyperopia: Corrected Hyperopia is corrected by placing an additional, positive lens in front of the eye. The stronger the lens, the more the focus point is moved forward. Spherical Aberration • Human cornea is “aspherical” • Human lens has progressive index of refraction Current Research Question: • Why are some eyes myopic or hyperopic? • Why are so many eyes emmetropic? • Not random as after birth % emmetropic increases. • Most cases of myopia start later, in teens. Associate with “close-work”. • Two theories: – Extra muscular forces for accommodation etc. – Misguided growth Astigmatism Christman, 1971, p.150. Radial Zakia, 1997, p.220. Accommodation The Lens & Accommodation The lens changes shape to focus objects at different distances. Can also compensate for some myopia, hyperopia Marmor & Ravin, 1997, p.16 Presbyopia Presbyopia Marmor & Ravin, 1997, p.17 Accommodation vs Age • Fixed Focus by 50 • “Presbyopia” Gregory, 1997, p.39. Hyperopia and Accommodation Hyperopia & Accommodation When young, hyperopia may compensated by making the lens more round. Myopia and Accommodation Myopia & Accommodation When young, myopia may not be obvious as it can be compensated by flattening the lens. The Lens and Aging • Presbyopia • Yellowing • Opaque (Cataracts) Cataract: young .





