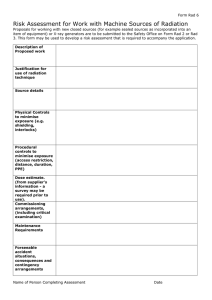
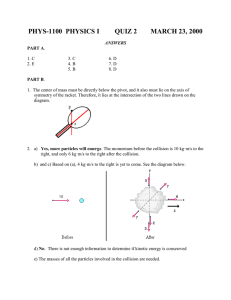
Two additional Examples for Sketching FM and PM Signals EE 370
advertisement

EE 370 Chapter V: Angle Modulation Two additional Examples for Sketching FM and PM Signals Example 1: Sketch the FM signal that results when modulating the message signal m(t) shown below with kf = 2(2) and c = 2 (10) rad/s. m(t) 2 1 0.3 t –4 –7 –10 –2 2 4 8 14 14 6 5 6 –1 –2 fi(t) in Hz is equal to 10 10 11 12 12 12 12 14 10 6 6 6 10 10 10 10 t Phase Discontinuity here because of delta in m(t) Phase Discont. = 0.3*kf = 1.2 rad Example 2: Sketch the PM signal that results when modulating the message signal m(t) shown below with kp = 2 and c = 2 (14) rad/s. To sketch the PM signal, we can compute dm(t)/dt and sketch the frequency modulated signal when dm(t)/dt is input to an FM block similar to Example 1. EE 370 Chapter V: Angle Modulation m(t) 8 5.2 4 1.5 t –10 –7 –4 –2 2 –2 3 4 6 7 8 –4 –6.5 –8 dm (t ) m (t ) dt 8 4 3.7 1.5 –10 –8 –6 –4 –2 2 4 5 6 –1.2 –4 –8 fi(t) in Hz is equal to 18 18 14 14 6 6 14 14 16 16 14 14 14 14 12 12 16 16 t Phase discont. because of discont. in m(t) [delta function in dm(t)/dt] Phase Discont. = 1.5*kp = 3 rad Phase discont. because of discont. in m(t) [delta function in dm(t)/dt] Phase Discont. = 3.7*kp = 7.4 rad Phase discont. because of discont. in m(t) [delta function in dm(t)/dt] Phase Discont. = – 1.2*kp = – 2.4 rad