Power Supply CHAPTER 5
advertisement

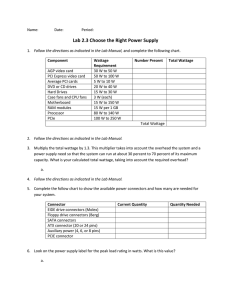
CHAPTER 5 Power Supply Chapter Overview Power Supplies Power Supply Problems Computer Power Supply Unit (Computer PSU) typically is designed to convert 110 V or 230 V AC power from the mains to usable lowvoltage DC power for the internal components of the computer. The most common computer power supplies are built to conform with the ATX form factor The official specifications were released by Intel in 1995, and have been revised numerous times since, the most recent being version 2.3,[1] released in 2007. This enables different power supplies to be interchangeable with different components inside the computer.. Overview of Power Supplies The standard power supply Converts AC to DC “Conditions” power by evening out changes. Requires a fan Standard power in U.S. is 110 volts alternating current (VAC) oscillating at 60 hertz (Hz). You must consider physical size, wattage, and connector types when replacing a power supply. Power Supply Sizes Power supply sizes are based on the type of case and motherboard connections. The AT-style is found on older computers and earlier Pentium systems. The ATX-style (current technology) is found on Pentium II and later systems. You should compare the existing power supply with the new one before replacing it. On –off power control circuit. Not the button on ATX boards is built into the MB, on AT style it comes from the PS. AT style The AT form factor is the first modern form factor to be widely used. AT (Advanced Technology) was released in 1984 by IBM 6 ATX style The ATX (for Advanced Technology Extended) form factor was created by Intel in 1995. It was the first big change in computer case and motherboard design in many years. 7 24-pin ATX12V 2.x power supply connector(20-pin omits the last four: 11, 12, 23 and 24) Color Signal Pin Pin Signal +3.3 V Color Orange Orange +3.3 V 1 13 Orange +3.3 V 2 14 −12 V Blue Black Ground 3 15 Ground Black Red +5 V 4 16 Power on Black Ground 5 17 Ground Black Red +5 V 6 18 Ground Black Black Ground 7 19 Ground Black Grey Power good 8 20 No connection Purple +5 V standby 9 21 +5 V Red Yellow +12 V 10 22 +5 V Red Yellow +12 V 11 23 +5 V Red Orange +3.3 V 12 24 Ground Blac +3.3 V sense Brown Green 8 Power Supply Wattage A watt is a unit of electrical power equivalent to one volt-ampere. Total wattage needs are determined by adding the power required for each device, plus more power for startup. General-use computers require 130–205 watts. Servers and high-performance workstations require 350–500 watts. AC and DC Voltages Alternating Current (AC) Alternating Current (AC) flows one way, then the other way, continually reversing direction. An AC voltage is continually changing between positive (+) and negative (-). Direct Current (DC) Direct Current (DC) always flows in the same direction, but it may increase and decrease. A DC voltage is always positive (or always negative), but it may increase and decrease 11 Power Supply Connectors Connections to Peripheral Hardware Extenders and Splitters Extenders are wire sets that have a molex connector on each end, used to extend power connection. Splitter A splitter increases the number of connections. 15 Power Failures Power failures can have internal or external causes. External failures, which are more common, include Surges ( increase in the voltage source, very high voltage for a very short time) Spike ( very short over voltage measured in nanoseconds) Sags (decrease of voltage at the power source) Brownouts ( sage lasts longer than 1 second) Blackouts ( complete power failure) Power Protection Devices A surge suppressor Filters the effects of voltage spikes and surges Smoothes out power variations An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is an inline battery backup. Power Supply Problems Alternative Direct Chapter Summary The AT-style power supply is used for older motherboards and the ATX-style power supply is used for newer motherboards. Peripheral devices use Molex connectors and mini connectors. Different types of power failures can cause computer problems and can damage computer equipment. Surge suppressors and UPS devices can protect computer equipment.