KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM & MINERALS ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT EE 202
advertisement

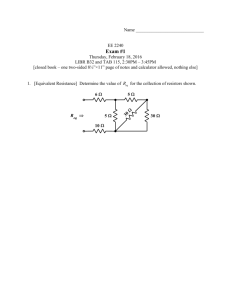
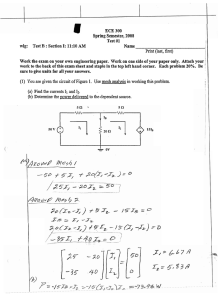
KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM & MINERALS ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT EE 202 EXAM I DATE: Wednesday 3/10/2012 TIME: 6:00 PM-7:30 PM ID# Name KEY Section# Maximum Score Q1 Q2 Q3 TOTAL 30 35 35 30 Score Problem #1 (30) (a) The equivalent resistance R eq between the two terminals A and B is 2 2 A R eq 2 2 B (I) 2 (II) 2.8 (III) 1 (IV) 2.5 (V) 1.2 (VI) 3 (VII) 1.5 (VIII) 3.3 (b) In the circuit shown below , the value of v1 Vx is 5 Vx - + - 10 V 0.4 v 1 (I) 10 V (II) - 10 V (III) 4 V (V) - 6 V (VI) 0 V (VII) 6 V (IV) - 4 V (VIII) 5 V is (c) In the circuit shown below , the value of and the power absorb by R 1 are -3 A 3A R2 is R3 + - 10 V R1 (I) 6 A , - 30 W (II) - 6 A , - 30 W (III) 6 A , 30 W (IV) - 6 A , 30 W (V) 3 A , - 30 W (VI) - 6 A , - 60 W (VII) - 3 A , 60 W (VIII) 3 A , 60 W (d) In the circuit shown below , the value of v 2 is 1 1A 10 V + - v 1 2 1 + - 5V (I) 2 V (II) - 2 V (III) - 5 V (IV) 5 V (V) - 3 V (VI) 3 V (VII) 0.5 V (VIII) - 0.5 V (e) In the circuit shown below , the value of 2 i is 4 7 6A i 3 24 A 5 24 (V) A 5 (I) (II) - 1 6 A 5 (VI) - 8 A 6 A 5 (IV) 2 A (VII) 8 A (VIII) - 2 A (III) Problem #2 (35) 10 i x A I3 R R Vx - I1 R I2 3 Vx V + - 110 V ix + - R For the circuit shown above : (a) If R = 1 write the mesh currents equations necessary to solve for the mesh currents I,I ,I 1 2 and put the equations in a matrix form (DO NOT SOLVE THE 3 EQUATIONS) (a) Solution R= 1 KVL on Mesh 1 1I 1 + 1(I 1 - I 3 ) + 110 + 1I 1 = 0 3I 1 - I 3 - 110 KVL on Mesh 2 1(I 2 - I 3 ) + 3v x - 110 = 0 Since v x 1(I 2 - I 3 ) 4I 2 - 4I 3 110 Mesh 3 10i x I 3 Since i x -I 1 10I 1 I 3 0 3 0 -1 I 1 -110 0 4 -4 I 2 110 10 0 1 I 3 0 If R = 5 in the previous circuit the mesh currents are found to be (b) I1 -1.7 A I 2 = 22.4 A I 3 16.9 A Find the power absorbed or delivered ( indicate it) by the voltage sources ? (b) Solution R= 5 P 110 110 I 1 - I 2 (3) OR P 110 (deliver) 110 I 2 - I 1 110 -1.7 - 22.4 110 -1.7 - 22.4 = - 2651 W ( Absorbing ) ( OR 2651 W ( Delivering ) P 3v x 3v x I 2 OR P 3v x (deliver) 3(5) I 2 - I 3 I 2 15 22.4 - 16.9 22.4 1848 W (Absorbing) OR - 1848 W ( Delivering ) - 3v x I 2 Problem #3 (35) 3 Vx Supper node 1 20 V v1 2 I - 6 v2 Supper node 2 - 3 Vx V v3 - 4 10 A v4 R For the circuit shown above (I) If R = 1 write the node voltage equations necessary to solve for the node voltages v , v , v , v and put the equations in a matrix form (DO 1 2 3 4 NOT SOLVE THE EQUATIONS) (I) Solution R= 1 KCL on Supper Node 1 v 1 v 1 -v 4 v 2 -v 3 + - 10 + =0 2 3 6 5v 1 +v 2 - v 3 - 2v 4 60 KCL on Supper Node 2 v 3 -v 2 v 3 v 4 v 4 -v 1 + + + =0 6 4 1 3 -4v 1 - 2v 2 5v 3 16v 4 0 Since v 3 - v 4 3V x 3 v 1 - v 4 3v 1 - v 3 - 2v 4 0 Since v 1 - v 2 20 5 1 -1 -2 v 1 60 -4 -2 5 16 v 2 0 3 0 -1 -2 v 3 0 1 -1 0 0 v 20 4 (II) If If R = 12 in the previous circuit and the nodes voltages now are : v 1 26.67 V , v 2 = 6.67 V , v 3= - 32 V , v 4 56 V Find the power absorbed or delivered (indicate it) by the independent voltage source P ? 20 V (II) Solution R= 12 P 20I 20 (3) KCL on node v1 we have P (deliver) OR 20 - 20I v 1 v 1 -v 4 + +I =0 2 3 26.67 26.67 - 56 + +I =0 2 3 I = - 3.56 A P 20 20I 20(-3.56) = - 71.167 W (Absorbing) OR 71.167 W (Delivering)