Currency Futures and Options Markets PART I.FUTURES CONTRACTS
advertisement

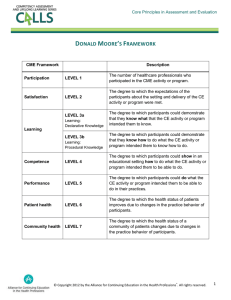
FNC 470 – Moore Chapter 8 Notes Spring 2006 Currency Futures and Options Markets PART I.FUTURES CONTRACTS I. CURRENCY FUTURES A. Background 1. Long history 2. Extremely volatile due to information driven nature 3. Price Discovery Role 1972: Chicago Mercantile Exchange opens Monetary Market (IMM). the International 2. IMM provides a. an outlet for hedging currency risk with futures contracts. Definition: contracts written requiring a standard quantity of an available currency at a fixed exchange rate at a set delivery date. b. Available Futures Currencies/Contract Size: 1.) British pound / 62,500 2.) Canadian dollar /100,000 3.) Euro / 125,000 4.) Swiss franc / 125,000 5.) Japanese yen / 12.5 million 6.) Mexican peso / 500,000 7.) Australian dollar / 100,000 -1- FNC 470 – Moore Chapter 8 Notes Spring 2006 c. Transaction costs: commission payment to a floor trader d. Leverage is high 1.) Initial margin required is relatively low (less than 2% contract value). of FUTURES CONTRACTS: SAFEGUARDS e. Maximum price movements 1.) Contracts set to a daily price limit restricting maximum daily price movements. 2.) If limit is reached, a margin call may be necessary to maintain a minimum margin. f. Global futures exchanges: 1.) I.M.M. International Monetary Market 2.) L.I.F.F.E. London International Financial Futures Exchange 3.) C.B.O.T. Chicago Board of Trade 4.) S.I.M.E.X.Singapore International Monetary Exchange 5.) D.T.B. Deutsche Termin Bourse 6.) H.K.F.E. Hong Kong Futures Exchange B. Forward vs. Futures Contracts Basic differences: 1. Trading Locations 2. Quotes 3. Regulation 4. Margins 5. Frequency of delivery 6. Credit risk 7. Size of contract 8. Transaction Costs -2- FNC 470 – Moore Chapter 8 Notes Advantages of futures: 1.) Easy liquidation 2.) Well- organized and stable market. Disadvantages of futures: 1.) Limited to 7 currencies (WRONG) 2.) Limited dates of delivery 3.) Rigid contract sizes. -3- Spring 2006 FNC 470 – Moore Chapter 8 Notes Spring 2006 Real Future’s Contract Specifications and quotes Source: http://www.cme.com/clearing/clr/spec/contract_specifications.html?type=cur CME Australian Dollar Futures Trade Unit 100,000 Australian dollars Settle Method Physically Delivered Point 1 point = $.0001 per Australian dollar = $10.00 per contract Descriptions Contract Listing Six months in the March Quarterly Cycle. Mar, Jun, Sep, Dec. Strike Price N/A Interval Product Code Clearing=AD Ticker=AD GLOBEX=6A AON=LA (50 Threshold)& Trading Venue: Floor Minimum Regular Fluctuation Calendar Spread All or None Trading Venue: CME® Globex® Mon/Thur 5:00 p.m.-4:00 Margin Hours p.m. Sun & Hol 5:00 p.m.-4:00 p.m. 0.0001=$10.00 0.00005=$5.00 0.00005=$5.00 Initial $1,283 -4- Maintenance $950 FNC 470 – Moore Chapter 8 Notes -5- Spring 2006 FNC 470 – Moore Chapter 8 Notes Spring 2006 Mechanics of a Future’s Contract Australian Dollar Futures Contract Information and Quotes from CME CME® Globex® FUTURES CME Australian Dollar Futures CME Globex quotes as of 07/20/06 06:00 am (cst) MTH/ STRIKE SEP06 DEC06 MAR07 JUN07 SEP07 DEC07 TOTAL TOTAL --- SESSION --OPEN HIGH .7503 .7475 ------------- .7509 .7496B ------------- LOW .7483 .7475 ------------- PT EST VOL LAST SETT CHGE .7499A .7489A ------------- ------------------- +9 2898 +10 3 UNCH UNCH UNCH UNCH EST. VOL ---- PRIOR SETT DAY --- VOL INT .7490 30991 54135 .7479 68 584 .7466 9 .7452 4 .7438 2 .7424 VOL OPEN INT. 31,059 54,734 Question 1. Suppose you want to long 1 September 2006 futures contract. How much initial margin must you deposit into your account? Question 2. Suppose you bought the September futures contract at .7499 and at the end of the day it settled at .7418. How much would be added or subtracted from your account? Question 3. At what price on the long June 2006 contract would you get your first margin call? Question 4. If you received a margin call, to what amount (account level) must you bring your balance to? Question 5. What is the notational value of Australian Dollars at risk for the September 2006 Contract (one-side)? -6- FNC 470 – Moore Chapter 8 Notes Spring 2006 All Prices are DELAYED by a minimum of 15 minutes. AUD Expiry Bid Ask Open High Low Last Trade Sep 06 0.7501 0.7505 Dec 06 0.7490 0.7494 Mar 07 Jun 07 -7- Last Trade Date 18/7/06 Last Change Traded Previous Trade Volume Settlement Time 10:49 0.7493 0.7468 0.7468 0.7468 FNC 470 – Moore Chapter 8 Notes Spring 2006 Uses of Currency Future’s Contracts 1. Suppose you are due to receive $AU 1,000,000 from a customer on the date the September 2006 future’s contract is due to expire. The current spot price (US direct quote) is $0.7512 and the September futures is selling at $0.7499. Do you want to go long or short in the contract to hedge your currency risk? How many contracts? 2. Assume the above information. How much did you pay for “insurance” to guarantee your ultimate selling price? 3. Assume that the spot rate on the settlement date is $0.7553. How much did you gain or lose on the future’s contract? How much did you gain or lose on the foreign exchange transaction with your customer? How much is your net gain or loss? 4. Now, assume that the spot rate on the settlement date is $0.7453. How much did you gain or lose on the future’s contract? How much did you gain or lose on the foreign exchange transaction with your customer? How much is your net gain or loss? -8- FNC 470 – Moore Chapter 8 Notes Spring 2006 Options on Futures 4. Definition: A contract from a writer ( the seller) that gives the right not the obligation to the holder (the buyer) to buy or sell a standard amount of an available currency future’s contract at a fixed exchange rate for a fixed time period. 5. Expiration Dates of Currency Options: a. American Exercise date may occur any time up to the expiration date. 7. Exercise Price a. Sometimes known as the strike price. b. The exchange rate at which the option holder can buy or sell the contracted currency. -9- FNC 470 – Moore Chapter 8 Notes Spring 2006 Example of Australian Dollar Options on Future’s PIT OPTIONS CME Australian Dollar Options Pit-Traded prices as of 02/27/06 12:50 pm (cst) MTH/ STRIKE OPEN --- SESSION --HIGH LOW ZA MAR06 CME AUSTRALIAN DOLLAR OPTIONS 7050 ---------7100 ---------7250 ---------7300 ---------7350 ---------7400 ------.200A 7450 .050 .050 .050 7500 ---------7550 ---------7600 ---------7650 ---------7700 ---------7750 ---------7800 ---------7900 ---------8300 ---------ZA APR06 7400 7450 7500 LAST SETT PT CHGE ---- PRIOR DAY ---SETT VOL INT CALL (Cents per Australian Dollar) ------UNCH 3.400 ------UNCH 2.900 ------UNCH 1.430 ------UNCH .960 ------UNCH .540 .200A ----5 .250 .050 ----6 5 .110 ------UNCH 5 .050 ------UNCH .020 ------UNCH .010 ------UNCH .005 ------UNCH CAB ------UNCH CAB ------UNCH CAB ------UNCH CAB ------UNCH CAB AUSTRALIAN DOLLAR OPTIONS CALL ------------------.440A .440A ------------- ---------- UNCH -6 UNCH ZA JUN06 AUSTRALIAN DOLLAR OPTIONS CALL 7400 1.120 1.120 1.120 1.120 7500 ------.720A .720A 7600 ------------7700 ------------7900 .100 .100 .100 .100 8000 ------------- ------------------- -8 -8 UNCH UNCH -1 UNCH - 10 - EST VOL .700 .500 .340 5 5 1.200 .800 .500 .310 .110 .060 20 63 63 69 46 29 79 62 221 178 7 70 9 33 43 7 10 10 3 7 10 10 53 95 3 6 284 21 10 FNC 470 – Moore Chapter 8 Notes Spring 2006 PIT OPTIONS CME Australian Dollar Options Pit-Traded prices as of 02/27/06 12:50 pm (cst) MTH/ STRIKE OPEN --- SESSION --HIGH LOW LAST SETT PT CHGE EST VOL ---- PRIOR DAY ---SETT VOL INT ZA MAR06 AUSTRALIAN DOLLAR OPTIONS PUT (cents per Australian Dollar) 7000 ---------------UNCH CAB 7050 ---------------UNCH CAB 7100 ---------------UNCH .005 7150 ---------------UNCH .010 7200 ---------------UNCH .015 7250 ---------------UNCH .030 7300 ---------------UNCH .060 7350 ---.150B ---.150B ---+1 .140 7400 ---.400B ---.400B ---+5 .350 7450 ---------------UNCH .710 7500 1.300 1.300 1.300 1.300 ---+15 5 1.150 7550 ---------------UNCH 1.620 7600 ---------------UNCH 2.110 ZA APR06 7300 7400 AUSTRALIAN DOLLAR OPTIONS PUT ------------------------- ------- UNCH UNCH .490 .930 ZA JUN06 7100 7200 7400 AUSTRALIAN DOLLAR OPTIONS PUT ------------------------------------- ---------- UNCH UNCH UNCH .410 .640 1.430 - 11 - 1 2 10 1 1 115 1 40 1 120 58 328 202 155 59 3 10 10 38 203 1 FNC 470 – Moore Chapter 8 Notes Spring 2006 Uses of Currency Options on Future’s Contracts 1. Suppose you are due to receive $AU 1,000,000 from a customer on the date the March 2006 future’s contract is due to expire. The current spot price (US direct quote) is $0.7383 and the March futures is selling at $0.7380. Do you want to buy a call or put with a $0.7400 strike price in the contract to hedge your currency risk? How many contracts? 2. Assume the above information. How much did you pay for “insurance” to guarantee your ultimate selling price? 3. Assume that the spot rate on the settlement date is $0.7353. How much did you gain or lose on the future’s contract? How much did you gain or lose on the foreign exchange transaction with your customer? How much is your net gain or loss? 4. Now, assume that the spot rate on the settlement date is $0.7453. How much did you gain or lose on the future’s contract? How much did you gain or lose on the foreign exchange transaction with your customer? How much is your net gain or loss? - 12 -