V=knapsack volume, weight limit n- elements number w(1),w(2),...,w(n) – values
advertisement

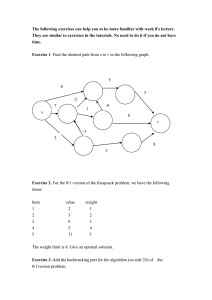
Knapsack problem V=knapsack volume, weight limit n- elements number w(1),w(2),...,w(n) – values v(1),v(2),...,v(n) – volumes, weights I. Heuristic (greedy procedure): value/ volume, in the increasing order of this indicator: Element Value volume V= 10. A 75 7 B 150 8 C 250 6 Element Value volume V= 5. A 100 2 B 10 2 C 120 3 Element Value volume V= 30 A 50 5 B 140 20 C 60 10 Element A B C D Value Volume V= 6 2 1 3 2 3 4 4 5 Element A B C D 200 50 155 40 115 30 90 25 Value Volume V= 95 D 35 4 E 10 3 F 100 9 Linear programming problem: 𝑛 ∑ 𝑤(𝑖) 𝑥(𝑖) → 𝑚𝑎𝑥 𝑖=1 𝑛 ∑ 𝑣(𝑖) 𝑥(𝑖) ≤ 𝑉 𝑖=1 𝑥(𝑖) = 0,1 II. K-optimal algorithm (heuristic) A. k=1 B. For all the subsets of the set of elements with cardinality k, which fit into the knapsack: we put them into the knapsack and complete the knapsack like in the heuristics I C. III. While k<n-1, k:=k+1 and go to B. Otherwise choose the best solution Dynamic algorithm (exact) Table with dimensions „knapsack volume +1” x „elements number +1” 1. First row and column fill with „0”s 2. i:=1 3. IF i=n+1, STOP, interpret the solution 4. Consider column i and its individual elements s, s=0,1,,,,V. In each element s draw a horizontal arrow for column i-1, if it is not possible or not profitable to put element i into the knapsack of capacity s, and draw an arrow going down from column i-1, with the height equal to the volume of element i, if it is possible and profitable element i into the knapsack of capacity s. In the first case copy the value from the beginning of the arrow at the end of the arrow, in the second case add to the value from the beginning of the arrow the value of element i and put it at the end of the arrow. 5. i:=i+1, go to 3. Multiple knapsack problem – the same element can be available in more than one copy. Dynamic algorithm – the same, but additionally consider arrows with heights equal to multiplications of elements weight. Element Value Volume Numer of copies V= 16 A 15 7 4 B 10 5 3 C 4 2 4 Knapsack problem 1. decision variables: x(i)= 0-1 (put – not put) for each element i=1,..,n 2. objective function: w(1)x(1)+w(2)x(2)+...+w(n)x(n)--> max 3. constraint: w(1)x(1)+w(2)x(2)+...+w(n)x(n)<=V