The Tipping Point How to Start a Revolution
advertisement

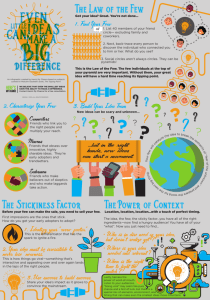
The Tipping Point How to Start a Revolution What is the Tipping Point Pressure causes toppling Unexpected becomes expected Threshold Boiling point Information Epidemic Spreads like a virus Geometric progression Epidemic Tips When….. People, information and conditions appropriate: Message Changes and effect Quickly The Tipping Point The Law of the Few The Stickiness Factor The Magic Number 150 Conclusion Diffusion Model How Ideas are Spread 2 Types of Communication Word-of-Mouth Rumors How Ideas are Spread cont. 3 Types of Communicators Connectors Mavens Salespersons The Stickiness Factor Presentation of an idea can affect how the idea is received and whether people take action upon it. Whether it “Sticks” Context A persons actions are as much a product of the environment in which that person is placed as they are of that persons character. The Magic Number 150 The upper limit of social circles The maximum amount of people that one can maintain a functioning social relationship with History in evolution of human beings, development of brain and cognition The Magic Number 150 (cont.) Examples: Hutterite colonies Military hierarchy Manufacturing facilities Any more than one fifty is beyond the threshold of cognition Extreme breakdown of social structure Lessons of the Tipping Point 1. 2. 3. Concentrate resources on a few key areas. People who create successful epidemics deliberately test their intuitions. Belief that change is possible. The Diffusion Model A detailed, academic way of looking at how a contagious idea or “product” or innovation moves through a population. The Tipping Point……….. Wrap the main points up…