Pitch and Music

Pitch and Music
Pitch
• Pitch is the subjective perception of frequency
Period - amount of time for one cycle
Frequency - number of cycles per second
(1/Period)
Air Pressure time ->
Pitch
• Pure Tones - are sounds with only one frequency f = 400 hz f = 800 hz
Tone Height
• Tone Height is our impression of how high or low a sound is
• but there’s something more to our impression of how something sounds than just its tone height…
Chroma
• Tone Chroma is the subjective impression of what a tone sounds like
• Notes that have the same Chroma sound similar
500 Hz
400 hz
800 Hz
Chroma
• Tones that have the same Chroma are octaves apart
Chroma
• chroma is best represented as a helix
• chroma repeats every octave
• tones with the same chroma are above or below each other on a helix
Chroma
• Tones that are octaves apart have the same chroma
• one octave is a doubling in frequency
Chroma
• frequency is determined (in part) by location of stimulation on the basilar membrane
Chroma
• frequency is determined (in part) by location of stimulation on the basilar membrane
• but that relationship is not linear (it’s logarithmic)
Chroma
• doublings of frequency map to equal spacing on the basilar membrane
Pure Tones are Very Rare in
Nature!
• What are real sounds composed of?
Pure Tones are Very Rare in
Nature!
• What are real sounds composed of?
• Virtually all sounds are composed of several (or many) frequencies all going at once
Pure Tones are Very Rare in
Nature!
• What are real sounds composed of?
• Virtually all sounds are composed of several (or many) frequencies all going at once
• “Extra” frequencies are called harmonics
up position down
What are harmonics?
imagine a guitar string:
up position down
What are harmonics?
imagine a guitar string:
What are harmonics?
But more than one frequency can “fit” between the end points up position time -> down
up position
What are harmonics?
In fact many frequencies can be superposed .
f
0 f
2 time -> down f
1
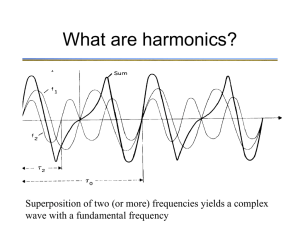
What are harmonics?
Superposition of two (or more) frequencies yields a complex wave with a fundamental frequency
The Missing Fundamental
• Your brain so likes to track the fundamental of a set of harmonics that it will perceptually fill it in even when it is absent missing fundamental
Timbre (pronounced like:
Tamber)
Pronounciation of “timbre”
• pure tones are very rare
• a single note on a musical instrument is a superposition (i.e. several things one on top of the other) of many related frequencies called harmonics
Timbre
• the characteristic of a particular set of harmonics is called timbre
– e.g. the set of harmonics generated when a particular key is pressed on a piano
• timbre is why we can tell the difference between the same notes played on difference instruments
Timbre
• Although any musical “note” is a superposition of harmonics, you still hear it as a single pitch (you hear its tone height)
• The pitch that you hear is (usually) the fundamental frequency (except in the artificial case of the “missing fundamental”)
Musical Intervals
• in music, notes are played together or in quick succession
• pairs of notes share a relationship called an interval
Musical Intervals
• Within each pair, the higher pitch (f2) is some multiple of the lower pitch (f1):
– e.g. 200 hz and 400 hz -- f2 is two times f1
Musical Intervals
• f
1
= 400 f
2
– (f
2
= 800
= 2 x f
1
)…octave
• f
1
= 400 f
2
– (f
2
= 600
= 3/2 x f
1
)…perfect 5th
• f
1
= 500 f
2
– (f
2
= 800
= 8/5 x f
1
)…minor 6th
• f
1
= 400 f
2
– (f
2
= 550
= 11/8 x f
1
) octave perfect 5th minor 6th not quite a perfect fourth?!
Consonance and Dissonance
• Consonance is the degree to which two tones played together sound “good”
• Dissonance is the opposite
Consonance and Disonance
• Consonance seems to decrease with increasing complexity of the ratio of the tones
Music is combinations of intervals played in series (with some rhythm)
• Combination of three different intervals is a chord (major or minor) major minor
• Additional intervals modify the sound of the chord
4 notes/6 intervals
(major 7)
3 notes/3 intervals
4 notes/6 intervals
(dominant 7)