SPSS Tutorial 2: Exercise One

SPSS Tutorial 2:
The aim of this tutorial is to gain experience with hypothesis testing using SPSS
Exercise One
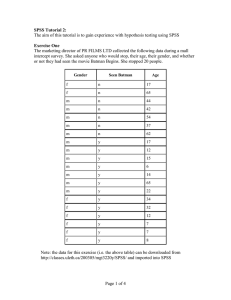
The marketing director of PR FILMS LTD collected the following data during a mall intercept survey. She asked anyone who would stop their age, their gender, and whether or not they had seen the movie Matrix Revolutions. She stopped 20 people.
Gender Seen Matrix Age m m m m m m f f f f f f m m m m f f m m y y y y y y y y y y y y n y n n n n n n
12
15
6
14
65
22
34
7
7
32
12
8
54
37
62
17
17
65
44
42
Note: the data for this exercise (i.e. the above table) can be downloaded from http://classes.uleth.ca/200303/mgt3220y/Admin%20stuff/ and imported into SPSS
1.
What is the relationship between a person's gender and whether or not they have been to see Matrix Revolutions? Is it the case, for example, that more girls than boys go to see it?
2.
What is the null and alternative hypothesis
3.
What statistical test should be performed, and what level of significance
4.
Using SPSS conduct the test
5.
What are the critical values of the test statistic
6.
Should the null hypothesis be accepted or rejected. What can be concluded
7.
Are people over 27 more or less likely to have been to see Matrix Revolutions than people who are 27 or under?
8.
What is the null and alternative hypothesis
9.
What statistical test should be performed, and what level of significance
10.
Using SPSS conduct the test
11.
What are the critical values of the test statistic
12.
Should the null hypothesis be accepted or rejected. What can be concluded
13.
It is often useful here to convert a continuous variable such as age into groups. So, rather than dealing with a different value for age for each person you have, you need to convert this ratio scale variable (age) into a nominal scale variable (age group). To do this, on the Transform menu click on “compute”. In the dialog box that opens enter the New Target variable name (age group). You also have to give it a type and label. In the Functions box move (ANY) into the numeric expression field. Then replace the first ? with the age variable. Use the key pad to type in the expression <=27. Replace the second question mark with the number
0. SPSS will automatically code all other values as 1.
14.
After converting the variable what test should be conducted?
Exercise Two
A psychologist was interested in self esteem in 12 and 13 year olds. Specifically, she wanted to know if social skills training improves self esteem.
To test her hypothesis she gave a Self Esteem test at the beginning of the academic year to 16 children selected at random from grade 7 at a local junior high. The children then received two social skills lessons per week for the next ten weeks. At the end of that period she gave the self esteem test again.
Child
Arthur
Jack
Nathan
Clint
Kevin
20
20
21
21
22
1st SE test score
26
25
23
22
21
2nd SE test score
Shaun
Sam
Jo
Gerry
Emma
Mel
Kim
Nat
Shaz
Victoria
Eliza
26
27
28
28
30
30
23
23
24
26
26
26
29
29
27
34
31
29
28
28
28
24
The data for this exercise can be imported the data from the excel file located at: tp://classes.uleth.ca/200303/mgt3220y/Admin%20stuff/
1.
What are the null and alternate hypotheses
2.
What sort of statistical test should she perform
3.
Using SPSS run the test
4.
Must she accept or reject the null hypothesis. Are the results significant, and if so at what level
5.
What can she conclude
Exercise Three
A survey of 20 bank workers (labelled 2) and plumbers (labelled 1) were asked how many days they had had off work in the previous year due to respiratory problems (i.e. cold) and stomach problems. The results are given below.
Participant Occupation
Respiratory
Disorders
Stomach
Disorders
3
4
1
2
5
6
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
5
0
3
4
7
5
3
9
2
2
15
16
17
18
19
20
11
12
13
14
7
8
9
10
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
8
0
4
5
4
4
3
1
7
3
2
0
0
2
1
1
2
2
6
2
1
8
4
6
7
0
2
Note: the data for this exercise (i.e. the above table) can be downloaded from http://classes.uleth.ca/200303/mgt3220y/Admin%20stuff/ and imported into SPSS
Exercise 3
1.
Work out means for each dependent variable for each group and produce a table like the one below. Report standard deviations for each mean. Produce a clear caption for your table describing exactly what it shows.
Occupation
Mean number of days lost
Respiratory problems Gastric problems
Plumbers
Bank workers
2. Do these data provide evidence that plumbers in the population as a whole take more days off work due to gastric problems than days off work due to respiratory problems?
3. Same as number 2, but this time for bank workers.
4. Is there a significant difference in the total number of days taken off work (for either gastric or respiratory problems) between plumbers and bank workers.