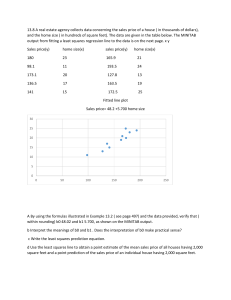
One Few ...
advertisement

CHARACTERISTIC
MONO- OLIGO- MONO- COMPOLY POLY POLIS- PETITIC C. TION
STRUCTURE # firms?
differentiated?
entry is:
market power?
CONDUCT:
interdependece?
Marginal Cost Pricing?
PERFORMANCE:
High prices?
Economic Profits?
Efficient capacity util?
Efficient investment?
One
Few Many
Unique ?
Yes
Blocked Impeded Easy
YES
YES YES
Many
No
Easy
NO
NO
NO
NO
YES
Yes
Yes
No
No
YES
NO
Yes
Yes
No
No
NO
NO
Yes No
No
No
Under Yes
No Yes
PRICE OR COST (per basket)
Profit Maximization
$14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Average
total cost
D
d
Demand
Marginal
cost
1
2
Marginal
revenue
3
4
5
6
7
QUANTITY (baskets per hour)
8
9
4 COPIER PRODUCING
Price ($/copier)
PLANTS
12
#3
#2
10
#4
#1
8
6
4
Most Efficient
Investment
(lowest point)
2
0
0
5
10
15
LRAC
(envelope)
20
Copiers per month (000’s)
25
4 COPIER PRODUCING
Price
($/copier)
PLANTS
12
LRMC
10
8
6
4
2
LRAC
0
0
5
10
15
Copiers per month
20
25
PROFIT MAXIMIZATION
Price
($/copier)
14
12
LRMC
DEMAND
MR
10
8
6
4
MR=MC
2
LRAC
0
0
5
10
15
20
1000s Copiers per month
25
PROFIT MAXIMIZATION
Price
($/copier) TOTAL COST
14
12
LRMC
DEMAND
MR
10
8
6
TC
MR=MC
4
2
LRAC
0
0
5
10
15
Copiers per month
20
25
PROFIT MAXIMIZATION
Price
($/copier)
14
12
LRMC
DEMAND
TR MR
10
8
6
4
MR=MC
2
LRAC
0
0
5
10
15
Copiers per month
20
25
PROFIT MAXIMIZATION
Price
($/copier) TOTAL COST
14
12
DEMAND
PRO-MR
FIT
10
8
LRMC
6
TC
MR=MC
4
2
LRAC
0
0
5
10
15
Copiers per month
20
25
OTHER EFFICIENCIES?
Price
($/copier)
14
12
DEMAND
P=LRMC
MIN SRAC
MR
10
8
6
4
MR=MC
2
MIN LRAC
0
0
5
10
15
Copiers per month
20
25
OTHER EFFICIENCIES?
Price
($/copier) NONE!! (ALLOCATIVELY
14
INEFFICIENT)
DEMAND P=LRMC
12
MR
10
MIN SRAC
INEFFICIENT
CAPACITY UTILIZATION
8
6
4
MR=MC
2
MIN LRAC
0
0
5
10
NOT EFFICIENT
1INVESTING
5
20
25
Copiers per month
MONOPOLY
• HIGH PRICES (P>SRAC)
• HIGH LONG RUN PROFITS (P>LRAC)
• INEFFICIENT CAPACITY (SRAC NOT
THROUGH MIN OF LRAC)
• INEFFICIENT CAPACITY
UTILIZATION (NOT AT MIN SRAC)
• INEFFICIENT ALLOCATION OF
RESOURCES (P>MC)
PRICE (per computer)
The Kinked Demand Curve
Confronting an Oligopolist
$1100
1000
900
B
Demand curve
facing oligopolist if
rivals match price
cuts but not price
hikes
0
Demand curve facing
oligopolist if rivals
match price changes
M
A
D
C
Demand curve
facing oligopolist
if rivals don't
match price
changes
8000
QUANTITY DEMANDED (computers per month)
OLIGOPOLY MODELS
Price ($/copier)
25
Average Explicit Cost
20
Long Run Average Cost
Demand
american choice
{
4X european choice
{ {
{ 3X {
{ {
15
10
5
0
0
5
10
japanese choice
{
1X{
15
20
1000s Copiers per month
25
PRICE MONOPOLY PRICE
CHAMBERLAIN COMPETITIVE
PRICE
COURNOT
BERTRAND
012345
10
20
NUMBER OF FIRMS
N
OLIGOPOLY
• HIGH PRICES (P>SRAC)
• HIGH LONG RUN PROFITS (P>LRAC)
• INEFFICIENT CAPACITY (SRAC NOT
THROUGH MIN OF LRAC)
• INEFFICIENT CAPACITY
UTILIZATION (NOT AT MIN SRAC)
• INEFFICIENT ALLOCATION OF
RESOURCES (P>MC)
pa
F
MC
ATC
Demand
K
MR
0
qa
QUANTITY (units per period)
PRICE OR COST
(dollars per unit)
PRICE OR COST
(dollars per unit)
Equilibrium in Monopolistic
Competition
The short run
The long run
MC
ATC
pg
G
Initial
deman
d
Later
demand
0
qg Later MR
QUANTITY(units per period)
MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION
Price
($/copier)
12
LRMC
10
LRAC
8
6
Demand
4
Long Run Profit
Maximizing Output
2
0
0
5
10
MR
15
20
Copiers per month (000s)
25
MONOPOLISTIC
COMPETITION
• HIGH PRICES (P>SRAC)
• NO LONG RUN PROFITS (P=LRAC)
• INEFFICIENT CAPACITY (SRAC NOT
THROUGH MIN OF LRAC)
• UNDERUTILIZED CAPACITY (AT
LOWER OUTPUT THAN MIN SRAC)
• INEFFICIENT ALLOCATION OF
RESOURCES (P>MC)
Market Entry
Market entry pushes
price down and . . .
PRICE
S1
p1
p2
E1
QUANTITY
MC
S2
p1
p2
E2
New firms
enter
Reduces profits of
competitive firm
f1
f1
Market
deman
d
q1 q2
QUANTITY
ATC
COMPETITION
Price ($/copier)
SUPPLY
Price ($/copier)
12
LRMC
10
8
LRAC
6
4
DEMAND
0
2
0
1 BILL 2 BILL 3BILL 0
Copiers per month
MARKET
5
10
15
20
25
Copiers per month
FIRM POINT OF VIEW
COMPETITION
Price ($/copier)
SUPPLY
Price ($/copier)
12
SRAC
10
A
8
6
SRAVC
SHUT DOWN PRICE
4
DEMAND
0
0
1 BILL 2 BILL 3BILL 0
Copiers per month
MARKET
SRMC
2
B
5
10
15
20
25
1000s Copiers per month
FIRM POINT OF VIEW
COMPETITION
Price ($/copier)
SUPPLY
Price ($/copier)
12
LRMC
10
8
PROFIT
LRAC
6
4
DEMAND
0
2
0
1 BILL 2 BILL 3BILL 0
Copiers per month
MARKET
5
10
15
20
25
Copiers per month
FIRM POINT OF VIEW
ENTRY DUE TO PROFIT
Price ($/copier)
SUPPLY
SHIFT
Price ($/copier)
12
LRMC
10
8
LRAC
6
4
DEMAND
0
2
0
1 BILL 2 BILL 3BILL 0
Copiers per month
MARKET
LOSS
5
10
15
20
25
Copiers per month
FIRM POINT OF VIEW
COMPETITIVE EQUILIBRIUM:
THROUGH NATURAL MARKET FORCES
Price ($/copier)
Price ($/copier)
12
LRMC
10
SUP
PLY
8
LRAC
6
4
DEMAND
0
2
0
1 BILL 2 BILL 3BILL 0
Copiers per month
MARKET
5
10
15
20
25
1000s Copiers per month
FIRM POINT OF VIEW
PERFECT COMPETITION
• LOWEST PRICES (P= MIN SRAC)
• NO LONG RUN PROFITS (P=LRAC)
• EFFICIENT CAPACITY (SRAC
THROUGH MIN OF LRAC)
• FULLY UTILIZED CAPACITY (AT
SAME OUTPUT AS MIN SRAC)
• EFFICIENT ALLOCATION OF
RESOURCES (P=MC)
PORTER’S INDUSTRY
STUDY
• STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS (# of firms,
product differentiation, barriers to entry,
government involvement, cost conditions,
supply and demand conditions, global,etc
• CONDUCT: Analysis of competitive
behavior, interdependence, industry
strategies,
• PERFORMANCE: Price, Profitability,
Efficiency, Quality, etc.
PAYOFF MATRIX FOR THE
PRISONER’S DILEMMA
LIDDY
H
U
N
T
DON’T
TELL
DON’T
TELL
TELL
BOTH
FREE
TELL
Hunt-jail
Liddy-free
& write bk
Liddy-jail BOTH IN
Hunt-free JAIL
& writes bk
SOLUTION TO
PRISONER’S DILEMMA
• EXCHANGE
INFORMATION
• ENFORCEMENT (ALTER
PAYOFF MATRIX)
• REPETITION
PAYOFF MATRIX FOR THE
PRISONER’S DILEMMA:
LOWERING PRICES
F
I
R
M
II
FIRM I
DON’T LOWER
CHANGE PRICE
Both gain
profits
DON’T
CHANGE
LOWER I broke
PRICE
II gains
monopoly
II broke
I gains
monopoly
No Profit
PAYOFF MATRIX FOR THE
PRISONER’S DILEMMA: RAISING
PRICES
F
I
R
M
II
FIRM I
RAISE
PRICE
DON’T
CHANGE
Both gain
profits
II broke
I gains
monopoly
RAISE
PRICE
DON’T I broke
CHANGE II gains
monopoly
No Profit