Read: Loftus for Tuesday Vokey for April 14
advertisement

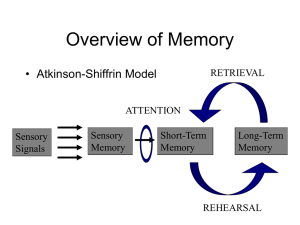
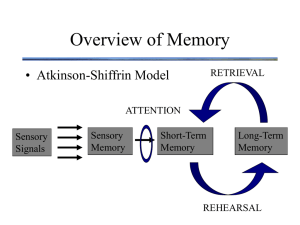
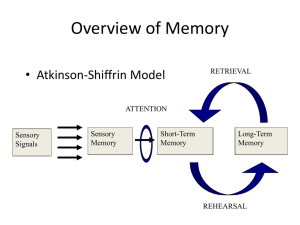
Read: Loftus for Tuesday Vokey for April 14 Idea Journals due on the 16th Read: Textbook on reserve: Cognition Idea Journals due on the 16th Think: What is memory? Think: Memory is any time information persists in your brain -doesn’t require consciousness -doesn’t require retreival Overview of Memory RETRIEVAL • Atkinson-Shiffrin Model ATTENTION Sensory Signals Sensory Memory Short-Term Memory Long-Term Memory REHEARSAL Overview of Memory RETRIEVAL • Atkinson-Shiffrin Model ATTENTION Sensory Signals Sensory Memory Short-Term Memory Do stuff with this information = “working” memory Long-Term Memory REHEARSAL “Types” of Memory • Sensory Memory – brief ( < 1 second) – preattentive / parallel processing (very large capacity) Sensory Memory Capacity • Describe a simple experiment that could measure the capacity of “memory” Capacity • Describe a simple experiment that could measure the capacity of “memory” • Briefly present some letters or digits and then ask the subject to report them – Called “whole report” Capacity + Capacity F S F E G S+ A U T O C G Capacity “Recall as many letters as you can” Capacity • George Sperling - Systematic investigation of memory capacity – Result: subjects accurately recall 3 or 4 items – What can you conclude from this result? Capacity • Could it be that subjects had encoded but failed to retrieve the information? Capacity • For example: what if recalling interferes with memory? What if they forgot the information before they could report it? • How could you modify the experiment to measure the instantaneous capacity, before any forgetting can occur? Capacity • Partial Report - briefly present letters or digits and ask subject to report only some of them “Report the letters in the row indicated by the arrow” Capacity + Capacity U E S B O D+W A I B V S Capacity + Capacity + Capacity Which Letters? Capacity • Partial Report • Result: subjects can recall any 3 or 4 letters that are indicated by the arrow ! Capacity • Partial Report • Result: subjects can recall any 3 or 4 letters that are indicated by the arrow ! • What does this mean about the capacity of memory? Capacity • There is some part of the perception system that stores huge amounts of information… – in fact, if only a single letter is probed, instantaneous capacity is seen to be unlimited Duration • There is some part of the perception system that stores huge amounts of information… • But for how long? How would you design an experiment to measure the duration of this high-capacity memory system? Duration • There is some part of the perception system that stores huge amounts of information… • But for how long? How would you design an experiment to measure the duration of this high-capacity memory system? • Vary the onset of the probe Duration • Partial Report # of letters potentially recalled 10 4 0 0 ms 500 ms never Probe Delay Duration • Partial Report 10 # of letters potentially 4 recalled 0 0 ms 500 ms Delay never Interpretation: 1. Information dwells in a brief storage “buffer” 2. duration of storage lasts about 1/2 of one second Iconic Memory • a brief storage of “raw data” in the visual system Echoic Memory • Auditory information is stored in a similar sensory “buffer” – Echoic memory seems to last for several seconds Properties of Sensory Memory 1. Brief (iconic ~500ms; echoic ~2 seconds) Properties of Sensory Memory 1. Brief (iconic ~500ms; echoic ~2 seconds) 2. Virtually unlimited capacity Properties of Sensory Memory 1. Brief (iconic ~500ms; echoic ~2 seconds) 2. Virtually unlimited capacity 3. pre-attentive