History of Irrigation 2 Running out
advertisement

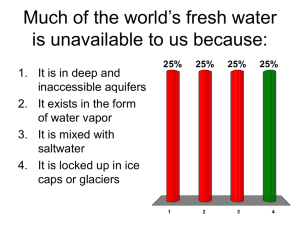
History of Irrigation 2 Running out Agriculture and groundwater Groundwater in Agriculture Expansion of food production over the last 3040 years driven by irrigation Much of this using groundwater Advantage of increased productivity due to timely irrigation and secure application In India: surface irrigated land doubled from 1950 to 1985; groundwater irrigated land increased 113 times. By 1990 more than half In the US with 3rd highest irrigated area in the world, 43% irrigated by groundwater Groundwater depletion Withdrawing ground-water may cause the land to subside Under the North China Plain, which produces more than half of China's wheat and a third of its corn, the annual drop in the water table has increased from 1.5 meters a decade ago to up to 3 meters today under the Punjab and Haryana, water tables are falling by up to 1 meter per year. Aquifer depletion could reduce India's grain harvest by one fifth. Consequences of GW Overdraft: 1925 Land Subsidence Eloy, Arizona 1952 1955 1977 1975 San Joaquin Valley, CA 1985 Groundwater depletion Last two decades spread from isolated pockets to large areas of irrigated cropland Widespread in: Central and northern China, Northwest and Southern India, parts of Pakistan, much of western US, North Africa, the Middle East and the Arabian Peninsular May now be the single biggest threat to irrigated agriculture, exceeding the buildup of salt in the soil Ogallala Aquifer 37% of the water used for irrigation in the US 175,000 sqmiles of 8 states More than 5 trillion gallons per year pumped 95% used for irrigation Caused dramatic decline in water table (average 13 feet since the 1950s Recharge so low that it is considered non-renewable The Edward Aquifer The Edward Aquifer Originally groundwater under absolute ownership. That is Owners of overlaying land can pump as much as they can put to beneficial use Supply the city of San Antonio plus irrigation Aquifer was mined resulting in declining water tables In 1993 Texas introduced new legislation introducing property based approach met with opposition therefore not implemented The Edward Aquifer Act revised in 1995 severing ownership of water from land Mandatory metering Groundwater rights based on proven recent water use Declining target level of total water right by 11% before 2008 Allow sale of water right by owners installing water conservation equipment Allow leasing of water right limited to 50% Running Out Area pr capita peaked in 1978 and fallen by 5% since. By 2020 17-28% below 1978 Global water use has tripled since 1950 In Most Years the Rivers Don’t Make it to the Ocean Among the rivers running dry part of the year are: Colorado River Amu Darya Yellow River Yangze River Indus River Aral Sea has lost 50% of surface and 75% of volume Lake Chad has shrunk by some 95% Running out of options 1950 to mid 70s about 1000 new dams every year Selected the best and cheapest sites first New projects became more complex and expensive 1980s to concern over higher cost were added increased concern over social and environmental impacts By early 1990s only 260 large dams per year Irrigation running out of steam Expansion rate decreasing the last 20 years Next 25 years unlikely to grow with more than 0.6% pa less than population growth Best sites have been used, new irrigation more expensive In India and Indonesia cost of new development has more than doubled since 1970 Government unwilling or unable to take on new projects 50-70% of irrigation systems are in badly need of repair, cost about 1/5 of new projects World Bank worried about countries not willing to pay because money not well spend Running out of options Pace of dam building will slow even further The anti-dam movement is growing in strength International debate over where, when and under which conditions should dams be build The Sardar Sarovar Dam in Western India one of the most protracted and controversial The Narmada River, now has 30 large, 135 medium and 3000 small dams DAMMING THE NARMADAOne of the Eight Modern Wonders Abuilding TIME, January 24, 1994 Damming the Narmada Conceived in 1946 and begun in 1961, the Narmada Valley Development Project is awesome in scope. Thirty large and more than 3,000 smaller dams will divert India’s Narmada River and 40 tributaries into irrigation canals and generate nearly 3,000 MW of electricity….. DAMMING NARMADA CONCEIVED FOUNDATION REFERRED TO TRIBUNAL AWARD CONST. STARTED SUPREME COURT STAY (80 m) JUDGEMENT RESUMED 100 METERS 110.64 METERS 1946 1962 1969 1979 1985 1995 2000 2000 2003 2004 Construction at the Dam Site Dam reaches 110.64 m 93% concrete completed But the problems are still there Daily drudgery of women for fetching water from many kilometers Struggle for water Women’s struggle for water in rural areas Water Supply through Tankers and Trains Long Queues for Domestic Water Migration of human and cattle population in search of water Police preventing a selfimmolation bid by two activist of Sankalp Seva Samiti at the east zone office compound of Ahmedabad municipal corporation in Rakhiyal area on Thursday over water supply problem Newsline Photo And they have not given up!! KALPASAR - Availability of Fresh Water Average 870 MCM Maximum 3307 MCM Average 4807 MCM Maximum 15907 MCM Average 512 MCM Maximum 746 MCM Water Availability KALPASAR Average 12,317 MCM Maximum 56858 MCM SARDAR SAROVAR Average 11,101 MCM Average 6016 MCM Maximum 36786 MCM The Old Paradigm From the dawn of the first irrigation initiative up to the 1970-80’s the emphasis has been on increasing supply of water: More canals More dams Bigger pipes and pumps Water delivered for free Centralized management Consequences of the Old Paradigm Users put low value on water Inefficient use No local responsibility Lack of maintenance Low payment of fees Environmental impact Conflict over water use Conflicts and water users: Agriculture vs industry and urban Transboundary issues both between jurisdictions within same nations and between nations Conflict between neighbors