Document 16063198
advertisement

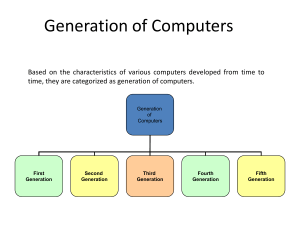
Is This Enough Money? Hardware Components • System unit – Houses CPU and memory • All other devices are linked to the system unit Figure 2.1: Computer System Components Hardware Components (cont) Processing Characteristics and Functions • Machine cycle time: time to execute the instruction phase and the execution phase • Clock speed: electronic ______ produced at a predetermined rate ( pc sales # 3 gigahertz ) • Wordlength: number of ______ that can be processed at one time 4-8-16-32-64 • Physical characteristics of the CPU – Digital circuits on chips – Electrical current flows through silicon Memory Characteristics and Functions: Storage Capacity Table 2.1: Number of Bytes Types of Memory • Random access memory (______) – Temporary – Volatile • ______ (read-only memory) – Usually nonvolatile Multiprocessing • Multiprocessing: simultaneous _________ of two or more instructions • Parallel processing: linking hundreds or thousands of processors operating in parallel • Grid computing: collection of computers working to solve a _________ problem Secondary Storage and Input and Output Devices • Secondary storage – Also called _________ storage – Nonvolatile – Greater capacity and _________ economy than memory Secondary Storage Access Methods • Sequential access: _________ must be retrieved in order • Direct access: records can be _________ in any order Secondary Storage Devices • Magnetic tapes • Magnetic disks • Redundant array of independent/inexpensive disks (RAID) • Compact disc read-only memory (CD-ROM) • CD-recordable (CD-R) discs (CD-RW) discs • Digital versatile disc (DVD) • Memory cards • Expandable storage Input Devices • Personal computer input devices – Keyboard – Mouse • • • • • Voice-recognition devices Terminals Touch-sensitive screens Bar-code scanners Optical data readers Input Devices (continued) • • • • Point-of-sale (POS) devices Automatic teller machine (ATM) devices Magnetic ink character recognition (MICR) devices Radio-frequency identification Output Devices • • • • Display monitors Liquid crystal displays (LCDs) Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) Printers and plotters Computer System Types • • • • • • • • Handheld computers Portable computers Thin client Desktop computers Workstations Servers Mainframe computers Supercomputers Overview of Software • Computer programs: _________ of instructions • Documentation: describes program functions • Systems software: coordinates the _________ of hardware and programs • Application software: helps users solve particular _________ Supporting Individual, Group, and Organizational Goals • Sphere of influence: the scope of problems and opportunities addressed by a _________ organization – Personal – _________ – Enterprise Table 2.5: Classifying Software by Type and Sphere of Influence Systems Software: Operating Systems Operating Systems are also responsible for the execution of the following activities: • Performing common _________ hardware functions • Providing a user _________ and input/output management • Providing a degree of _________ independence • Managing system _________ • Managing _________ tasks • Providing _________ capability • Controlling _________ to system resources • Managing files Current Operating Systems Table 2.6: Popular Operating Systems Across All Three Spheres of Influence Types and Functions of Application Software • Proprietary software: unique _________ for a specific application, usually developed and owned by a single company • Off-the-shelf software: _________ software • _________ package Personal Application Software • • • • • Word processing programs spreadsheet programs database programs graphics programs ETC Workgroup Application Software • Workgroup application software: supports teamwork, whether _________ are in the same location or dispersed around the world • Groupware: software that helps groups of people work together more _________ and _________ Enterprise Application Software • Software that benefits an entire organization • Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software: programs that manage a company’s vital business operations for an entire multisite, global organization Programming Languages • Sets of keywords, symbols, and a system of rules for constructing statements • Allow humans to communicate instructions to be executed by a computer • Syntax: a set of rules associated with a programming language • Different languages have characteristics that make them appropriate for particular types of applications Software Issues and Trends • Software bugs – Program defects that keep it from _________ correctly • Copyrights and _________ • Global _________ support