Reading Assignment! We’ll discuss the chapter by Gregory
advertisement

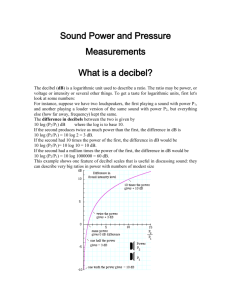
Reading Assignment! We’ll discuss the chapter by Gregory in your book on Friday of next week Hearing: Detection Loudness Localization Music Speech Detection and Loudness • Sound level is measured in decibels (dB) - a measure of the amplitude of air pressure fluctuations Detection and Loudness • Sound level is measured in decibels (dB) - a measure of the amplitude of air pressure fluctuations • dB is a log scale - 1 dB difference = 10 times the actual air pressure Detection and Loudness • Sound level is measured in decibels (dB) - a measure of the amplitude of air pressure fluctuations • dB is a log scale - 1 dB difference = 10 times the actual air pressure • We have a dynamic range that is a factor of 7.5 million! Detection and Loudness • minimum sound level necessary to be heard is the detection threshold Detection and Loudness • detection threshold depends on frequency of sound: • very high and very low frequencies must have more energy (higher dB) to be heard • greatest sensitivity (lowest detection threshold) is between 1000 hz to 5000hz Detection and Loudness • Detection can be compromised by a masking sound • even masking sounds that are not simultaneous with the target can cause masking (forward and backward masking) Detection and Loudness • Loudness is the subjective impression of sound level (and not identical to it!) Detection and Loudness • For example, tones of different frequencies that are judged to be equally loud have different SPLs (dB) Detection and Loudness • Hearing loss due to exposure to high-intensity sounds (greater than 100 dB) can last many hours Localization • recall the lake analogy: task is to localize the positions of the boats on a lake using the pattern of ripples at two points on the shore Localization • All you have is a pair of instruments (basilar membranes) that measure air pressure fluctuations over time Localization • There are several clues you could use: Localization Left Ear Right Ear Compression Waves Localization • There are several clues you could use: 1 arrival time - sound arrives first at ear closest to source Localization Left Ear Right Ear Compression Waves Localization • 1. 2. There are several clues you could use: arrival time phase lag (waves are out of sync) - wave at ear farthest from sound source lags wave at ear nearest to source Localization Left Ear Right Ear Compression Waves Localization • There are several clues you could use: 1. 2. 3. arrival time phase lag (waves are out of sync) sound shadow (intensity difference)sound is louder at ear closer to sound source Localization • What are some problems or limitations?