Geography 2015N

Geography 2015N
•
OUTGASSING
•
TORRENTIAL RAINS
•
LAKES AND OCEANS
•
DISSOLVED AND UNDISSOLVED
ELEMENTS
•
PRESENT VOLUME 1,360,000,000 km 3
•
VOLUME IS STABLE
Water source
Oceans
Ice caps, glaciers
Ground water
Fresh-water lakes
Inland seas
Soil moisture
Atmosphere
Rivers
Percent of total water
97.24%
2.14%
0.61%
0.009%
0.008%
0.005%
<0.001%
<0.0001%
Source: U.S. Geological Survey
Some fast-moving molecules escape from the liquid
In cool air, H
2
O molecules are more likely to join nuclei
CHANGES
DOES NOT
CHANGE
MASS/VOLUME g H
2
O / m 3 air
Specific humidity : the mass of water vapour (g) per mass of air (kg)
Maximum specific humidity is the maximum mass of water vapour that can be held by 1kg of air at a given temperature
MASS OF WATER VAPOUR
TOTAL MASS OF DRY AIR g H
2
O / kg air
A ratio that compares the amount of water vapour in the air to the maximum water vapour capacity at that temperature
The relative humidity of saturated air is 100%
RH = [H
2
0 vapour content/H
2
0 capacity] x 100
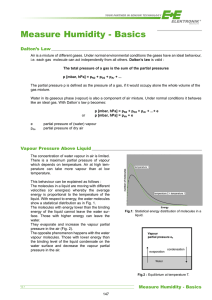
The portion of atmospheric pressure that is made up of water vapour molecules
(mb or kPa)
SATURATION VAPOUR PRESSURE:
The pressure that water vapour molecules would exert if the air were saturated
(at a given temperature)
RELATIVE
HUMIDITY
SPECIFIC
HUMIDITY
http://www.csgnetwork.com/canhumidexcalc.html
Geography 2015N
Why do surfaces facing the wind have more frost?
BLACK FROST
•
A surface is required for condensation
•
Condensation nuclei >0.1
m best
•
About 10-1000 large nuclei
cm -3
(more in lower troposphere and over land)
•
Hygroscopic or hydrophobic
Source: Dust, volcanoes, factory smoke, forest fires, ocean spray salt, sulphate particles from phytoplankton
Fog forms if T d is reached
Cold water advection fog
WHY DOES FOG
FORM HERE?
Warm water advection fog
CAN ADVECTION
FOG FORM OVER
LAND MASSES?
YES
Pages 142-155
Laboratory 1 Notes
Absolute stability
Environmental lapse rate < moist adiabatic lapse rate
Environmental lapse rate >
Dry adiabatic lapse rate
Solar heating of Earth’s surface
Warm air advection at surface
Air moving over a warm surface
Cold advection
Radiational cooling of clouds
LIFTING
OF ENTIRE
AIRMASS
Rainshadow