EUROPE I Review Questions? Course Web Page
advertisement

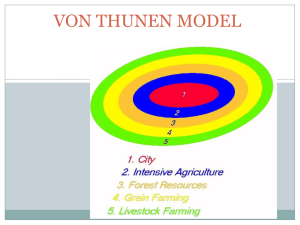
EUROPE I Review Questions? Course Web Page Europe I MAJOR GEOGRAPHIC QUALITIES WESTERN EXTREMITY OF EURASIA Peninsular Europe in 2 senses Moderate climate Gulf stream, marine west coast Moisture laden westerlies Continental east Mediterranean climate Hot dry summer Cool wet winter MAJOR GEOGRAPHIC QUALITIES WORLD INFLUENCE Numerous NATION-STATES Rome to Britannia, Imperialism Manufacturing dominance Cradle of industrial revolution Fragmented and differentiated Linguistic pluralism AGING URBANIZED POPULATION PARADOX of INTEGRATION and DEVOLUTION REGIONS Western Europe Eastern Europe British Isles UK+ Northern Europe Scandinavia =NSD + Mediterranean Europe PHYSICAL LANDSCAPES • Western Uplands • North European Lowland • Central Uplands • Alpine System RELATIVE LOCATION Central to the land hemisphere Maximum efficiency for contact with the rest of the world Close to the sea. Navigable waterways Airline connectivity Moderate distances Europe’s Situation VON THUNEN’S ISOLATED STATE A classic model in geography Fashioned in 1826 to explain the economic patterns developing in Europe Based on concentric land use rings surrounding a market town Land use was a function of land rent, itself determined by transportation costs. The Isolated State became the foundation for modern location theory. VON THUNEN’S ISOLATED STATE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION ‘industrial intensification’ Developed 1st in the UK between 1750-1850 Evolved from technical innovations that occurred in British industry Proved to be a major catalyst for increased urbanization Diffuses from Britain outward into Western Europe