Training session on schemes Drosophila
advertisement

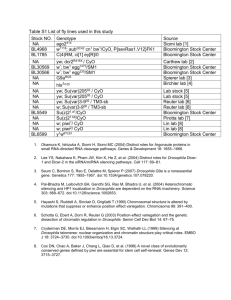
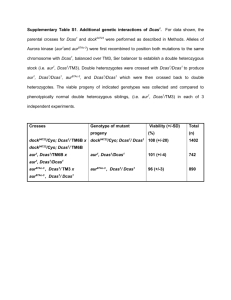
Training session on Drosophila mating schemes STEP 1: Remind yourself of the key differences between mitosis and meiosis: • crossing-over / interchromosomal recombination during prophase I (➊) • separation of homologous chromosomes during telophase I (➋) • an additional division in meiosis (➌) Mitosis and meiosis diploid generating sister chromatids for each of the homologous chromosomes ➊ separating sister chromatids ➋ ➌ haploid synapsis interchromosomal recombination separating homologous chromosomes STEP2: Remind yourself of the basic rules of Drosophila genetics: • law of segregation • independent assortment of chromosomes • linkage groups and recombination (recombination rule) • balancer chromosomes and marker mutations Law of segregation / linkage groups Homologous chromosmes are separated during meiosis Law of segregation / linkage groups 1 2 1 • each offspring receives one parental and one maternal chromosome • loci on the same chromsome are passed on jointly (linkage) Complication: recombination in females interchromosomal recombination takes place randomly during oogenesis Recombination rule: there is no recombination in males (nor of the 4th chromosome) Complication: recombination in females wildtype heterozygous homozygous mutant 7 instead of 3 different genotypes Balancers and stock keeping • lethal mutations are difficult to keep as a stock and will eventually segregate out • remedy for work on mice: genotyping of every new generation through PCR analysis of tail tips - impossible in flies! Balancers and stock keeping • lethal mutations are difficult to keep as a stock and will eventually segregate out • remedy in Drosophila: balancer chromosomes Balancers and stock keeping • balancers carry easily identifiable dominant and recessive markers Balancers and stock keeping • balancers carry easily identifiable dominant and recessive markers • balancers are homozygous lethal or sterile Balancers and stock keeping only heterozygous flies survive and maintain the stock • balancers carry easily identifiable dominant and recessive markers • balancers are homozygous lethal or sterile • the products of recombination involving balancers are lethal • During mating schemes, balancers can be used to prevent unwanted recombination - providing an additional means to the recombination rule. • You can use balancers and their dominant markers strategically to follow markerless chromosomes through mating schemes. Rules to be used here: • 'X' indicates the crossing step; female is shown on the left, male on the right • sister chromosomes are separated by a horizontal line, different chromosomes are separated by a semicolon, the 4th chromosome will be neglected • maternal chromosomes (inherited from mother) are shown above, paternal chromosomes (blue) below separating line • the first chromosome represents the sex chromosome, which is either X or Y - females are X/X, males are X/Y • generations are indicated as P (parental), F1, 2, 3.. (1st, 2nd, 3rd.. filial generation) • to keep it simple: dominant markers start with capital, recessive markers with lower case letters Now apply your knowledge: • follow a step-by-step explanation of a typical crossing task experienced during routine fly work • you will be prompted to make your choices at each step of the mating scheme; take this opportunity before forwarding to see a solution Task: To study the potential effect of a 2nd chromsomal recessive lethal mutation m (stock 1) on brain development, you want to analyse certain neurons in the brain of m mutant embryos. These neurons can be specifically labelled with ß-Gal using a 2nd chromosomal Pelement insertion P(lacZ,w+) (stock 2). To perform the experiment, you need to recombine m and P(lacZ,w+) onto the same chromosome. Design a suitable mating scheme. Tip: w+ on the P-element gives orange eyes. , Hu Identify the eye colours of these flies Task: To study the potential effect of a 2nd chromsomal recessive lethal mutation m (stock 1) on brain development, you want to analyse certain neurons in the brain of m mutant embryos. These neurons can be specifically labelled with ß-Gal using a 2nd chromosomal Pelement insertion P(lacZ,w+) (stock 2). To perform the experiment, you need to recombine m and P(lacZ,w+) onto the same chromosome. Design a suitable mating scheme. Tip: w+ on the P-element gives orange eyes. CyO If CyO * * Identify all other markers of these flies * TM6b,, Hu Sb * Task: To study the potential effect of a 2nd chromsomal recessive lethal mutation m (stock 1) on brain development, you want to analyse certain neurons in the brain of m mutant embryos. These neurons can be specifically labelled with ß-Gal using a 2nd chromosomal Pelement insertion P(lacZ,w+) (stock 2). To perform the experiment, you need to recombine m and P(lacZ,w+) onto the same chromosome. Design a suitable mating scheme. Tip: w+ on the P-element gives orange eyes. CyO If CyO Identify the balancer chromosomes TM6b,, Hu Sb Task: To study the potential effect of a 2nd chromsomal recessive lethal mutation m (stock 1) on brain development, you want to analyse certain neurons in the brain of m mutant embryos. These neurons can be specifically labelled with ß-Gal using a 2nd chromosomal Pelement insertion P(lacZ,w+) (stock 2). To perform the experiment, you need to recombine m and P(lacZ,w+) onto the same chromosome. Design a suitable mating scheme. Tip: w+ on the P-element gives orange eyes. cross , Hu Define the first cross! Assign ♀ & ♂ to these stocks Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m Selecting F1 stock 2 first? second? third? m + ; Y stock 1 ; Now select gender and genotype! Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m Selecting F1 stock 2 first? second? third? m + ; Y stock 1 ; • take females (to allow for recombination) • select against curly wings (to have Pelement & mutation) Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m Designing the F1 cross + m + haploid gametes gonad Remember: recombination occurs at random In the+germline of the P(lacZ,w ) selected females, recombination takes no recombination place * * * * * * m * * P(lacZ,w+) m recombination each layed egg has its individual recombination history Challenge: how to select for the F2 flies carrying correctly recombined chromosomes? Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m Designing the F1 cross + m + choose the stock for the males Stocks available: 1st step: stabilise recombinant chromosomes with a balancer Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m F2 selection m + + first? F2 second? w Y P(lacZ,w+),[m]* CyO + Y P(lacZ,w+),[m]* If ; third? + TM6b ; w w [m]* CyO + w [m]* If [m]* = potentially present + Sb not important here; ignored hereafter Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m Identify the eye colours! first F2 second w Y P(lacZ,w+),[m]* CyO + Y P(lacZ,w+),[m]* If ; third + TM6b ; w w [m]* CyO + w [m]* If [m]* = potentially present + Sb not important here; ignored hereafter Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m Define your selection criteria for 2nd and 1st chromosomes first F2 second w Y P(lacZ,w+),[m]* CyO + Y P(lacZ,w+),[m]* If ; + TM6b ; w w [m]* CyO + w [m]* If select for white background, to see orange eyes third select orange eyes, [m]* for = potentially present for Cy, against If + Sb not important here; ignored hereafter Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m Selecting recombinants F2 w P(lacZ,w+),[m]* ; Y CyO Challenge: determine whether recessive "m" is present Choose female from available stocks Key strategy: backcross to "m" stock Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m performing the back cross F2 w P(lacZ,w+),[m]* ; Y CyO X + m ; + CyO Problem: Each individual represents a unique recombination event. Solution: perform many(1) parallel single crosses, in each using ONE potentially recombinant male(2) and 3 to 5 females of stock1. (1) If the chromosomal positions of m and P(lacZ,w+) are known, the recombination frequency can be calculated; typically between 20-100 single crosses are required. (2) Males can mate several females. Even if they die early, females store enough sperm to lay eggs for a while. Hence, the likelihood that a single male successfully establishes a large enough daughter generation is considerably higher than a single female. stock 1 Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m performing the back cross F2 w P(lacZ,w+),[m]* ; Y CyO F3 All flies Cy? Canthe youlethal spot mutation the If yes, recombinants? "m" is present on the putatively recombinant Define your criteria! chromosome. X + m ; + CyO stock 1 2nd? m P(lacZ,w+),[m]* m CyO CyO P(lacZ,w+),[m]* CyO CyO To establish the recombinant stock, you need to distinguish these two genotypes, i.e. select for orange eyes. Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m performing the back cross F2 w P(lacZ,w+),[m]* ; Y CyO X F3 1st? m P(lacZ,w+),[m]* + w + Y m CyO ; CyO P(lacZ,w+),[m]* CyO CyO + m ; + CyO stock 1 Since you have w+ background, this strategy does not work To establish the recombinant stock, you need to distinguish these two genotypes, i.e. select for orange eyes. Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m F2 w P(lacZ,w+),[m]* ; Y CyO X Rethink your strategy: • given the complexity of genetic crosses, trial and error is often unavoidable • careful planning is pivotal! Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m single males! F2 w P(lacZ,w+),[m]* ; Y CyO Choose female from available stocks aid 1 stock X 2 possibilities: • You could use strategy 1, but add a parallel F1 cross between stock 1 and aid 1 to bring m into w mutant background (thus preparing it for the backcross in F2). Try whether it works for you! • Here we will use an alternative strategy, establishing stable stocks and test for lethality. to establish stable fly stocks cross single potentially recombinant males to the balancer stock Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m establishing stable stocks F2 w P(lacZ,w+),[m]* ; Y CyO F3 1st? 2nd? If P(lacZ,w+),[m]* w w w Y take males & females aid 1 stock X CyO P(lacZ,w+),[m]* ; If CyO CyO CyO select! • • • • for Cy for orange eyes against If against white eyes Task: Recombine P(lacZ,w+) with lethal mutation m select stable stocks F3 w P(lacZ,w+),[m]* ; Y CyO F4 1st? X w P(lacZ,w+),[m]* ; Y CyO 2nd? All flies Cy? P(lacZ,w+),[m]* P(lacZ,w+),[m]* w w w Y P(lacZ,w+),[m]* CyO ; 1 If yes, the marker "m" is present on the putatively recombinant chromosome. 2 CyO P(lacZ,w+),[m]* CyO CyO 1 maintain as stock Now continue with independent crossing tasks