Honors Chemistry Organic Chemistry
advertisement

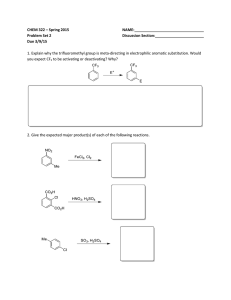
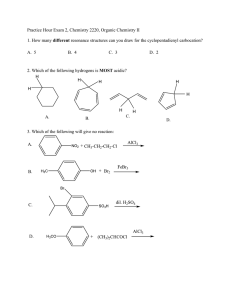
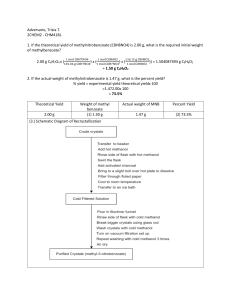
Honors Chemistry Organic Chemistry hcorganicws3.doc Name: _______________________________________ Date: ___________________ Period: ______ 1. The following molecule would best be described as: H O H3C OH H a. b. c. d. An unsaturated cis-fatty acid. An unsaturated trans-fatty acid. A saturated cis-fatty acid. A saturated trans-fatty acid. 2. Match the items with their most appropriate descriptions: _____ 1. amines _____ 2. addition reaction _____ 3. phenyl group _____ 4. benz(a)anthracene _____ 5. structural isomers _____ 6. aromatic hydrocarbon _____ 7. –COOH _____ 8. –OH _____ 9. functional group common to aldehydes and ketones _____ 10. methanol _____ 11. C6H5OH _____ 12. condensation reaction a. n-butane and methylpropane b. carcinogen in burned meat and cigarettes c. organic bases d. hydrogenation e. hydroxyl f. carboxyl g. carbonyl h. containing benzene or benzene-like structures i. from wood distillation / metabolized into formaldehyde j. benzene as a substituent k. reaction in the formation of esters l. phenol 3. Which term doesn’t go with the others? (Circle one) alkyl group substituent division branch 4. Write the process for the addition reaction between propene and chlorine gas. Name the compound. 5. Determine the hybridization, bond angle and molecular geometry central to the oxygen in an alcohol. 6. The formal name for aspirin is _________________________________, and has the structure (draw below). 7. A gasoline additive MTBE (methyltert-butylether) is used as an anti-knock additive that also helps reduce CO emissions. Draw the structure for this compound. 8. Draw the structure and write the name for the compound that will form from the oxidation of 3,3dimethylhexan-2-ol. 9. Explain what is meant by “resonance” as it pertains to the benzene ring. Why is a circle commonly used when representing the middle of the ring structure? 10. What is the most common use of hydrocarbons? 11. Draw the general formula for the polymer that would form from the monomer polyvinyl chloride (PVC), CH2=CHCl 12. Draw and name all the structural isomers of n-hexane (Hint: There are 5 including n-hexane itself).