Cystic fibrosis
advertisement
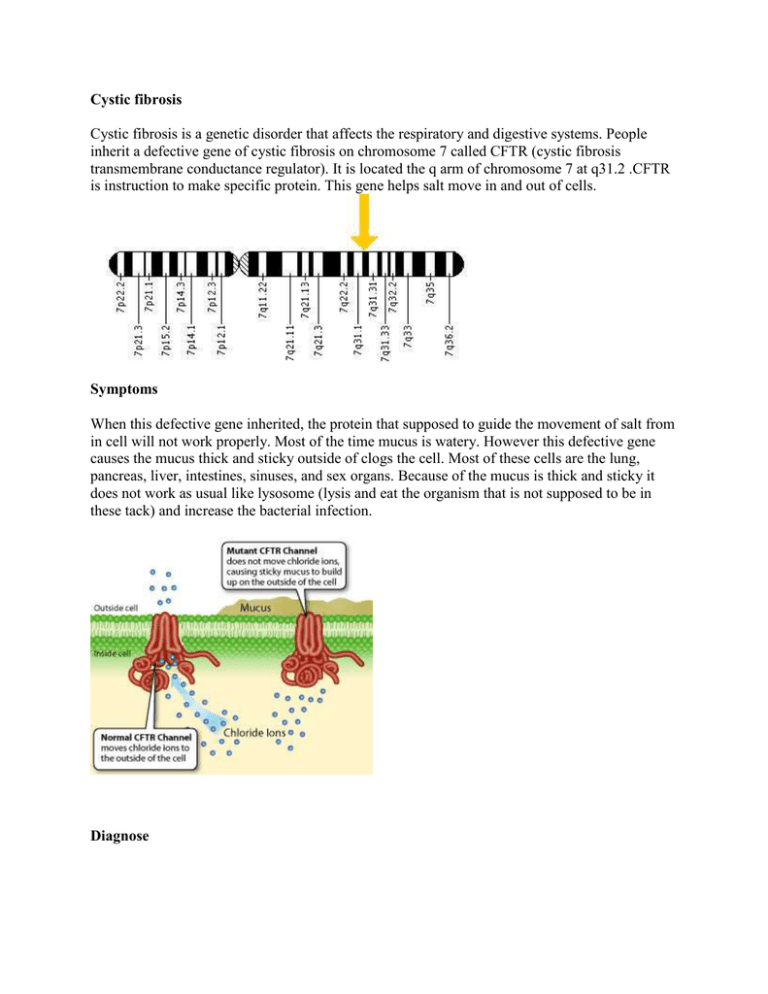
Cystic fibrosis Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder that affects the respiratory and digestive systems. People inherit a defective gene of cystic fibrosis on chromosome 7 called CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator). It is located the q arm of chromosome 7 at q31.2 .CFTR is instruction to make specific protein. This gene helps salt move in and out of cells. Symptoms When this defective gene inherited, the protein that supposed to guide the movement of salt from in cell will not work properly. Most of the time mucus is watery. However this defective gene causes the mucus thick and sticky outside of clogs the cell. Most of these cells are the lung, pancreas, liver, intestines, sinuses, and sex organs. Because of the mucus is thick and sticky it does not work as usual like lysosome (lysis and eat the organism that is not supposed to be in these tack) and increase the bacterial infection. Diagnose The person who has Cystic fibrosis will have a higher concentration of salt in their system. So, the physician uses sweat test from different spot of the patient to analyze the concentration of the salt in patient body. The genetic test can be identified by taking a sample of blood. Treatment Because of there is no cure for this genetic disorder, some medication used to increase the life of the person. Most of these treatments accomplished by cleaning the mucus form the system using different kind of technique. Some of the techniques are chest therapy, inhaled antibiotics, and gene therapy (inserting healthy CFTR gene and check if it works). Facts about Cystic fibrosis More than 1,000 different mutations in the CFTR gene have been identified in cystic fibrosis patients. The most common mutation (observed in 70% of cystic fibrosis patients) is a three-base deletion in the DNA sequence, causing an absence of a single amino acid in the protein product. About 2,500 babies are born with cystic fibrosis in the U.S. each year. More than 10 million Americans carry the cystic fibrosis gene but don't know it.






