Homework 1 Key
advertisement

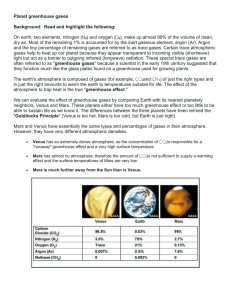
Homework 1 Key 1) The greenhouse effect is the mechanism whereby the gases in the atmosphere absorb infrared radiation emitted by the planet's surface, re-radiating some of the energy back toward the surface. The greenhouse effect allows the planet's surface temperature to be greater than the plant's effective radiating temperature. Global warming refers to the increase in surface temperature that has been observed at the Earth's surface over the past ~150 years. It is widely believed that an enhancement of the greenhouse effect through anthropogenic emission of IR-absorbing gases (greenhouse gases) is the primary cause of global warming. 2) Weather occurs on a timescale of days to a month. Climate refers to the statistics of weather over longer periods of time, decades to centuries. Changes in the weather can be predicted with relatively high skill for up to a week; our ability to predict changes in the climate is highly uncertain. If climate warms, the distribution of weather will be affected. Possible examples include: more frequent warm days, “hotter” or more extreme warm days, less frequent cold days, less or more rain, less snow, less or more clouds. 3) Questions of Origin deal with the source of knowledge. Questions of Validity deal with the accuracy of knowledge, i.e., whether or not knowledge agrees with experimentation and observation. In terms of Fig. 1.4, an example of a question of origin would be “Who made the graph?” or “Who recorded the thermometer data?” A question of validity would be “Would another set of temperature observations confirm or disprove the trend?” or “Would future temperature observations continue the display trend?” 4) a) T-->C-->A Negative Feedback; Stable Equilibrium o------------| b) T--oC-->A Positive Feedback; Unstable Equilibrium o------------| c) T-->C--oA Positive Feedback; Unstable Equilibrium o------------| d) T--oC--oA Negative Feedback; Stable Equilibrium o------------| 5) a) E(in) = S(1-A) Venus = 528.6 W/m2 Earth = 959 W/m2 Mars = 462.54 W/m2 b) Te = ( E(in)/ 4^.25 Venus = 219.7 K Earth = 255 K Mars = 212.5 K c) Tg = Ts-Te Venus = 503.3 K Earth = 33 K Mars = 5.5 K 6)a) Albedo – The ratio of the reflected energy to the incident energy (the total energy that “falls on” the surface) for a given surface. Changes in albedo are important for climate, as it determines how much energy the planet can absorb. b) Positive Feedback Loop – A system where a small disturbance will be amplified. The system's response will be greater than the “initial response” (i.e., the response exhibited by a similar system with no feedback). c) Infrared Radiation – Radiation with a wavelength longer than visible light, between 0.7 and 1000 m. This is the primary form of energy emitted from the Earth's surface. d) Unstable Equilibrium – A state in which the system will remain if left undisturbed, but slight disturbances will amplify throughout the system, ultimately carrying the system to a new, stable state.