CHM 112 WORKSHEET FOR ALKENES, ALKYNES AND HALOCARBONS Spring 2002
advertisement

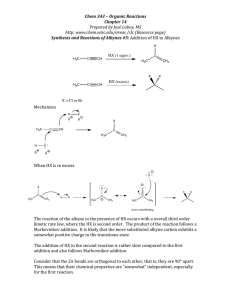
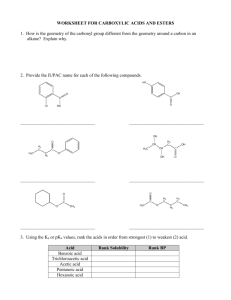
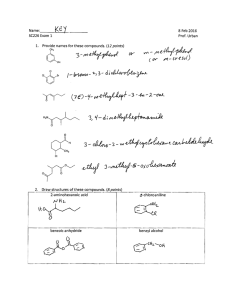
CHM 112 WORKSHEET FOR ALKENES, ALKYNES AND HALOCARBONS Spring 2002 1. Explain, based on the appropriate IMFs, why the melting points and boiling points of alkenes and alkynes are so low. Since the bonding in these molecules is non-polar covalent, the forces between molecules are weak dispersion forces and the crystals they form are molecular crystals with weak interactions between lattice points. Weaker forces require less energy to overcome. Therefore, the melting points and boiling points are lower. 2. Explain why double and triple carbon-carbon bonds are planar while a single C-C bond is not. For single bonds, carbon forms sp3 hybrid orbitals that arrange themselves 109.5o away in three-dimensional space. Carbon in a double bond forms sp2 hybrid orbital and these are arranged at 120o on a plane while carbon in a triple bond undergoes sp hybridization and the resulting orbitals are180o apart, in a line. 3. Write the IUPAC name for each of the following compounds. CH 3 H C CH 3 H3C H C C H3C CH CH 3 CH C H Br CH 3 CH H3C CH 2 Br CH 3 2-methyl-2-butene 3, 4-dibromo-1-cyclohexene 4, 5, 6-trimethyl-2-octene H3C H2 C H3C CH CH Cl CH 2 CH 3 CH CH 2 C Br Cl H2C H C C Cl Cl C H CH 3 C H2 CH 2 H3C 4-bromo-3-methyl-1-hexyne 5, 5-dichloro-3-nonene 1, 1-dichloro-2-ethyl cyclopentane 4. Write the full or condensed structural formulas for each of the following compounds. 1, 4-diiodo-1-cyclohexene 4-isopropyl-1-octene H3C I CH 3 CH H C H2C I 2, 2-dichloro-5, 5, 6-trimethyl-3-decyne H2 C CH C H2 C H2 CH 3 C H2 2-bromo-1-iodo-3-methyl cyclopentane I Cl CH 3 CH 3 C H3C C H2 C CH C C Cl C H2 CH 3 Br C H2 CH 3 CH 3 H H cis-2-pentene C H3C C CH 2 H3C 5. Look at the structures for 6-dodecene below. Which one has a trans double bond configuration and which one has a cis configuration? How do the configurations affect the overall shape of the molecule? trans-6-dodecne cis-6-dodecene The hydrogens are on opposite sides of the molecule in the first image so it must be trans while the hydrogens are on the same side in the second image so this must be the cis configuration. When the same groups (i.e. hydrogens or carbon chains) are on the same side of the double bond, the chain bends or appears to have a kink in it. 6. Complete the following reactions: H C H3C + H2O C OH H2 C H+ CH3 CH3 H3C C CH3 CH3 Br2/CCl4 CH3 CH3 Br Br Cl H C CH 3 HCl CH C H2 H2C Cl H3C H2 C C C H2 Cl C H2 CH 3 C H2