Electrochemistry
advertisement
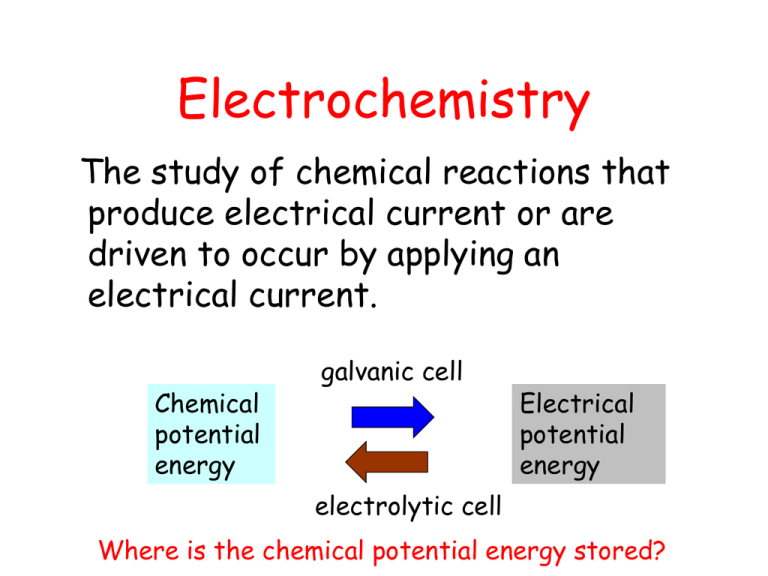
Electrochemistry The study of chemical reactions that produce electrical current or are driven to occur by applying an electrical current. Chemical potential energy galvanic cell Electrical potential energy electrolytic cell Where is the chemical potential energy stored? Reactions • In aqueous solution or molten salts (ionic reactions) • Heterogeneous – at electrode surfaces – Gases formation – Plating of metals/eroding (dissolving) metals Solutions • Homogeneous mixtures – variable composition • Two components: – Solute – Solvent (usually water – aqueous solutions) • Molarity – unit of concentration – M = moles of solute/VL of solution – Moles = M x VL Types of solutes • Non-electrolytes – do not dissociate, remain as molecules in solution (all molecules) such as sugars, alcohols sugar (s) sugar (aq) Types of solutes continued • Electrolytes – dissociate in solution – Strong electrolytes -100% dissociation into ions – high conductivity (all ions) NaCl (s) Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) – Weak electrolytes – partial dissociation into ions – poor/low conductivity (ions and molecules) CH3COOH (aq) H+ (aq) + CH3COO- (aq) Solubility • “like dissolves like” – Ionic salts - Water – Molecular compounds – non-aqueous solvents • Usually solubility increases with increasing temperature • Solubility rules Types of conduction movement of charged particles • Metallic conduction - electrons in metals • ionic or electrolytic conduction - ions in molten salts or aqueous solutions • gaseous conduction - ions and electrons in the gas phase (atomic plasmas) Geiger-Muller Tube for radioactive decay particles Redox Processes electron transfer • oxidation - – loss of electrons – oxidation number increases Ag Ag+ + e- • reduction - – gain in electrons – decrease in oxidation number Fe+2 + 2e- Fe Redox Reactions Both oxidation and reduction MUST occur in the reaction and the number of electrons exchanged MUST be balanced Consider silver plating a copper penny Cu + 2Ag+ Cu+2 + 2 Ag What is being oxidized? Cu Cu+2 + 2e- What is being reduced? Ag+ + e- Ag MUST balance number of electrons exchanged x 2






