lecture 2 : the problem situation we discuss: • mind maps
advertisement

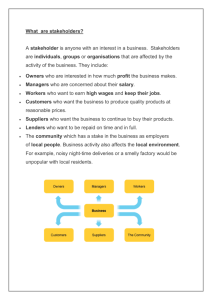
lecture 2 : the problem situation we discuss: • the components of a problem situation • mind maps • rich pictures Spring 2011 - ÇG IE398 - lecture 2 1 Spring 2011 - ÇG IE398 - lecture 2 2 components of a problem • issues and problems that are the subject of inquiry occur within a context that we call the “problem situation” (the context is that part of a system's environment that can neither be influenced nor controlled) • involved in each problem situation, are –decision makers – objectives – decision criterion – performance measure – control inputs or courses of action • we can make these more clear as follows Spring 2011 - ÇG IE398 - lecture 2 3 • goal indicates overall purpose e.g. setting up an ambulance service • objective is more specific than a goal e.g. finding the best location for an ambulance service (the textbook makes no distinction between a goal and an objective) • decision criterion: a rule by which we judge the achievement of an objective e.g. maximising expected profits or the rate of return on investments; minimising total distance travelled, or the longest distance travelled etc. • performance measure: an output that serves to measure system performance • objective function: mathematical expression of performance measure, expressing o/p as a function of control i/p’s, (decision variables) Spring 2011 - ÇG IE398 - lecture 2 4 • stakeholders (roles assumed with respect to the narrow system of interest): – problem owners who have control over some aspects of the problem situation, such as choosing a course of action – problem users who use the “solution”, ie. implement the decisions of problem owners – problem customers, the affected beneficiaries or victims of the solution to be implemented – analysts (e.g. the OR analyst or the IE) address the problem and develop a solution that must be approved by peroblem owners Spring 2011 - ÇG IE398 - lecture 2 5 • role definition is important; e.g. consider the case of screening for breast cancer: – if the Health Minister initiates the project, concern will be about effective allocation of funds, priorities, trade-offs, costs; the entire health system will be the of interest – if doctors or women’s groups initiate the project, concern will be about minimising incidence of cancer and fatalities, not directly over costs – users may need to be persuaded and trained lest they sabotage implementation – roles may need to be reassigned for efficiency or efficacy Spring 2011 - ÇG IE398 - lecture 2 6 mind maps and rich pictures these are useful as a first step in setting down and representing our perception of the problem situation where: •all aspects of a problem situation are mapped on a free-style diagram with or without pictures •including as much or as little detail as necessary •independently of any particular W (ie. world view) but as a joint product of conflicting views of the situation •without trying to identify any systems as yet •redrawn as many times as needed in the course of the project Spring 2011 - ÇG IE398 - lecture 2 7 Spring 2011 - ÇG IE398 - lecture 2 8 Spring 2011 - ÇG IE398 - lecture 2 9 these diagrams should show: • elements of structure; stable or slow-changing aspects such as buildings, equipment, products, rules, advantages, difficulties etc. • elements of process; dynamic aspects that change fast such as activities, material flows, information etc. • relationships between structure and process and consequences of these relationships • soft as well as hard facts • multiple aspects to facilitate learning and discussion • not too many connectors, precedences or flows Spring 2011 - ÇG IE398 - lecture 2 10 Spring 2011 - ÇG IE398 - lecture 2 11 Spring 2011 - ÇG IE398 - lecture 2 12