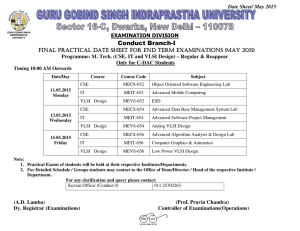
Spectral RTL Test Generation for Microprocessors Nitin Yogi and Vishwani D. Agrawal
advertisement

Spectral RTL Test Generation
for Microprocessors
Nitin Yogi and Vishwani D. Agrawal
Auburn University
Department of ECE
Auburn, AL 36849, USA
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
1
Outline
Microprocessor testing Issues
Problem and Approach
RTL faults
Spectral analysis & test generation
Test set compaction
RTL DFT
Experimental Results
Conclusion
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
2
Microprocessor Testing Issues
Issues arising from Increased Design Complexity
Increased Test Generation Complexity
Viable Test Method: RTL test generation
Advantages:
Low testing complexity
Early detection of testability issues
Increased Demands on Testing
Viable Test Method: Functional at-speed tests
Advantages:
Jan. 9, 2007
Better defect coverage
Detection of delay faults
VLSI Design Conference 2007
3
Problem and Approach
The problem is …
Develop an RTL-based ATPG method to
generate functional at-speed tests.
And our approach is …
Circuit characterization using RTL:
RTL test generation
Analysis of information content and noise in RTL
vectors.
Test generation for gate-level implementation:
Generation of spectral vectors
Fault simulation and vector compaction
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
4
Faults Modeled for an RTL Module
Inputs
Combinational
Logic
RTL
stuck-at
fault
sites
Outputs
FF
FF
A circuit is an interconnect of several RTL modules.
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
5
Walsh Functions and Hadamard Spectrum
w0
Walsh functions (order 8)
w1
w2
w3
• Walsh functions form an orthogonal and
complete set of basis functions that can
represent any arbitrary bit-stream.
• Walsh functions are the rows of the
Hadamard matrix.
• Example of Hadamard matrix of order 8:
H8 = 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 -1 1 -1 1 -1 1 -1
1 1 -1 -1 1 1 -1 -1
1 -1 -1 1 1 -1 -1 1
1 1 1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1
1 -1 1 -1 -1 1 -1 1
1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 1 1
1 -1 -1 1 -1 1 1 -1
w4
w5
w6
w7
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
6
.
.
.
Input 2
Input 1
Analyzing Bit-Streams
Vector 1
Vector 2
.
.
.
Bit-stream
0 to -1
Bit-stream of
Input 2
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
7
Spectral Characterization of a Bit-Stream
Bit stream
to analyze
Correlating with Walsh functions by
multiplying with Hadamard matrix.
Hadamard Matrix
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
Bit
stream
Spectral
coeffs.
Essential component
(others regarded noise)
8
Generation of New Bit-Streams
Perturbation
Spectral
components
Generation of new bit-stream by
multiplying with Hadamard matrix
Essential
component
retained; noise
components
randomly
perturbed
Sign function
New bit stream
-1 to 0
Bits changed
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
9
PARWAN Processor
Reference: Z. Navabi, Analysis and Modeling of
Digital Systems. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1993.
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
10
Power Spectrum for “Interrupt” Bit-Stream
Analysis of 128 test vectors.
Normalized Power
Essential
components
Some noise
components
Random
level
(1/128)
Spectral Coefficients
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
11
Power Spectrum for “DataIn[5]” Signal
Normalized Power
Analysis of 128 test vectors.
Some
essential
components
Some noise
components
Theoretical
random noise
level
(1/128)
Spectral Coefficients
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
12
Power Spectrum for Random Signal
Normalized Power
Analysis of 128 random vectors.
Theoretical
random noise
level
(1/128)
Spectral Coefficients
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
13
Selecting Minimal Vector Sequences Using ILP
Fault simulation of new sequences
A set of perturbation vector sequences {V1, V2, .. , VM} is
generated.
Vector sequences are simulated and all gate-level faults
detected by each are obtained.
Compaction problem
Find minimum set of vector sequences that cover all detected
faults.
Minimize Count{V1, … ,VM} to obtain compressed seq. {V1,… ,VC},
where {V1, … ,VC} {V1, … , VM}, and
Fault Coverage{V1, … ,VC} = Fault Coverage{V1, … ,VM}
Compaction problem is formulated as an Integer Linear
Program (ILP) [1].
[1] P. Drineas and Y. Makris, “Independent Test Sequence Compaction through Integer Programming," Proc. ICCD’03, pp. 380-386.
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
14
RTL DFT
Goals of DFT:
Improve controllability and observability
Most hard-to-detect faults were experimentally found to
have poor observability
XOR tree as DFT
Low area overhead
Low performance penalty
Hard-to-detect RTL faults used for observation test points
10 observation test points selected
XOR tree
Hard-to-detect
RTL faults
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
To test
output
15
Experimental Results
RTL characterization
PARWAN processor
No of RTL
Faults
No. of
vectors
CPU (s)
RTL coverage
(%)
Gate-level
fault
coverage(%)
737
134
640
96.30%
81.22%
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
16
Experimental Results
Gate-level Fault Coverage
RTL Spectral ATPG*
Gate-level ATPG*
(FlexTest)
Random vecs.
Circuit
Cov.
(%)
No. of
vecs.
CPU
(secs)
Cov.
(%)
No. of
vecs.
CPU
(secs)
Cov.
(%)
No. of
vecs.
Parwan
98.23%
2327
2442
93.40%
1403
26430
80.95%
2814
Parwan
(with
DFT)
98.77%
1966
2442
95.78%
1619
20408
87.09%
2948
*Sun Ultra 5, 256MB RAM
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
17
Experimental Results
Parwan processor
Test coverage (%)
100
80
RTL spectral
ATPG
60
Gate-level
ATPG
40
Random
vectors
20
RTL fault
vectors
0
1
10
100
1000
10000
No. of vectors
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
18
Experimental Results
Parwan processor (with DFT)
Test coverage (%)
100
80
RTL spectral
ATPG
60
Gate-level
ATPG
40
Random
vectors
20
RTL fault
vectors
0
1
10
100
1000
10000
No. of vectors
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
19
Conclusion
Spectral RTL ATPG technique applied to PARWAN
processor.
Proposed ATPG method provides:
Good quality “almost” functional at-speed tests
Lower test generation complexity
Enables testability appraisal at RTL
RTL based XOR tree as DFT was found to improve
results.
An alternative approach: Use functional vectors instead
of RTL vectors.
Yogi and Agrawal, “Spectral Characterization of Functional
Vcetors for Gate-Level Fault Coverage Tests,” Proc. VDAT,
August 2006
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
20
Thank You !
Questions ?
Jan. 9, 2007
VLSI Design Conference 2007
21