Slide 1 Slide 2 Undetermined Coefficients
advertisement

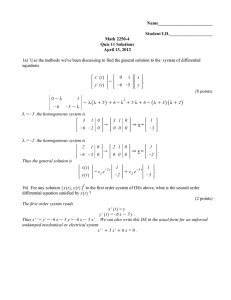
Slide 1 Undetermined Coefficients Superposition Approach Differential Equations Section 4.4 Slide 2 When does this approach work? The coefficients on the left-hand side of the differential equation must be constants. g(x) must be either a constant, a polynomial function, an exponential function eax, a sine or cosine function sin βx or cos βx, or finite sums and products of these functions. Slide 3 Method of Solution Step 1 – Step 2 – – Solve the associated homogeneous equation to obtain the complementary function yc. "Guess" at a particular solution of the homogeneous equation and equate coefficients to obtain the particular solution yp. Refer to Table 4.1 on p.172 if necessary until you get the hang of "guessing". Step 3 – Write the general solution y = yc + yp . Slide 4 What's the catch? If any terms in yp are duplicates of terms in yc, then you must multiply by xn, where n is the smallest positive integer that eliminates that duplication.