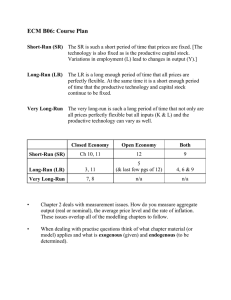
According to the graph above, which of the following statements about... (A)The economy is in long-run equilibrium.
advertisement

According to the graph above, which of the following statements about the economy is true? (A)The economy is in long-run equilibrium. (B)The LRAS curve will automatically shift to the right, restoring long-run equilibrium. (C)In the short run, if wages are sticky the SRAS will shift to the right, lowering prices. (D)The economy is in a recession, requiring decreases in spending to restore full-employment. (E)Wages will eventually decrease, restoring full-employment in the long run. According to the graph above and starting with equilibrium point R, which of the following shifts identifies the short-run and the long-run impact of demand-pull inflation? (A)Short-Run = R to N ; Long-Run = M to N (B)Short-Run = R to M ; Long-Run = R to N (C)Short-Run = R to Q ; Long-Run = Q to N (D)Short-Run = R to M ; Long-Run = R to Q (E)Short-Run = R to N ; Long-Run = N to Q The economy of a country is currently in equilibrium at point A in the diagram above. If the government does nothing and wages are flexible, which of the following will most likely occur in the long-run? (A)Falling wages will shift the aggregate demand curve to the right, producing full-employment. (B)Rising wages will shift the aggregate demand curve to the right, producing full-employment. (C)The economy will remain at point A. (D)Rising wages will shift the aggregate supply curve to the right, producing full-employment. (E)Falling wages will shift the aggregate supply curve to the right, producing full-employment. According to the graph above, which of the following is true about the long-run equilibrium of the economy depicted? (A)The economy is in long-run equilibrium. (B)The aggregate demand curve will shift to the left to restore long-run equilibrium. (C)The long-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the right to restore long-run equilibrium. (D)Without a fiscal policy stimulus, the economy will remain in a recession. (E)As wages increase, the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left to restore long-run equilibrium. An economy is in a short-run equilibrium at a level of output that is less than full-employment output. If there were no fiscal or monetary policy interventions, which of the following changes in output and the price level would occur in the long run? (A)Output = Increase ; Price Level = Decrease (B)Output = Increase ; Price Level = Increase (C)Output = Decrease ; Price Level = Decrease (D)Output = Decrease ; Price Level = Increase (E)Output = No change ; Price Level = No change In the long run, if aggregate demand decreases, real gross domestic product (GDP) and the price level will change in which of the following ways? (A)Real GDP = Decrease ; Price Level = Decrease (B)Real GDP = Decrease ; Price Level = Increase (C)Real GDP = No change ; Price Level = Decrease (D)Real GDP = Increase ; Price Level = Decrease (E)Real GDP = No change ; Price Level = Increase