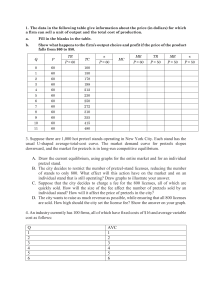
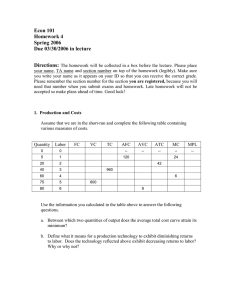
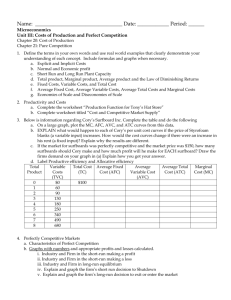
Key Macro Graphs - Production Possibilities Curve
advertisement

Key Macro Graphs - Production Possibilities Curve - Full employment, recession, and points that are unattainable - Which point leads to greater economic growth? (more capital goods) - Opportunity costs - With specific opportunity costs for use with Comparative Advantage and Trade problems. - Money Market - Show the effect of monetary (contractionary or expansionary) on the money supply, the quantity of money demanded, and the nominal interest rate. - Long-run AD/AS - In recession (below full employment) - Above full employment - In long-run equilibrium - Show the effects (on output and price level) of: - Changes in aggregate demand (C, G, I, or Xn) - Changes in aggregate supply - Show the effects (on output and price level) of: - Fiscal policy (Don’t forget about the spending and tax multipliers!) - Expansionary - Contractionary - Monetary policy - Expansionary - Contractionary - In other words, be able to show how changes in the interest rate will affect aggregate demand (through a change in investment spending or interestsensitive consumer spending, like car loans). - Demonstrate economic growth using the LRAS curve. - LRAS = the Natural Rate of Unemployment - Show how the economy will return to long-run equilibrium. - Bank Balance Sheets – you won’t have to draw them (probably), but you will have to interpret them. - Phillips Curve (long-run and short-run) - Movement along the SRPC (caused by a change in AD) - Shift of the SRPC (caused by a change in AS or a change in inflationary expectations) - LRPC is vertical at the natural rate of unemployment. - Represent full employment, recession, and above full employment as points on the Phillips Curve (long-run and short-run together are required). - Loanable Funds - Demonstrate how changes in the demand for and/or supply of loanable funds affect the real interest rate. - Foreign Exchange Market - Show how changes in the demand for or supply of a currency will affect its value on the foreign exchange market. (Interest rates, price level, income (GDP), and tastes and preferences – all of these determine demand for a country’s currency) Key Micro Graphs - PPC (regular and with opportunity cost Comparative Advantage and Trade) - Supply and Demand (basic market structure) - Elasticity of Supply and Demand (determine elasticity from graph) - Supply and Demand with Price Ceiling - Supply and Demand with Price Floor - Supply and Demand with Quota - Supply and Demand with Per-unit Tax (calculate price, new consumer and producer surplus, tax revenue, and deadweight loss) - Consumer Surplus, Producer Surplus, and Deadweight Loss in all the above - Cost Curves: Marginal cost, Average variable cost, Average fixed cost, Average total cost, Long-run average total cost - Perfect competition: firm and industry (and side-by-side) - Equilibrium price and quantity for firm and market - Shift supply and demand curves as needed. - Short-run changes - Long-run equilibrium (price = average total cost) - Area of profit or loss - Monopoly - Profit-maximizing quantity - Profit-maximizing price - Area of economic profit or loss - Socially optimal (or allocatively efficient) level of production - Production where there is zero economic profit (price = ATC) - Monopoly with price discrimination. - Oligopoly matrix (Game theory) - Dominant strategy if there is one. - Nash equilibrium - Factor Markets (primarily the labor market) - Side-by-side graphs of the labor market for firm and industry in a perfectly competitive labor market. - Graph of a monopsonistic labor market. Including the quantity of labor the monopsonist will hire and the wage it will pay. - Market Failure (externalities) - Lorenz Curve – You may or may not see one on the multiple choice section. You’re certainly not going to have to draw one. Just re-familiarize yourself with what the Lorenz curve shows and what its shape is. See the Lorenz Curve PowerPoint in Micro Unit 5 if you need a quick review.