FACTORING INTEGRATED MATHEMATICS
advertisement

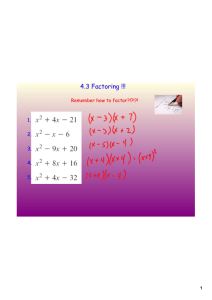
INTEGRATED MATHEMATICS FACTORING FACTORING USING GCF • Students will calculate the GCF of 2 or 3 terms of a polynomial. • Students will apply concepts of GCFs and Factoring to write the factored form of a polynomial. FACTORING USING GCF Steps 1. Find the greatest common factor (GCF) 2. Divide the polynomial by the GCF. The quotient is the other factor. 3.Express the polynomial as the product of the quotient and the GCF. FACTOR 𝑬𝒙. 𝟏) 𝟐 𝟔𝒙 + 𝟑𝒙 FACTOR 𝑬𝒙. 𝟐) 𝟒 𝟓𝒚 − 𝟐𝟎𝒚 𝟑 FACTOR 𝑬𝒙. 𝟑) 𝟐 𝟏𝟔𝒂 + 𝟐𝟎𝒂 FACTOR 𝑬𝒙. 𝟒) 𝟏𝟓𝒙 𝟓 − 𝟏𝟐𝒙 𝟒 + 𝟐𝟕𝒙 𝟑 − 𝟑𝒙 𝟐 FACTOR 𝑬𝒙. 𝟓) − 𝟒𝒏 𝟑 − 𝟐𝒏 𝟐 − 𝟔𝒏 TRY THESE 𝟏)𝟒𝒙 𝟑 − 𝟐𝒙 𝟐 𝟐)𝟏𝟎𝒙 𝟓 − 𝟏𝟓𝒙 𝟐 𝟑)𝟏𝟖𝒙 𝟑 − 𝟐𝟕 𝟑 𝟐 𝟒)𝟒𝒙 − 𝟏𝟐𝒙 − 𝟏𝟖𝒙 𝟕 𝟓)𝟏𝟑𝒙𝒚 𝟑 − 𝟏𝟐𝒙 𝟐 𝒚 − 𝟏𝟖𝒙𝒚 𝟕 DIFFERENCE OF TWO SQUARES Students will apply concepts of Perfect Squares and Factoring to write the factored form of the Difference of Two Squares. DIFFERENCE OF TWO SQUARES There must be two terms that are both squares Examples of squares There must be a minus sign between the two terms PERFECT SQUARES 1² = 1 2² = 4 3² = 9 4² = 16 5² = 25 6² = 36 7² = 49 8² = 64 9² = 81 10² = 100 11²= 121 12² = 144 13² = 169 14² = 196 15² = 225 16² = 256 17² = 289 18² = 324 19² = 361 20² = 400 FACTORING DIFFERENCE OF T WO SQUARES FORMULA 2 A – 2 B = (A + B)(A – B) FACTOR Ex. 6) x 4 2 FACTOR Ex. 7) 4 x 25 2 FACTOR Ex. 8) m 16n 6 2 FACTOR Ex. 9) 36 x 25 y 2 2 FACTOR Ex. 10) 1 x 2 FACTOR Ex. 11) 169 y 81z 2 2 TRY THESE 𝟏) 𝒙 𝟐 − 𝟗 𝟐)𝟏𝟎𝟎𝒙 𝟐 − 𝟏𝟔 𝟑)𝟑𝟔𝒙 𝟒 − 𝟏𝟐𝟏 𝟒)𝟒𝒙 𝟐 − 𝒚 𝟐 𝟓)𝟐𝟓𝒂 𝟐 − 𝟒𝟗𝒃 𝟐 FACTORING COMPLETELY Students will apply concepts of GCFs, Perfect Squares, and Factoring to write the factored form of the Difference of Two Squares. FACTORING COMPLETELY Means to factor until factoring is no longer possible FACTOR. LOOK FOR GCF FIRST! Ex. 12) 5 20 y 6 FACTOR. LOOK FOR GCF FIRST! Ex. 13) a b 4ab 3 3 FACTOR. LOOK FOR GCF FIRST! Ex. 14) 18a b 50a 2 2 6 FACTOR. Ex. 15) 12m 3n 4 8 FACTOR. Ex. 16) 50 x 2 4 TRY THESE 𝟏) 𝟐𝟕𝒙 𝟐 − 𝟏𝟐 𝟐)𝟓𝟎𝒙 𝟐 − 𝟖 𝟑)𝟏𝟖𝒙 𝟒 − 𝟕𝟐 𝟒)𝟐𝟎𝒙 𝟐 − 𝟒𝟓𝒚 𝟐 𝟓)𝟕𝟓𝒂 𝟐 𝒃 − 𝟐𝟕𝒃 𝟑 FACTORING TRINOMIALS FACTORING A TRINOMIAL: 2 𝑥 + 𝐵𝑥 + 𝐶 Students will apply concepts of factoring to write the factored form of a trinomial. FACTORING A TRINOMIAL: 2 𝑥 + 𝐵𝑥 + 𝐶 1. Write two sets of parenthesis, ( )( ). These will be the factors of the trinomial. 2. Think of factors of c that add up to b. FACTOR Example 1 x 5x 6 2 FACTOR Example 2 13 14m m 2 FACTOR Example 3 x 8 x 15 2 FACTOR Example 4 x 9 x 20 2 FACTOR Example 5 x 8 x 20 2 FACTOR Example 6 x 4 x 12 2 RULES SUMMARY If C is positive (+), use the sign of B twice. If C is negative (-), use a + and a -. Bigger number is the sign of B. TRY THESE 𝟏) 𝒙 𝟐 + 𝟖𝒙 + 𝟏𝟐 𝟐) 𝒙 𝟐 − 𝟓𝒙 + 𝟔 𝟑) 𝒛 𝟐 + 𝟏𝟐𝒛 − 𝟐𝟖 𝟒) 𝒙 𝟐 − 𝟗𝒙 − 𝟐𝟐 𝟓) 𝒂 𝟐 + 𝟐𝒂 + 𝟏