Chapter 17
The History of Life
Section 17- 4
Patterns of Evolution
Macroevolution
Large
Scale Evolutionary
Changes That Take Place Over
Long Periods of Time
Macroevolution
Key Concept:
There Are Six Important
Patterns of Macroevolution:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Mass Extinctions
Adaptive Radiation
Convergent Evolution
Coevolution
Punctuated Equilibrium
Developmental Gene Changes
Mass Extinctions
Extinction
– Occurs Constantly
– 99% Earths Life Forms Extinct
Mass
Extinctions
– Wipe Out Ecosystems
– Disrupt Energy Flow
– Collapse Food Webs
Extinction
Extinction
More than 99% of all species that have ever lived
are now extinct.
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Mass Extinctions
Causes?
–Asteroids?
–Volcanic/Geologic Activity?
Effects
–Habitats Left Unoccupied
–Ecological Opportunity
–Evolution Explosion
Extinction
What effects have mass extinctions
had on the history of life? Mass
extinctions have:
provided
ecological opportunities for organisms
that survived by making new habitats available
resulted in rapid evolution that produced many
new species
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Adaptive Radiation:
Single
Species or Small Group
of Species Evolve Into
Several Different Forms That
Live In Different Ways
–Darwin’s Finches
–Age of Reptiles
–Age of Mammals
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
CONVERGENT EVOLUTION
How would you compare the fins in
these 2 organisms?
In what way are these organisms displaying
examples of convergent evolution?
Coevolution
The
Process By Which Two
Species Evolve In Response
To Changes In Each Other
–Figs & Wasp
–Orchids & Moths
Coevolution- Fig and Wasp
Coevolution- Orchids and Moth
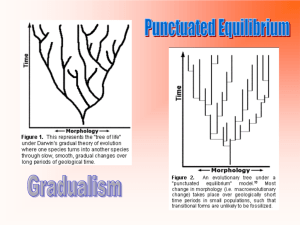
Punctuated Equilibrium
Brief
Periods of Rapid
Evolutionary Change That
Interrupt Long Periods of
Gradual Evolution
Punctuated Equilibrium
Punctuated
Equilibrium
Darwin felt that
biological change
was slow and
steady, an idea
known as
gradualism.
Punctuated Equilibrium
Punctuated equilibrium
is a pattern of evolution
in which long stable
periods are interrupted
by brief periods of more
rapid change.
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Developmental Genes & Body Plans
Hox
Genes : a group of
related genes that control the
body plan of the embryo
along the anterior-posterior
(head-tail) axis.
Determine the type of
segment structures (e.g.
legs, antennae, and wings)
HOX GENE
Developmental Genes & Body Plans
Small Changes In
Timing of Genetic
Control During
Embryonic
Development,
Make Big
Changes In The
Resulting
Organism
17–4 Patterns of Evolution
A. Mass Extinctions- dinosaurs
B. Adaptive Radiation- species
evolved into several different
forms that live in different ways
C. Convergent Evolutionunrelated organisms come to
resemble one another
17–4 Patterns of Evolution
D. Coevolution- process by which two
species evolve in response to
changes in each other over time
E. Punctuated Equilibrium- patterns of
long, stable periods interrupted by
brief periods of more rapid change
Gradualism- patterns of slow,
gradual change
Flowchart
SPECIES
that are
Unrelated
form
Related
in
under
under
in
in
Different
environments
Interrelationships
Similar
environments
Intense
environmental
pressure
Small
populations
can undergo
can undergo
can undergo
can undergo
can undergo
Coevolution
Convergent
evolution
Extinction
Punctuated
equilibrium
Adaptive
radiation:
Aka:
Divergent
evolution