Beyond Dominant and Recessive Alleles

Beyond Dominant and
Recessive Alleles
The whole story . . .
• Not all phenotypes are dictated by dominant and recessive alleles (in fact, very few are).
• Some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive. Most phenotypes are controlled by the following mechanisms:
• Incomplete Dominance
• Codominance
• Multiple Alleles
• Polygenic Traits
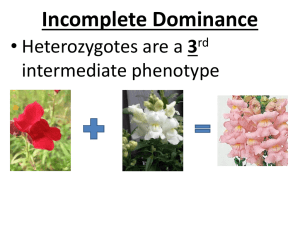
Incomplete Dominance
• When one allele is not completely dominant over another and the heterozygous phenotype is an intermediate (blending) between the two homozygous phenotypes.
Example: WW = White Flowers
RR = Red Flowers
RW = Pink Flowers
Codominance
• Similar to incomplete dominance, except that no new phenotype is created (not a blending of the other phenotypes).
• Instead, both of the homozygous phenotypes are being expressed simultaneously
Example: C B C B = Black feathers
C W C W = White feathers
C B C W = has some Black and some
White feathers
Multiple Alleles
• Occurs when there is more than 2 possible alleles that can be inherited from the parents. (Each parent only has 2 alleles, but in this case there are several possible types of alleles.)
ABO Blood Groups
•
There are 3 possible alleles for blood type:
• I A , I B , and i
•
Alleles I A and I B are codominant, while i is recessive.
Polygenic Traits
• In polygenic traits, more than one gene is used to determine the genotype and phenotype of a particular trait (ex. skin color).
• This allows for an extremely large variety of phenotypes.