India Seeks Self Rule
advertisement

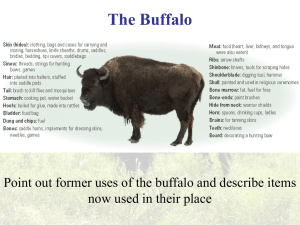
India Seeks Self Rule Chapter 8, Section 3 Objectives: Investigate the impact of WWI and the Amritsar massacre on Indian nationalism. Evaluate the ideas of Mohandas Gandhi. Analyze how Gandhi led resistance to political oppression in India. PDN • What do you know or think of when you hear Gandhi? India’s Struggle for Independence • During WW1, more than 1 million Indians served. – British promised Indians greater self-government. • Once fighting ended, British continued to have no care for Indian beliefs and customs. • Frustration led to call for independence. A New Leader Emerges • Congress = middle-class or elite. • Mohandas Gandhi united Indians across class lines. • Student of law, helped fight discriminating legislature. • Nonviolent, called it “satyagraha” or “soul force.” • National hero, joined Congress party. The Muslim League • Muhammad Ali Jinnah – influential Muslim leader. • The Muslim League and the Congress party helped bring independence to India. PDN 11.20.15 • Ali Jinnah was an influential leader of what? The Amritsar Massacre • 1919, British pass Rowlatt Acts, allowed British officials to arrest and imprison any Indian citizen suspected of sedition (tried without a jury). • Gandhi opposed act, bc it also threatened freedoms • April 13th, 1919, large but peaceful crowd of protestors jammed into an enclosed field in Amritsar. – 400 people were killed by army orders – 1100 were wounded – Gandhi sees that India needs to be self ruled. Gandhi’s Philosophy of Civil Disobedience • Nonviolent Protest • Gandhi = horrified by Amritsar • Preached nonviolence based off ancient Hindu and Jain doctrine of Ahimsa. • By using power of love, anyone could be converted. • Believed in civil disobedience • Ended harsh treatment of untouchables Restoring National Pride • 2 decades (20 years) Gandhi initiated a series of nonviolent actions against British rule. • Boycotted British goods like cotton textiles. • Abandoned western style clothing for the dhota. • When protests led to violent riots, Gandhi would fast and pray. His Actions caught attention of British Government and world. Gandhi Takes a Stand • Mobilized mass support by standing against British salt monopoly. – Salt production was a sole right to British empire. – They would tax sales, and maintain government in India PDN Monday November 23, 2015 • What event showed Gandhi that India must become an independent nation? The Salt March • Early 1930s, Gandhi writes the British viceroy and states his intention to break salt laws and condemn British rule as a curse. • March 12th, 1930, Gandhi set out with 78 followers on a 240 mile march to the sea. As they marched through villages, more and more people joined. • April 6th, Gandhi picks up a lump of sea salt by the edge of the water. Soon arrested. • Coastal villagers followed his lead, tens of thousands were jailed. World Opinion Shifts • Newspapers criticized Britain’s harsh reaction to the protests. • Stories revealed police brutality on peaceful marchers. • The Salt March embarrassed Britain. • Finally British began handing over power to Indians. The Future of India • 1939, new world war exploded. • Britain outraged Indian leaders by postponing independence and bringing Indians into the war without consulting them. • Millions of Indians helped Britain during WWII. • 1945, India’s independence could no long be delayed after helping win WWII. • 1947, India becomes an independent nation. India’s Flag