Document 15957942
advertisement

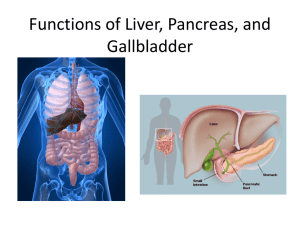
Anatomy and Physiology Liver Largest solid organ in the body Plays role in: ○ Digestion ○ Absorption ○ Metabolism 2 Anatomy and Physiology Liver Plays role in ○ Blood clotting ○ Manufacture of important chemicals ○ Storage of nutrients 3 Anatomy and Physiology Gallbladder stores bile until needed Pancreas produces and excretes most of the intestinal enzymes 4 Common Signs and Symptoms Liver Disease Jaundice Pain is the most common symptom 5 Diagnostic Tests Liver function tests measure bilirubin, albumin, alkaline phosphatase Ultrasound, X-rays, CAT scan Biopsy Blood tests to measure pancreatic function 6 Liver Diseases Hepatitis Inflammation of the liver Causes include chemical actions of drugs, toxic substances, chronic alcoholism, group of viruses Viral hepatitis is the most prevalent 7 Liver Diseases Hepatitis Symptoms ○ Jaundice ○ Malaise ○ Anorexia ○ Myalgia 8 Liver Diseases Hepatitis Symptoms ○ Fever ○ Abdominal pain ○ Dark-colored urine (hepatomegaly) ○ Clay or light-colored stools 9 Liver Diseases Hepatitis Treatment ○ Rest ○ Good nutrition Prevention ○ Good hygiene ○ Special care when handling needles and body fluids 10 Liver Diseases Viral Hepatitis occurs in five types A, B, C, D, E Hepatitis A: benign; spread by oral-fecal contact Hepatitis B: formerly called “serum hepatitis” spread by blood, urine, feces, saliva, and semen 11 Liver Diseases Hepatitis C: spread by blood or sex Hepatitis D: “delta virus” requires presence of hepatitis B to replicate Hepatitis E: spread through fecal-oral contact, commonly due to water contamination 12 Liver Diseases Cirrhosis Chronic, irreversible, degenerative Replacement of normal liver cells with nonfunctioning scar tissue called “hobnail liver” 13 Liver Diseases Cirrhosis Most common cause is chronic alcoholism Symptoms ○ Loss of appetite ○ Nausea ○ Indigestion ○ Weakness and weight loss 14 Liver Disease Liver Cancer Primary and benign tumors of liver are rare Usually discovered late or end stage Diagnosis confirmed by biopsy Treatment may involve surgery, radiation, chemotherapy 15 Gallbladder Diseases Cholecystitis Inflammation of gallbladder usually caused by obstruction of bile due to gallstone Diagnosis is made by ultrasound, cholecystogram 16 Gallbladder Diseases Cholecystitis Symptoms ○ Mild to severe RUQ pain ○ Nausea and vomiting after eating Treatment surgical excision 17 Gallbladder Diseases Cholelithiasis Gallstones in gallbladder or bile ducts Symptoms ○ Nausea ○ Vomiting ○ RUQ pain following meals with fat 18 Gallbladder Diseases Cholelithiasis Risk factors include excessive weight, increasing age, female 19 Gallbladder Diseases Cholelithiasis 5 F’s of cholelithiasis ○ Female ○ Fair complexion ○ Fat ○ Fertile ○ Forty or older 20 Pancreas Diseases Pancreatitis - Inflammation of pancreas Symptoms ○ Severe abdominal pain radiating to back ○ Nausea ○ Vomiting ○ Diaphoresis ○ Tachycardia 21 Pancreas Diseases Pancreatitis Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis are similar to acute Diagnosis is based on high blood amylase Treatment and prognosis depends on cause 22 Pancreas Diseases Pancreas Cancer Usually adenocarcinoma occurring in head of pancreas Symptoms: ○ Abdominal pain ○ Back pain ○ Nausea ○ Vomiting 23 Pancreas Diseases Pancreas Cancer Symptoms ○ Loss of appetite ○ Weakness ○ Jaundice ○ Fatigue 24 Pancreas Diseases Pancreas Cancer Diagnosis confirmed by biopsy Treatment ○ Surgical resection ○ Radiation and chemotherapy 25